The Nervous System - Canton Local Schools
advertisement
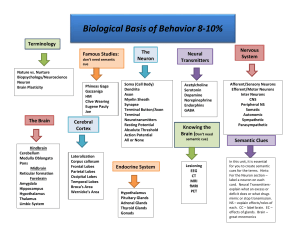
neurons and the brain Neuron: a nerve cell. The basic building block of the nervous system Dendrite: The bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward cell body Axon: the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers. Used to pass messages to other neurons or muscles and glands Myelin Sheath: A layer of fatty tissue surrounding the axon of many neurons. Speeds up message transmission • Neural connections are VERY small. It’s hard to see, even with a microscope • Terminal branches of one neuron connect to the soma or dendrite of another neuron creating a synapse Synapse: the connection point of one neuron to another Neurotransmitters: chemical messages that are sent across synapses to start an impulse (message) 1. Message formed and sent from the soma. Don’t forget that messages are simply neurotransmitters (chemicals) 2. Message travels down the axon 3. Message is sped up by the Myelin Sheath 4. Message reaches terminal branch and prepares to jump 5. Message jumps synapse 6. Message is received by the next neuron Nervous System: the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication system Central Nervous System (CNS): The brain and spinal chord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Two parts: 1. Autonomatic (ANS): controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs. AUTOMATIC 2. Somatic (SNS): controls the body skeletal muscles SKELETAL Mirror Neurons Video (TED Talks) Endocrine System: the body’s slow chemical communication system that uses hormones and the blood stream Hormones: chemical messengers, made by endocrine glands Pituitary Gland: regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands. Located under the Hypothalamus Adrenal Glands: a pair of endocrine glands just above the kidneys that produce adrenaline and noradrenaline which arouse the body in times of stress • The Nervous System is FAST and is ELECTROCHEMICAL • The Endocrine System is SLOW and uses HORMONES