1.01 Remember structural organization
advertisement

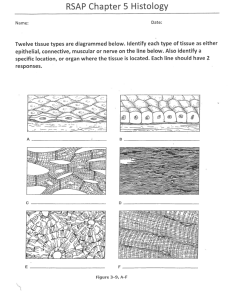
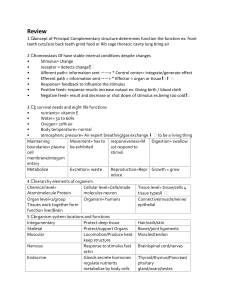
Essential Questions How is the human body organized? What are the structural components of the body? How does the body’s structural organization relate to its support and movement? 1.01 Remember structural organization 2 Composed of: 1.01 Remember structural organization 3 Types of tissues: Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue 1.01 Remember structural organization 4 Epithelial Tissue protects the body by covering internal and external surfaces, and produces secretions Skin covers the outside of the body lines the inside of the body Membrane two thin layers of tissue that join together cells may secrete a fluid 1.01 Remember structural organization 5 Epithelial tissues Squamous Cuboidal 1.01 Remember structural organization Columnar 6 formed by putting two thin layers of tissue together, cells may secrete a fluid Membranes are vital because they separate the cell from the outside world. They also separate compartments inside the cell to protect important processes and events. MUCOUS MEMBRANES– lines digestive, respiratory, reproductive and urinary systems – produces mucous to lubricate and protect the lining They line various body cavities that are exposed to the external environment and internal organs. Serous– double-walled membrane - produces a watery fluid (Serous fluid) lines closed body cavities the outer part of the membrane that lines the cavity is the PARIETAL membrane the part that covers the organs is the VISCERAL membrane. Pleural, Pericardial, Peritoneal PLEURAL MEMBRANE – lines thoracic or chest cavity and protects the lungs PERICARDIAL MEMBRANE – lines the heart cavity and protects the heart PERITONEAL MEMBRANE – lines the abdominal cavity and protects abdominal organs Are made of two layers of connective tissue. Synovial membraneLines the joint cavity and prevents friction in joints. Connective tissue supports and connects organs and tissue Adipose type of connective tissue that stores fat cells Cartilage firm, flexible support of the embryonic skeleton and part of the adult skeleton Tendons white bands of connective tissue attaching skeletal muscle to bone Ligaments strong, flexible bands of connective tissue that hold bones firmly together at the joints 1.01 Remember structural organization 11 – supports and connects organs and tissue These tissues are responsible for cushioning, supporting and maintaining form within the body and include adipose, cartilage, bone, tendons and ligaments Vascular LIGAMENTS – strong, flexible bands of connective tissue that hold bones firmly together at the joints TENDONS – white bands of connective tissue attaching skeletal muscle to bone CARTILAGE – firm, flexible support of the embryonic skeleton and part of the adult skeleton BONE- skeleton. Supports tissues and organs. VSCULAR-liquids blood tissue (Example RBC) Connective tissue Adipose Fibrocartilage 1.01 Remember structural organization Elastic cartilage 14 Repair of damaged tissue occurs continually. Two types Primary takes place in clean wound where infection is not present. Secondary larger and deeper wounds. place by granulation. Cicatrix –Scar tissue Takes Muscle tissue contracts and moves a body part Cardiac striated, involuntary contracts the heart Skeletal striated, voluntary attached to the skeleton Smooth nonstriated, involuntary provides movement in various body systems 1.01 Remember structural organization 16 Muscle tissue Cardiac Skeletal 1.01 Remember structural organization Smooth 17 Nervous tissue reacts to stimulation and conducts an impulse 1.01 Remember structural organization 18 – cells that react to stimuli and conduct an impulse Neurons are highly specialized cells that generate and transmit electrical impulses (action potentials) permitting rapid communication between distant areas of the body. Nervous tissue Neuron 1.01 Remember structural organization 20 Musclepink Connectiveblue Epithelialgreen Nerveyellow • Smooth • Cardiac • Skeletal • Hard – Cartilage, Bones • Soft – Adipose, Ligaments, Tendons • Skin • Membranes – Mucous and Serous • Neuron 1.01 Remember structural organization 23 1.01 Remember structural organization 24 1.01 Remember structural organization 25 Click here to hear heartbeat 1.01 Remember structural organization 26 1.01 Remember structural organization 27 1.01 Remember structural organization 28 1.01 Remember structural organization 29 1.01 Remember structural organization 30 1.01 Remember structural organization 31 The Skin 1.01 Remember structural organization The Tongue 32 1.01 Remember structural organization 33 1.01 Remember structural organization 34 Male Female 1.01 Remember structural organization 35 1.01 Remember structural organization 36 Anatomical position 1.01 Remember structural organization 37 Anatomical position Discuss the importance of anatomical position. 1.01 Remember structural organization 38 Directional terms 1.01 Remember structural organization 39 Directional terms 1.01 Remember structural organization 40 Directional terms 1.01 Remember structural organization 41 Body planes 1.01 Remember structural organization 42 Body cavities 1.01 Remember structural organization 43 1.01 Remember structural organization 44 1.01 Remember structural organization 45 Group Review Essential Questions How is the human body organized? What are the structural components of the body? How does the body’s structural organization relate to its support and movement? 1.01 Remember structural organization 47