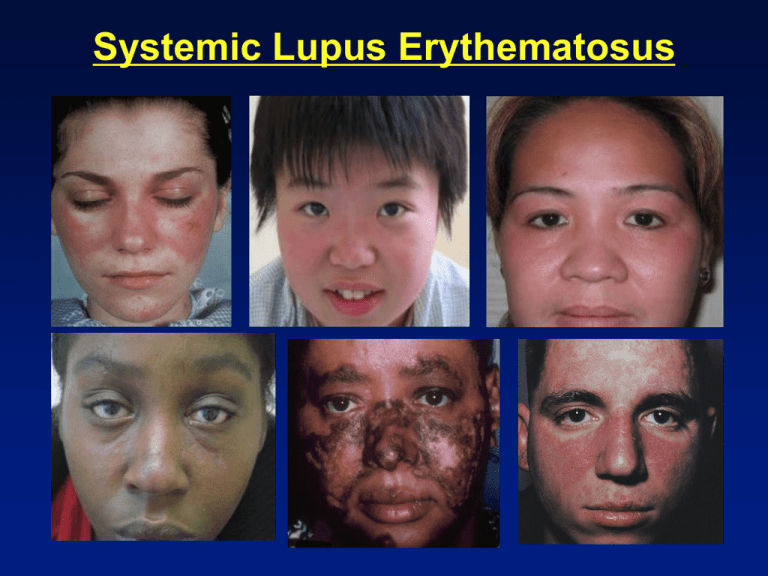
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Epidemiology of SLE
• Prevalence - 1/2,000 people
• Sex - 10:1 female predominance
• Age at onset
16-55 years: 65% (F:M = 10:1)
<16 years: 20% (F:M = 3:1)
>55 years: 15% (F:M = 7:1)
• Race - more common in Blacks, Hispanics,
and Asians than in Whites
Common Manifestations of SLE
Constitutional Symptoms
• Fatigue
• Fever
• Weight loss
Mucocutaneous Involvement
• Photosensitive rash
• Oral ulcers
• Alopecia
Arthralgias/Arthritis
Manifestations of SLE (con’d)
Kidneys - Glomerulonephritis
Central Nervous System - Headache, seizures, stroke
Peripheral Nervous System - sensory or motor
Lungs - pleuritis, pneumonitis, hemorrhage
Heart - pericarditis, myocardial infarction, valve disease
GI - serositis, mesenteric vasculitis, pancreatitis
Hematopoietic - lymphadenopathy, autoimmune
cytopenias, antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
Target Antigens in SLE
• Nuclear antigens (e.g., dsDNA)
• Cytoplasmic antigens (e.g., ribosomal proteins)
• Cell surface antigens (e.g., blood cells)
• Soluble antigens in sera (e.g., IgG, phospholipids)
Anti-dsDNA Antibodies
Evidence for a Pathogenic Role
• Presence correlates with renal involvement
• Serum levels correlate with disease activity
• Concentration is enriched in glomerular eluates
• Some monoclonal anti-dsDNA can produce lupus nephritis
Anti-DNA Mediated Renal Injury
Proposed Mechanisms
• Deposition of circulating immune complexes
• Binding of DNA to GBM (e.g., based on charge)
• Binding of anti-dsDNA to glomerular antigens
(e.g., due to polyspecificity - heparin sulfate, laminin)
Autoantibodies in CNS Lupus
(DeGiorgio et al.: Nature Med 7:1189,2001)
1) Some anti-DNA antibodies bind receptors
for glutamate.
2) Glutamate receptors contribute to learning
and memory.
3) Overstimulation of glutamate receptors can
cause excitotoxic neuron death.
Autoantibodies in CNS Lupus
(DeGiorgio et al.: Nature Med 7:1189,2001)
(continued)
4) Anti-DNA antibodies mediate neuronal
cell death.
5) CSF from a patient with CNS lupus
contain anti-DNA antibodies that mediate
neuronal death.
Antiphospholipid Antibodies
aPL antibodies bind complexes of phospholipids
and plasma proteins:
• Prothrombin-activator
complex
(activated factor X, factor V, prothrombin,
calcium, phospholipid)
• b2-glycoprotein
I
(a naturally occurring anticoagulant)
Antiphospholipid Antibody
Syndrome (APS)
• Venous thrombosis
• Arterial thrombosis
• Recurrent fetal loss
• Thrombocytopenia
Prevention of Fetal Loss with Crry-Ig
(Holers VM…Salmon JE: J Exp Med 195:211, 2002)
Other Postulated Mechanisms
• Defective clearance of apoptotic bodies
(persistence of self nuclear antigens)
• Failure of tolerance (T cells and/or B cells)
• Activation of B cells and/or dendritic
cells by self DNA or RNA through tolllike receptors (i.e., TLR-7 and TLR-9)
Special Serologic Studies in SLE
Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA)
Anti-dsDNA Antibodies
Anti-ENA Antibodies (RNP, Sm)
Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
Complement (C3, C4, CH50)
ACR Criteria For SLE
1. Malar rash
2. Discoid Rash
3. Photosensitivity
4. Oral ulcers
5. Arthritis
6. Serositis
7. Renal disorder
8. Neurologic disorder
9. Hematologic disorder
10. Antinuclear antibody
11. Immunologic disorder
Case History
Patient: 33-year-old woman
Symptoms: Fatigue, myalgias/arthralgias,
pleuritic chest pain
Signs: T-38.5oC
Nodes - mild diffuse adenopathy
Lungs - dullness at right base
Joints - synovitis at the wrists and MCPs;
small effusions in both knees
Differential Diagnosis
Infection
• Virus (HIV, hepatitis, EBV, Coxsackie)
• Gonococcus
• Subacute bacterial endocarditis
• Pneumonia
• Tuberculosis
Differential Diagnosis
Infection
•
•
•
•
•
Virus (HIV, hepatitis, EBV, Coxsackie)
Gonococcus
Subacute bacterial endocarditis
Pneumonia
Tuberculosis
Rheumatic Disease
• Rheumatoid arthritis
• Systemic lupus erythematosus
Differential Diagnosis
Infection
•
•
•
•
•
Virus (HIV, hepatitis, EBV, Coxsackie)
Gonococcus
Subacute bacterial endocarditis
Pneumonia
Tuberculosis
Rheumatic Disease
•
•
•
•
•
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Mixed connective tissue disease
Polymyositis
Polyarteritis nodosa
Differential Diagnosis
Infection
•
•
•
•
•
Virus (HIV, hepatitis, EBV, Coxsackie)
Gonococcus
Subacute bacterial endocarditis
Pneumonia
Tuberculosis
Rheumatic Disease
•
•
•
•
•
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Mixed connective tissue disease
Polymyositis
Polyarteritis nodosa
Malignancy
• Leukemia
• Lymphoma
Laboratory Data
Hgb - 11.3
Hct - 34
WBC - 3,200
Platelets - 220,000
LFTs - wnl
Creatinine - 1.0
Urinalysis - wnl
EKG - wnl
X-rays: Chest - small pleural effusion on the right
Hands/knees - swelling, no bony abnormalities
RF - 1:80
ANA - 1:160
Serology
CH50 - low
Anti-DNA - high
Laboratory Data
Hgb - 11.3
Hct - 34
WBC - 3,200
Platelets - 220,000
LFTs - wnl
Creatinine - 1.0
Urinalysis - wnl
EKG - wnl
*X-rays: Chest - small pleural effusion on the right
Hands/knees - swelling, erosions at MCP joints
RF - 1:80
*ANA - negative
Laboratory Data
Hgb - 11.3
Hct - 34
WBC - 3,200
Platelets - 220,000
LFTs - wnl
*Creatinine - 1.8
*Urinalysis - 2+ protein, RBCs
EKG - wnl
X-rays: Chest - small pleural effusion on the right
Hands/knees - swelling, no bony abnormalities
*RF - negative
*ANA - 1:160
Laboratory Data
Hgb - 11.3
Hct - 34
*WBC - 5,600
Platelets - 220,000
LFTs - wnl
*Creatinine - 1.8
*Urinalysis - 2+ protein, RBCs
EKG - wnl
X-rays: Chest - small pleural effusion on the right
Hands/knees - swelling, no bony abnormalities
RF - 1:80
*ANA - negative
Laboratory Data
Hgb - 11.3
Hct - 34
*WBC - 84,000
Platelets - 220,000
LFTs - wnl
Creatinine - 1.0
Urinalysis - wnl
EKG - wnl
X-rays: Chest - small pleural effusion on the right
Hands/knees - swelling, no bony abnormalities
*RF - negative
*ANA - negative
Principles of Management
Careful monitoring
Attention to psychosocial problems
Topical therapy for skin involvement
NSAIDs for arthritis/pleuritis
Treat associated medical problems
Steroids/cytotoxic drugs for refractory symptoms
and/or life threatening manifestations
Potential Biologically-Based Therapeutic
Interventions for Lupus (a partial list)
B Cell Targets
•
•
•
•
•
Anti-BLyS
Anti-CD20
Anti-CD22
Anti-B7
TACI-Ig
T Cell Targets
•
•
•
•
Anti-CD3
Anti-CD4
Anti-CD40L
CTLA4Ig
Cytokine Targets
•
•
•
•
Anti-IFN (a or g)
Anti-TNF-a
Anti-IL-10
Anti-IL-6R
Complement System Targets
• Anti-C5
• C3 convertase inhibitor (Crry-Ig)
Regulatory Cell Targets
• CD4+ CD25+ T Cells
Stem Cell Transplantation
Anti-BLyS (Belimumab)
Summary
BLISS-52
a Wallace
BLISS-76
et al. Presented at the American College of Rheumatology Annual Meeting, Nov 9, 2010, Poster 1172.
Changes in Serologic Measures
-9.7%
Anti-dsDNA
Median % Change
In Patients Positive at Baseline
-43.3%
-49.5%
51.9%
C4
38.5%
% Change Over Time
In Patients With Low Baseline C4
16.7%
# p <0.001, + p <0.01, * p <0.05
T Cell Costimulation
Inhibition of T Cell Costimulation
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus












