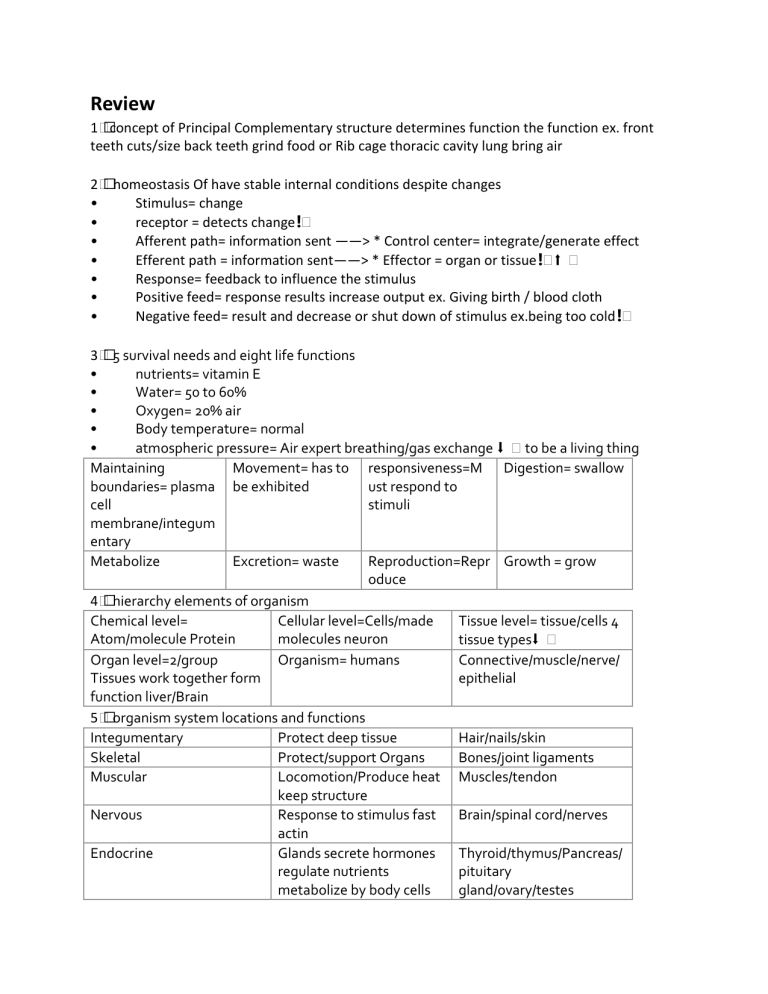
Review 1️⃣concept of Principal Complementary structure determines function the function ex. front teeth cuts/size back teeth grind food or Rib cage thoracic cavity lung bring air 2️⃣ homeostasis Of have stable internal conditions despite changes • Stimulus= change • receptor = detects change❗️ • Afferent path= information sent ——> * Control center= integrate/generate effect • Efferent path = information sent——> * Effector = organ or tissue❗️⬆ ️ • Response= feedback to influence the stimulus • Positive feed= response results increase output ex. Giving birth / blood cloth • Negative feed= result and decrease or shut down of stimulus ex.being too cold❗️ 3️⃣ 5 survival needs and eight life functions • nutrients= vitamin E • Water= 50 to 60% • Oxygen= 20% air • Body temperature= normal • atmospheric pressure= Air expert breathing/gas exchange ⬇ ️ to be a living thing Maintaining Movement= has to responsiveness=M Digestion= swallow boundaries= plasma be exhibited ust respond to cell stimuli membrane/integum entary Metabolize Excretion= waste Reproduction=Repr Growth = grow oduce 4️⃣ hierarchy elements of organism Chemical level= Cellular level=Cells/made Tissue level= tissue/cells 4 Atom/molecule Protein molecules neuron tissue types⬇ ️ Organ level=2/group Organism= humans Connective/muscle/nerve/ Tissues work together form epithelial function liver/Brain 5️⃣ organism system locations and functions Integumentary Protect deep tissue Hair/nails/skin Skeletal Protect/support Organs Bones/joint ligaments Muscular Locomotion/Produce heat Muscles/tendon keep structure Nervous Response to stimulus fast Brain/spinal cord/nerves actin Endocrine Glands secrete hormones Thyroid/thymus/Pancreas/ regulate nutrients pituitary metabolize by body cells gland/ovary/testes Cardiovascular lymphatic Pumps bloodTransports Oxygen/nutrient removes waste Returns fluid to blood White blood cells involve Heart/blood vessels Red bone Marrow/Thymus/ ly vessels/ly nodes/ Spleen Respiratory Keeps blood supplied with Nasal O2 and CO2 cavity/pharynx/Trachea/br onchi/lungs Digestive Eliminate indigestible food Oral cavity/esophagus breaks down food reserves stomach/rectum/liver/anus nutrients into body /large/small intestines Urinary Eliminate waste/regulates Kidney/ureters/urinary water/pH balance of blood bladder/urethras Reproductive men Produce offspring testees Scrotum/penis/prostate produce sperm sex gland‘s/vas deferen hormones glands deliver sperm Reproductive woman Produce offspring ovaries ovary/uterus produce eggs/sex tube/vagina/MAMMARY hormones memmary glands glands produce milk 6️⃣ by cavities/membrane types difference of ventricle/parietal serosa outside inter ske muscle 2 body cavities dorsal and ventral /closed two outside environment lined by double side fluid Dorsal=Lateral Cranial cavity= Vertebral cavity= Adomino pelvic surface Brain spinal cord cavity= both Ventricle= anterior Thoracic Abdominal Pelvic cavity= surface cavity=Heart/lungs cavity=Digestive urinary/reproductiv system e serous=closed outside/lined Mucous= communicate Visceral = Internal organ double line fluid outside lined muscous —>2 layer epithelial cells membrane Synovial= encapsulated line Cutaneous=external Patrietal=towards side by diff fluid products surface cover though wall —-> secretes a fluid membrane membrane known serous fluid 7️⃣ Basic chemistry atoms= smallest unit of matter Protons= + positive charge/1 atomic mass deter element Neurons= no electrical charge 0/ 1 amu deter isotope Electrons= negative charge = of proton 0 amu chem behavior Isotopes= most Atomic number=# ISO=same element commonly occur / of protons in diff structure/ same atomic same diff nucleus proton diff mass neutrons Solution=don’t settle/ ver Colloid=larger don’t settle Suspension= very large/ tiny/water / jello settles/blood Homogeneous Heterogeneous Heterogenous pH scale= Greater= lower Lower= greater pH Neutral=equal ↙️ measurement of H pH—> most acidic pH=-log[H+] ➡️ more basic in solution 0-14 (7)✅ 14-8 increase basic 7 normal/neutral 6-0 increase acidi bond=link/force between ionic bond=attraction in 2 covalent bond= atoms in mole/compund ions compound major interaction two type/-anione-acceptor atoms/sharing of 1 or more /+cation e-donor electrons major type intramolecular=interaction intermolecular Hydrogen bonds= force in s within a molecule not an forces=interactions electropositive H of 1 and actual bond between 2+ molecules. electronegative atom Synthesis=combo runs atoms/mole complex Anaboc=bond building A+B➡️AB Decomposition=Br eakdown mole small atoms require catalyst Catabolic=BondBreaking AB➡️A+B Exchange=Displace Anabolism=Use /replace both energy to grow and son/decom build Bonds are made Catabolism= uses and broken AB+C energy to break down ➡️AC+B or AB+CD➡️AD+CB 8️⃣Biochem- types of membrane proteins 4 categories of molecules ⬇ ️ carbohydrates=sug lipids=Insoluble in proteins=Build nucleic acids=BIG’S ars and starches water blocks of protein mole made of Starch by monomers➡️ plants/Glycogen by nucleotides animals –Monosaccharides- Triglycerides/Phos –Deoxyribonucleic the monomer of pholipids/ common acid (DNA) carbohydrate Steroids/Eicosanoi –Ribonucleic acid polymers ds (RNA) –Disaccharides Polysaccharides 4 levels of protein structure 1.Primary=linear sequence of AA backbone protein The sequence of amino acids forms the polypeptide chain. Secondary=AA interact w/each other(Alpha (a) helix ) coiled spring(Beta B pleated sheets) ribbons/ zig zag The primary chain forms spirals (a-helices) and sheets (b-sheets). 9️⃣4 tissue types-where each is found Epithelial tissue Nervous (epithelium)=cells Tissue=two covers body specialized cell surfaces or lines Neurons / cavities (lining Neuroglia – Dendrites receive epithelia➡️ or transmit stimuli surface)(Glandular soma/Axons epithelia transmit electrical ➡️Secretory impulses long tissue) glands distances Functions=Protectio n/Absorption/Filtrati on/Excretion/Secreti on (glandular epi)/ Sensory Reception 1. Polarity=(distinct opposite ends)➡️Apical surface upper/Basal Low •Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves Neurons=specialize d nerve cells that generate and conduct nerve impulses/ Neuroglia=Support ing cells support, insulate, protect neurons Tertiary:=2o structures interact reinforced by covalent and H bonds Quaternary=2+ different polypeptides interact w/each other Superimposed on secondary structure. aHelices and/or bsheets are folded up to form a compact globular molecule held together by intramolecular bonds. Quaternary structure of a functional transthyretin molecule. Four identical transthyretin subunits join to form a complex protein. Muscle Tissue=Involved in movement Connective Tissue=•Most abundant and widely distributed •Three kinds of muscle tissue: –Skeletal voluntary –Cardiac involuntary –Smooth involuntary Attached to bones and around entry & –Connective tissue proper –Cartilage –Bone –Blood •Functions: –Binding and support –Protection –Insulation –Storage 2. Specialized contacts=Fit closely together form sheets 3. Supported by connective tissues=sheets are supported by CT 4. Avascular, but innervated=No blood vessels fiber present 5. Regeneration=Rapid ly replaces lost cells by cell division exit sites of body (e.g., mouth, anus –Transportation MICROVILLI=•Increases surface area, absorption CILIA =Create a “current” to move substances through lumen shorter/more uniform in length. Brush w/bristles side view name brush border“ CT Fibers=•Three types of fibers provide support –Collagen •Strongest and most abundant •Provides high tensile strength •Cross-linked fibrils –Elastic fibers •Networks of long, thin, elastin fibers that allow for stretch and recoil –Reticular •Two subclasses »loose connective tissues •Areolar •Adipose •Reticular •Epithelium lining the trachea/long filamentous cilia along the apical surface/microtubules/•Usually see through a layer of cilia! •Four main classes of connective tissue: –Connective tissue proper –Cartilage –Bone Blood •Three types of cartilage: –Hyaline cartilage –Elastic cartilage –Fibrocartilage »dense connective tissues •Regular •Irregular •Elastic Cell Junctions=•Some cells are “free”(i.e. blood cells) •Most cells are tightly attached –Glycoproteins act as an adhesive –Tongue-and-groove –Cell junctions •Three ways cells can be bound to each other –Tight junctions –Desmosomes –Gap junctions •K+ diffuses out of cell through K+ leakage channels down its [gradient] •(-) proteins, carbohydrates, etc. cannot leave; cytoplasmic side = more negative •K+ is then pulled back by the more (-) interior b/c of electricostatic gradient •K+ drive to leave = drive to stay à RMP •Electrochemical gradient of K+ sets RMP •Na+ attracted to inside of cell b/c of (-) charge –Membrane is more permeable to K+ than Na+, so K+ primary influence on RMP




