An Overview ofProject Management
advertisement

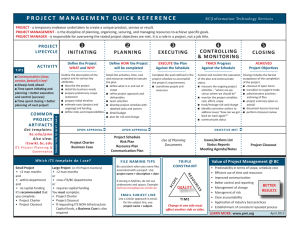
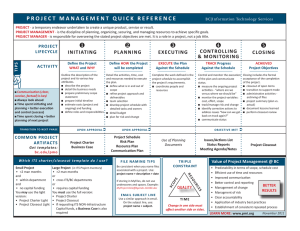
An Overview of Project Management New Supervisors’ Call 2/16/2012 Contact Information Elaine Lindsay Twedt, PharmD, MS, BCPS, CACP Business Manager, Pharmacy Recruitment and Retention Office (PRRO) VA Outpatient Clinic 1767 Village Park Dr. Orangeburg, SC 29118 (803) 378-4823 elaine.twedt@va.gov Outline • • • • • PM definition Brief History Introduction to PM Initiation, Planning, Execution, Closeout VA training and resources Polling Question How much do you know about the Project Management (PM) discipline? A. I have never heard of PM. B. I am familiar with PM, but have no formal training. C. I am knowledgeable in PM and apply it to my work. D. I am PMP® certified and I keep a copy of the PMBOK® on my coffee table at home. PM Defined • PM is the discipline of planning, organizing, securing, managing resources to achieve specific goals • A project is a temporary endeavor with a defined beginning and end • Undertaken to bring about beneficial change or added value Project vs. Not a Project Project • Temporary • Resource-constrained • Brings change • Examples – BCMA implementation – Pharmacy Research Project – American Pharmacists Month Celebration Not a Project • Permanent • Daily business operations • Repetitive, consistent • Examples – Filling prescriptions – Placing procurement order – Running Ambulatory Care Clinics A Brief History of PM • Worldwide – Vitruvius(1st century BC) – Henry Gantt(1861–1919), “Father of Planning and Control Techniques” – 1950’s: organizations apply PM tools and techniques to engineering projects • Veterans Health Administration – 2003: VA launched OneVA PM Certification and Training program to meet Office of Management and Budget’s (OMB) mandate for qualified IT project managers – rolling out to Education, Program Offices Introduction to PM Four-phase life cycle Project Initiation • Influences, stakeholders, project team • Project selection, cost-benefit ratio, present value, net present value • Project charter • Formulating good objectives (SMART) • Requirements specifications, Statement of Work (SOW), assumptions, constraints Project Planning Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Estimating and Scheduling • Expected = (O+ML+P)/3 • Scheduling Gantt Chart Example Project Execution • Monitoring and controlling is ongoing and used by the team • Change can be managed with a welldesigned change management system • Earned value shows the project manager the difference between what was planned and what has occurred at a certain point in time • Risk response plans can be used to manage risks • Conflict is inevitable and must be managed • Verify scope against agreed-upon requirements. Closing out with the customer involves both technical acceptance and sign-off. Project Closeout • Plan for closeout in the WBS and the schedule • Procurement and project or phase closeout ensure that all project requirements are met • Lessons learned impart valuable knowledge to your organization for use in future work • Closing out the project with the team, stakeholders, and yourself • Includes appropriate recognition and celebration of your efforts VA Project Management Training • For VISN employees of Program Office employees • http://vaww.onevapmcertification.va.gov • The George Washington University School of Business and ESI International • Up to 18 months to complete 7 core courses 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Managing Projects Project Leadership, Management, and Communications Scheduling and Cost Control Risk Management Quality for Project Managers Contract Management Principles and Practices Project Management Applications • Masters Certificate in Project Management from GWU Screenshot of VA PM home page Talent Management System (TMS) • www.tms.va.gov • 134 offerings for PM training Resources Available on PRRO site http://vaww.infoshare.va.gov/sites/vapharmacyinformatics/Prro/default.aspx • Under “Popular Documents;” also under “New Pharmacy Supervisors” tab • Click on “Project Management Tools” folder Questions?