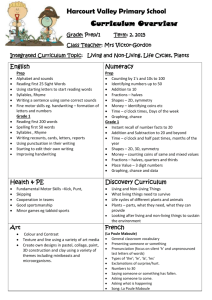
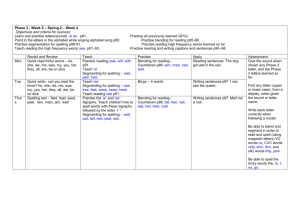
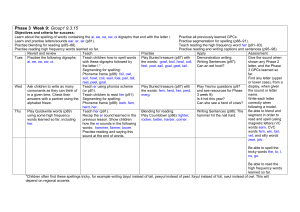
Powerpoint
advertisement

Barriers to Health Care 1 Labelling and stereotypes Waiting times/ lists Attitudes Costs Opening times Barriers to care services Opening times Lack of disabled access Location (geographical) language Lack of information discrimination Language 2 Barriers to access Definition Early Years examples Factors preventing the use of care •Shortage of provision •Location and transport •Cultural needs Social Care Examples •Attitude (stigma) •Cost (means-testing) •Eligibility Health Care examples •Physical barriers •Cost •Language/culture •Bed blocking •Prejudice, labelling, stereotyping •Lack of information •Geographical3 Care Provision Care Value Base Legislation Care practise Procedures Policies and standards 4 Care Value base • The CVB is an important concept, which has been adopted by the caring professions. • The CVB is incorporated in the codes of conduct and codes of practise of employers within the Health, Social Care and Early years professions. 5 Care Value Base Anti-discriminatory practise Promoting and supporting rights Promoting effective communication Maintaining confidentiality Acknowledging personal beliefs and identity 6 Access • There are many ways in which the public can • • access Health Care Services. Referrals – self referral - third party referral - professional referral Equal access to care services Why would unequal access prevent you from receiving the care you need? 7 REFERRAL SYSTEMS Service User Service user service User GP FRIEND OR RELATIVE GP Gp Social worker Home Help 8 Workshop Tasks Related to slides 2 and 3 • Identify as many barriers as you can, which may • • prevent people from obtaining the care services which they require. Identify the social groups that are most likely to experience cost, physical problems and language issues as ‘barriers’ to accessing the care they require Identify which group of people which are less likely to use a GP. Identify as many reasons for this. ( gender issue) 9 Workshop Tasks related to slides 4,5 & 6 • What is the care value base and how is it used in a care setting? • What is anti-bias/ discriminatory practise? • How do you promote effective communication? • Obtain a code of practise/ ethics from as many different care professions as you can and review them. (You may be able to download them from web pages) 10