MGT 2070 Assignment #3 – Solutions
advertisement
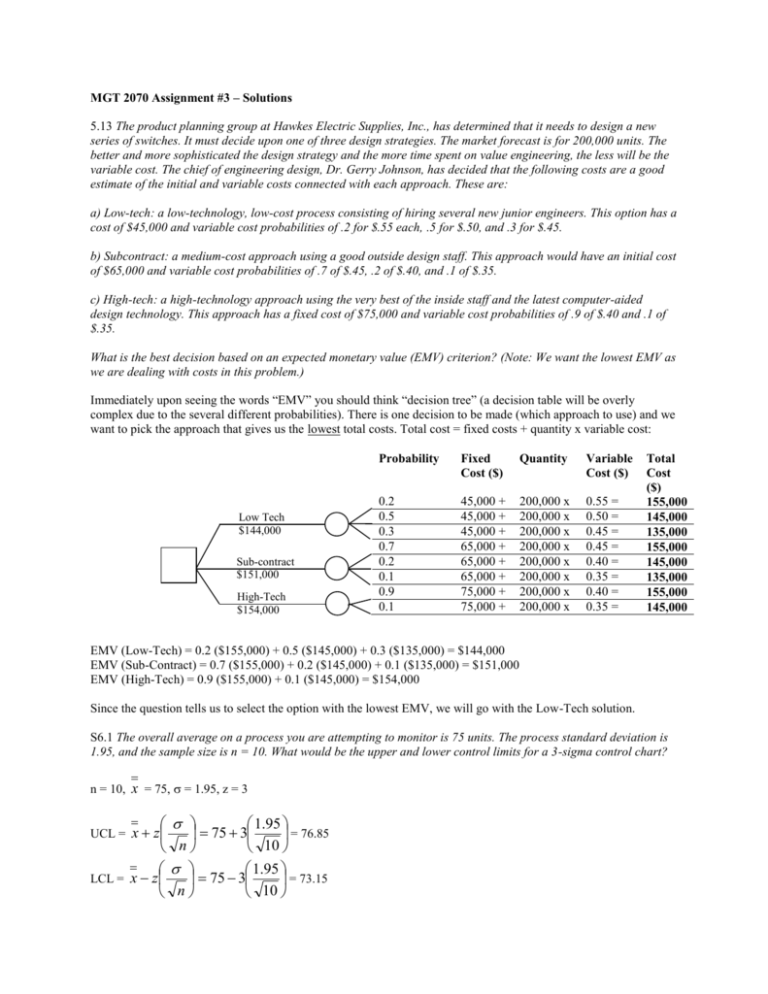
MGT 2070 Assignment #3 – Solutions 5.13 The product planning group at Hawkes Electric Supplies, Inc., has determined that it needs to design a new series of switches. It must decide upon one of three design strategies. The market forecast is for 200,000 units. The better and more sophisticated the design strategy and the more time spent on value engineering, the less will be the variable cost. The chief of engineering design, Dr. Gerry Johnson, has decided that the following costs are a good estimate of the initial and variable costs connected with each approach. These are: a) Low-tech: a low-technology, low-cost process consisting of hiring several new junior engineers. This option has a cost of $45,000 and variable cost probabilities of .2 for $.55 each, .5 for $.50, and .3 for $.45. b) Subcontract: a medium-cost approach using a good outside design staff. This approach would have an initial cost of $65,000 and variable cost probabilities of .7 of $.45, .2 of $.40, and .1 of $.35. c) High-tech: a high-technology approach using the very best of the inside staff and the latest computer-aided design technology. This approach has a fixed cost of $75,000 and variable cost probabilities of .9 of $.40 and .1 of $.35. What is the best decision based on an expected monetary value (EMV) criterion? (Note: We want the lowest EMV as we are dealing with costs in this problem.) Immediately upon seeing the words “EMV” you should think “decision tree” (a decision table will be overly complex due to the several different probabilities). There is one decision to be made (which approach to use) and we want to pick the approach that gives us the lowest total costs. Total cost = fixed costs + quantity x variable cost: Low Tech $144,000 Sub-contract $151,000 High-Tech $154,000 Probability Fixed Cost ($) Quantity Variable Cost ($) 0.2 0.5 0.3 0.7 0.2 0.1 0.9 0.1 45,000 + 45,000 + 45,000 + 65,000 + 65,000 + 65,000 + 75,000 + 75,000 + 200,000 x 200,000 x 200,000 x 200,000 x 200,000 x 200,000 x 200,000 x 200,000 x 0.55 = 0.50 = 0.45 = 0.45 = 0.40 = 0.35 = 0.40 = 0.35 = Total Cost ($) 155,000 145,000 135,000 155,000 145,000 135,000 155,000 145,000 EMV (Low-Tech) = 0.2 ($155,000) + 0.5 ($145,000) + 0.3 ($135,000) = $144,000 EMV (Sub-Contract) = 0.7 ($155,000) + 0.2 ($145,000) + 0.1 ($135,000) = $151,000 EMV (High-Tech) = 0.9 ($155,000) + 0.1 ($145,000) = $154,000 Since the question tells us to select the option with the lowest EMV, we will go with the Low-Tech solution. S6.1 The overall average on a process you are attempting to monitor is 75 units. The process standard deviation is 1.95, and the sample size is n = 10. What would be the upper and lower control limits for a 3-sigma control chart? n = 10, x = 75, = 1.95, z = 3 1.95 x z 75 3 = 76.85 n 10 1.95 LCL = x z 75 3 = 73.15 n 10 UCL = 7.21 Tom Miller and Jeff Vollmann have opened a copy service on Commonwealth Avenue. They estimate their fixed cost at $12,000 and their variable cost of each copy sold at $.01. They expect their selling price to average $.05. a) What is their break-even price in dollars? Price (P) Variable Cost (V) Fixed Cost (F) BEP$ = = $0.05 / unit = $0.01 / unit = $12,000 F 12,000 = $15,000 V 0.01 1 1 P 0.05 b) What is their break-even point in units? BEPx = F 12,000 = 300,000 units P V 0.05 0.01 Assignment #4 Due: Thursday August 2 In approximately 500 words, answer the following question: Using what you learned on your tour of the Big Rock plant, how has the company answered one of the following critical decisions of Operations Management: a) Service and Product Design; b) Quality Management; c) Process and Capacity Design; d) Location; or e) Layout. Your answer must identify which of the above decisions you have chosen to comment on. It should relate concepts from the text and lectures to what you learned during the plant tour.