Endocrine System, Nervous System and Homeostatic Control
advertisement

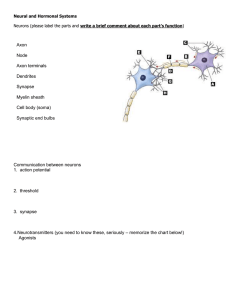
Endocrine System, Nervous System and Homeostatic Control Review for Unit Test #1 Endocrine system Information signaling system Glands produce hormones Circulate through blood vessels Regulate: – mood, growth and development, tissue function, and metabolism Hypothalamus The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and circadian cycles. Secretes hormones that tell other glands to create their hormones – GHRH Pineal Body Secretes Melatonin Melatonin may help regulate sleep patterns Pituitary Gland Growth Blood Pressure Sex Organ Functions Conversion of food into energy Water regulation Thyroid Controls how quickly the body burns energy, makes proteins, and how sensitive the body should be to other hormones. Parathyroid The sole function of the parathyroid glands is to maintain the body's calcium level within a very narrow range. Pancreas Regulates blood sugar by producing Insulin Adrenal gland Produces Adrenaline Fight or Flight Response – – – – Dilate pupils Increase heart rate Suppress non emergency process Boost oxygen and glucose supply Testes and Ovaries Both produce hormones to support body function Testes – Testosterone Ovaries – – Progesterone Estrogens Nervous system Made up of two major parts – – Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Central Nervous System Brain and Spinal Cord – – Nerves Ganglion Brain Consists of lobes, Each lobe having different functions. Function Process information Dictate reactions and behaviors Peripheral Nervous system Nerves from spinal cord to rest of body Create locomotion Etc… Feedback Loops Your nervous system is involved in almost all homeostatic control loops. Reflex arc Sensory Vs Motor Affector Vs Effector Neuron Function Dendrites Myelin Schwann Cells Axon Node of Ranvier Threshold Before a neuron can send out a signal the stimuli has to pass the threshold Action Potential An action potential is a nerve impulse An electrical shock sent down the axon Action Potential Synapse A synapse occurs where ever the action potential meets the end of the axon It needs to propagate across that gap It does this through chemical messengers Neurotransmitter= Acetylcholine Enzyme that destroys it = Acetylcholinesterase Synapse When Acetylcholine jumps across the gap, it tells the next neuron to fire it’s action potential and the process continues Homeostasis Summary Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal state within an organism. Organisms must respond and maintain homeostasis in relation to many factors. Organisms detect changes in their environment and respond to these changes in a variety of ways. These changes may occur at the cellular or organism level.