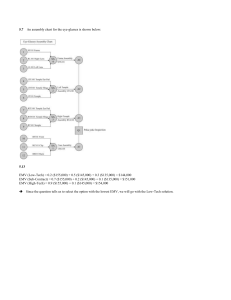
Decision tree
advertisement

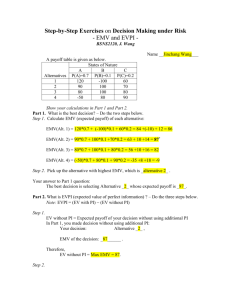
DECISION TREE Project Risk Management: A combined Analytic Hierarchy Process and Decision Tree Approach Dr.Prasanta Kumar Dey CONTENT What is the decision tree? The example of decision tree The advantage of decision tree The application of decision tree WHAT IS THE DECISION TREE? Decision tree is a decision support tool that uses a tree-like graph or model of decisions and their possible consequences, including chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility. Decision tree is commonly used in operations research, specifically in decision analysis, to help identify a strategy most likely to reach a goal. Another use of decision trees is as a descriptive means for calculating conditional probabilities. THE EXAMPLE OF DECISION TREE THE ADVANTAGE OF DECISION TREE Are simple to understand and interpret. Have value even with little hard data. Use a white box model. Can be combined with other decision techniques. Project Risk Management: A combined Analytic Hierarchy Process and Decision Tree Approach Dr.Prasanta Kumar Dey CONVENTIONAL PROJECT MANAGEMENT MODEL PROPOSED PROJECT MODEL RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS Risk identification Risk analysis Risk response RISK MANAGEMENT FLOW METHODOLOGY Identifying the work packages for risk analysis. Identifying the factors that affect the time, cost, and quality achievement of a specific work package. Analysis the effect and determining severity of failure Driving various alternatives responses for mitigating the effect of risk factors. Estimating cost for each alternative Determining the probability and severity of failure of a specific work package Forming a decision tree. Deriving expected monetary value or the cost of risk response in this case. Selecting the best option statistical analysis. IDENTIFICATION OF WORK PACKAGES Riving crossing Pipeline laying Stations construction Telecommunication and SCADA system WORK BREAKDOWN STRUCTURE AHP MODEL FOR DETERMINING RISKING OF PROJECT IDENTIFICATION OF RISK FACTORS Technical Risk scope change technology selections implementation methodology selection Equipment risk materials risk Engineering and design change Acts of God normal natural calamities abnormal natural calamities Financial, Economical and Political Risk inflation risk fund risk changes of local law changes in government policy improper estimation Organization Risk capability risk of owner’s project group contractors failure vendor’s failure consultant’s failure Statutory Clearance Risk environmental clearance land acquisition clearance from chief controller of explosives other clearance from government authorities LIKELIHOOD OF RISK IN A PROJECT PROBABILITY AND SEVERITY OF RISK FACTORS DECISION ALTERNATIVES do nothing carrying out detailed survey using superior technology engaging an expert project team taking all responses THE COST DATA FOR EACH PACKAGE AGAINST VARIOUS RESPONSES DECISION TREE FOR PIPELINE LAYING WORK PACKAGE DECISION TREE FOR RIVER CROSSING WORK PACKAGE DECISION TREE FOR STATION CONSTRUCTION WORK PACKAGE DECISION TREE FOR TELECOMMUNICATION AND CATHODIC PROTECTION WORK PACKAGE THE EMV FOR “ PIPELINE LAYING PROJECT” THE EMV FOR” PIPELINE LAYING ACROSS RIVER” THE EMV FOR ” STATION CONSTRUCTION” THE EMV FOR “TELECOMMUNTION AND SCADA SYSTEM THE DECISION EMERGE RISK RESPONSES To avoid To reduce To transfer To absorb CONCLUSION Risk management using a combined AHP and DTA provides an effective means for managing a complex project efficiently. Risk management makes an effect to quantify risk by modeling its probability and severity in line with the perceptions of experienced project executives subjectivity. REFERENCE http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree http://www.mindtools.com/dectree.html http://zh.wikipedia.org/zhhk/%E5%86%B3%E7%AD%96%E6%A0%91