class_1_intro_to_course-post_class_slides
advertisement

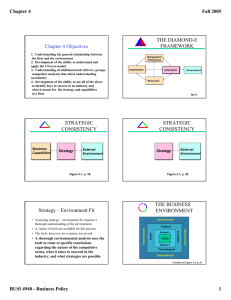
• A tough, challenging course • But so is management…and LIFE! • Identify and address strategic issues • Ambiguous, complex real-world issues • “Choice”, not solutions and answers • Five broad objectives: • • • • • Think – integrate; open; synthesis Process – organized analysis & argument Tools - mechanics Communication – written/verbal Teams – leverage for benefit; handle diversity • Not everyone wants to get into Management • Name • Major • Something interesting -some suggestions---• about your work e.g. “I’m a bungee-jumping cord tester…” • About your family/home e.g. “I have 3 pet iguanas and 1 kangaroo” • About your hobbies/interests e.g. “I invented the internet.” Syllabus Blackboard Learn Clickers – set up/test CHANNEL 61 Yes No What’s a clicker? 0% 0% W ha t ’s a c li ck e r? No 0% Ye s A. B. C. Yes No Not sure yet 0% 0% No ts ur e ye t No 0% Ye s A. B. C. Definition A concrete expression of how an organization intends to compete and win in the marketplace Strategy expressed in terms of Goals Product Focus and Market Focus Value Proposition Core Activities Note the rising levels of risk, investment, uncertainty of implications, and timeframes as you move down the list below . . . Choosing a cereal for breakfast Making a withdrawal at the ATM Purchasing an iPad Purchasing a car Sun-bathing Getting an education They involve major investments They have long-term implications, often in multiple areas They often involve high levels of risk/uncertainty Remember that any action can be viewed as being strategic, depending on your frame of reference. In the business context, your challenge is to think like the CEO, President or, General Manager of the organization, not as a VP of a functional area like Finance Marketing, Human Capital, etc. . . . ., and delineate those actions that are truly “strategic” from those that are “functional.” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q96pCI8aOQQ Which of these actions typically involve “strategic” decisions for an organization? Altering the products/services offered by the organization Altering the markets serviced by the organization Altering the way the organization creates value for its customers Streamlining customer-service procedures Increasing the size of the sales-force Improving payment terms with buyers. Switching to a different ERP-platform provider Hiring a new marketing manager Which of these actions typically involve “strategic” decisions for an organization? Altering the products/services offered by the organization Altering the markets serviced by the organization Altering the way the organization creates value for its customers Streamlining customer-service procedures Increasing the size of the sales-force Improving payment terms with buyers. Switching to a different ERP-platform provider Hiring a new marketing manager After just three years, Winchester Pizzas has franchise stores in nine southern states and master franchisees lined up in six more. Is targeting new stores in the rest of the US strategic? Yes No 0% No 0% Ye s A. B. 30 Barty Crouch’s Custom Computers has done well simply by word of mouth and a great Internet presence. But Barty Crouch Sr. feels increased awareness will grow the firm. Is shifting resources for a doubling of advertising strategic? Yes No 0% No 0% Ye s A. B. 30 Yes No 0% No 0% Ye s A. B. 30 Strategic actions are not made in a vacuum Competitors; Customers; Suppliers; Institutions; Innovators; Technology No industry is completely stable Most industries face considerable change Adapt . . or Drivers of Organizational Change in the Firm’s External Environment 1. Environmental Dynamics 2. Environmental Scope and Munificence 3. Environmental Uncertainty and Risk The increasingly turbulent environment Globalization of products and markets Political/Social/Economic/Technological Adapt .. Adapt . . Adapt or CHANGE CHANGE CHANGE Drivers of Organizational Change From Inside the Firm 1. Mission, Vision & Goals Instigated by the organization’s stakeholders. . . . 2. Strategy of the firm Instigated by the organization’s top management . . . 3. Organizational Capabilities Structure, processes and leadership. Effective business management IS NOT largely a matter of common sense. Effective business management IS a result of effective data collection, data interpretation, and the use of conceptual frameworks to diagnose and monitor activities in the firm and in its environment. (Allan Tudehope) Managers and strategists are information processors The Criterion of Consistency Consistency (“fit”) between the firm and its environment Strategy as the critical linking variable Internal Environment Business Capabilities BC Strategy S External Environment E Management Preferences Organization STRATEGY Resources Business capabilities Environment Business Capabilities • Resources • Management Preferences • Organizing Processes Strategy •Goals •Product/Market Focus •Value Proposition •Core Activities External Environment • Key Survival Factors • Drivers of Change We begin by understanding the ENVIRONMENT in which the firm competes What is it? A process for achieving consistency between the firm and its environment You will be required to use the skills acquired in your undergraduate business foundation courses Accounting, Decision Sciences, Finance, Information Systems, HR/OB, Management, Economics, and Marketing At each process stage, you will have tools and concepts to apply Each phase has been converted to a template with questions and steps to follow Primary phases involve Collecting as much relevant data as possible Organizing the data and analyzing the data Drawing conclusions or recommendations SBI Parts 1A & 1B Analyze the External Environment of the Firm Analyze the Strategy of the Firm Analyze the Capabilities of the Firm SBI Part 2A Identify Strategic Gaps SBI Part 2B Develop New Strategy SBI Part 3A 1. Prepare Complementary Functional Plans 2. Develop an implementation Plan SBI Part 3B Assess Financial Viability Identify Required Capabilities Changes It has three sequential parts: Part-1: Analyze the environment(A) and status of the firm (B) Deconstruct and understand the business landscape and the specific firm within that context Part-2: Assess strategic fit (A) and formulate new strategy (B) Assess E-S-BC fit issues and propose possible changes Part-3: Develop an implementation plan (A)and confirm financial viability of the proposal (B) Details of the implementation plan Details of expected results Part-1 Part-2 Part-3 • Political, Economic, Social, and Technological Forces • The BROAD environment • Influence multiple industries • Influence all firms in an industry ‘equally’ • Great indicators of what is BECOMING more influential….’early warning signals’ • May be ‘Rules of the game’ • Broad effects on demand, values, market needs Industry specific Different forces that affect profitability / opportunity for profitability Porter – a competition for economic value – Substitute or Rival? Substitute – same or similar function (met need) BUT via a different means (Pizza delivery v Frozen Pizza) Rival – same met need via same/similar function and means (Bing v. Google) Market Commonality; Resource Similarity (Chen, 1996) Still dependent on how you define the industry Primary Entry Barriers: Determinants of Rivalry Include • • • • • • POTENTIAL ENTRANTS Industry Growth The number and balance of rivals Differentiation Percentage of fixed costs Brand identity and product differences Exit barriers and corporate stakes SUPPLIER POWER Relative concentration Presence of substitutes Relative switching costs Relative threat of integration Importance of the supplies Differentiation of the supplies Economies of Scale Product Differentiation Capital Requirements Switching Costs Cost Disadvantages Independent of Scale Government Policy INDUSTRY RIVALRY BUYER POWER Determinants of Buyer Power Include Determinants of Supplier Power Include • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • SUBSTITUTE PRODUCTS The relative concentration of buyers and sellers The volume of purchases The relative switching costs of buyers and sellers Ability of buyers to backward integrate The buyers price sensitivity Power of Substitutes driven by • The relative price and performance of substitutes • Switching costs • Buyers propensity to substitute What is the average performance – growth, profitability, etc.? What are the KEY SURVIVAL FACTORS demanded? What are the DRIVERS OF CHANGE? What will the industry look like in the future? This requires research and analysis! Based on the powerful forces you have identified, what MUST a firm do minimally well to survive in this industry? Think ‘above’ the given/obvious ‘survival factors’ to identify KEY factors Prioritize them by how they relate to the most powerful forces affecting the industry • • • • Efficiencies Through E-Commerce/Technology Reliable Delivery Strong Service Solid Sales and Support Staff What trends from your PEST analysis are changing the nature of the environment? What forces of industry profitability are changing or may change in the near future? Prioritize these based on the scope and magnitude of their effect on firm performance and survival Increasing globalization of the industry; Changes in who buys the products and how they use it. Exit of major firms/”big players” Growing buyer for preferences a more standardized product instead of strongly differentiated products Changing societal concerns, attitudes, and lifestyles Based on current status (size, growth, profits, etc.), and on your knowledge of forces and trends, how attractive is this industry now? (Not how difficult is it to get into…just how attractive is it) Now, consider the trends you are aware of…how attractive (same, more, less) will the industry be in five years? Based on all you know about the industry, what combinations of product focus, market focus, and value proposition do you conclude are most viable for survival and success in this industry? Alternatively, which strategic orientations do you think are ‘bad ideas’ here? Industry research Patterns/clues – drill into possible KSFs/DOC Gather facts; document sources; verify if can Cover each component thoroughly P.E.S.T. and all 5 forces Identify, list, describe, cause/effect, etc. Synthesize - Analyze - Prioritize Don’t report data – Argue your conclusions then give the data that supports them Next class June 4: Do syllabus quiz on-line Online “Terms and Definitions” assignment Between classes June 6: Team preferences due via email REMEMBER: TEAMS of 7/8– Choice and/or Assignment 1 of each: MKTG, FIN, ACCTG, Risk/Ins/FinServ Subsequent Class June 9: Read Textbook: Ch. 2. Submit individual assignment Part 1 at 6 PM (2 hard copies) You should also review the Blackboard supplemental reading on Evaluating the Environment There will be GRADED clicker questions on the readings next class! Please come prepared!