Urbanization
advertisement
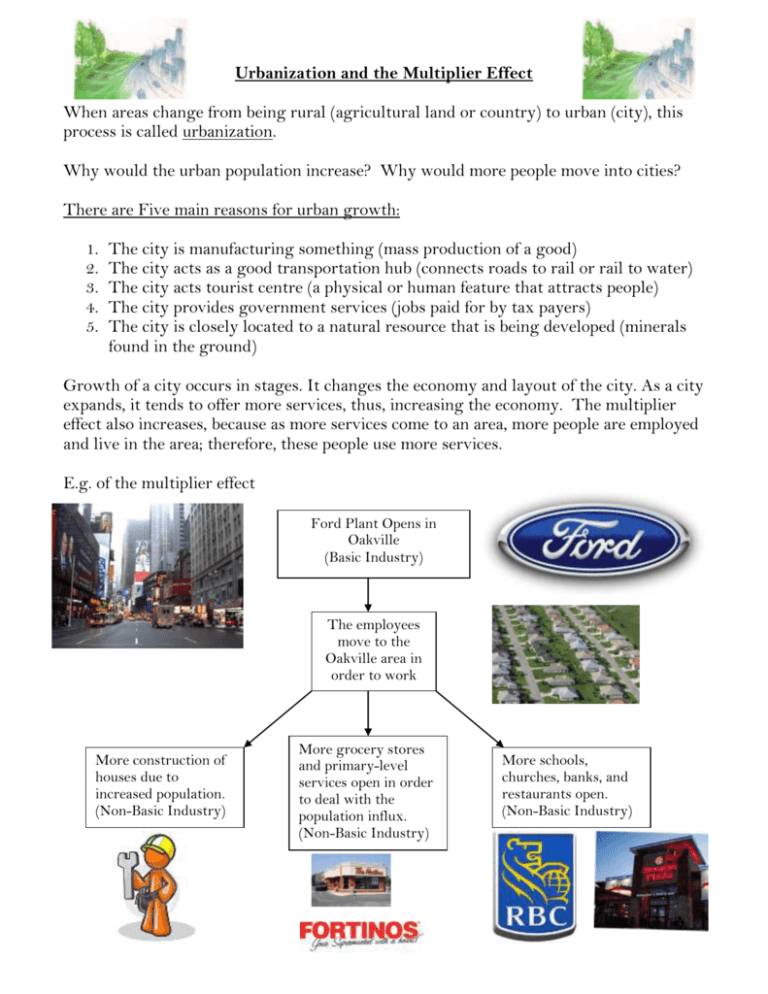
Urbanization and the Multiplier Effect When areas change from being rural (agricultural land or country) to urban (city), this process is called urbanization. Why would the urban population increase? Why would more people move into cities? There are Five main reasons for urban growth: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The city is manufacturing something (mass production of a good) The city acts as a good transportation hub (connects roads to rail or rail to water) The city acts tourist centre (a physical or human feature that attracts people) The city provides government services (jobs paid for by tax payers) The city is closely located to a natural resource that is being developed (minerals found in the ground) Growth of a city occurs in stages. It changes the economy and layout of the city. As a city expands, it tends to offer more services, thus, increasing the economy. The multiplier effect also increases, because as more services come to an area, more people are employed and live in the area; therefore, these people use more services. E.g. of the multiplier effect Ford Plant Opens in Oakville (Basic Industry) The employees move to the Oakville area in order to work More construction of houses due to increased population. (Non-Basic Industry) More grocery stores and primary-level services open in order to deal with the population influx. (Non-Basic Industry) More schools, churches, banks, and restaurants open. (Non-Basic Industry)