Industry
advertisement

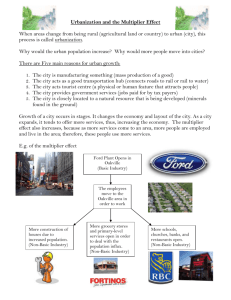
Basic and Non-Basic Industries Basic Industries • Industries that sell their products outside the community, bringing “new” money into the community Non-Basic Industries • Industries that sell their products within the community, not bringing “new” money into the community Decide if the description is an example of either a basic or non-basic industry: Job Description Coal miner in northeastern British Columbia Basic/Non-Basic Basic Hairdresser at a shopping mall Non- basic Art teacher Non- basic Actor at the Stratford Shakespearean Festival Teller at the local bank Vice-president of Scotiabank Professor at Queen’s University Basic Non- basic Basic Receptionist at a dentist’s office Basic Non- basic Air Canada pilot Basic School-bus driver Non- basic Multiplier Effect “total effect on the economy caused by an expansion or contraction in one part of it” Basic industries drive the multiplier effect Think of a ski resort •The money you pay to ski and stay goes to pay employee salaries • employees use this money to spend on things in the town • While at the resort, you may also spend money at a grocery store, dinner, Tim Hortons, new equipment, etc Therefore, your money spent has multiplied, because others have used it to buy goods and services within the community Christaller’s Central Place Theory 1933 Walter Christaller, a German geographer, formulated a model for explaining why: Large cities/towns are located far apart, while small towns/villlages are located close together. reasoned that “any good or service offered by a central place needs a minimum number of people surrounding it (hinterland) to stay in business” Threshold population High-order goods /services require large threshold pop, because expensive and bought infrequently (ex. car dealer, hospitals) Low-order goods /services small threshold pop, because inexpensive or bought often (ex. grocery store, post office) villages High order goods/services provided only in cities (A) Middle-order goods/services provided in cities (A) and towns (B) Low-order goods/services provided in cities (A), towns (B) and villages (C) Urbanization vs. Urban Growth Urbanization: process of changing from rural to urban (% living in cities) Urban Growth: The rate (# of people) at which a city grows Your Turn. . . Complete the chart below by indicating where you would find the services listed: Service Brain surgery Daycare for a child Major league baseball Daily newspaper Dental checkup Internet connection Symphony concert Elementary school Recreational centre Small town Small city Large City Homework. . . You will look at one SMART GROWTH principle (instructions on hand out), summarize it and report back to class