PPT
advertisement

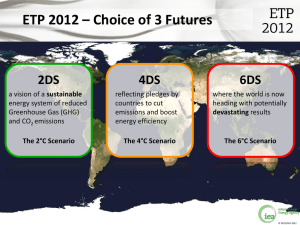
Tapping technology’s potential to secure a clean energy future Richard H. Jones Deputy Executive Director Korea, Seoul June 18, 2012 © OECD/IEA 2012 ETP 2012 – Choice of 3 Futures 2DS a vision of a sustainable energy system of reduced Greenhouse Gas (GHG) and CO2 emissions The 2°C Scenario 4DS reflecting pledges by countries to cut emissions and boost energy efficiency The 4°C Scenario 6DS where the world is now heading with potentially devastating results The 6°C Scenario © OECD/IEA 2012 Sustainable future still in reach Is a clean energy transition urgent? Are we on track to reach a clean energy future? Can we get on track? YES ✓ NO ✗ YES ✓ © OECD/IEA 2012 Recommendations to Governments 1. Create an investment climate of confidence in clean energy 2. Unlock the incredible potential of energy efficiency – “the hidden” fuel of the future 3. Accelerate innovation and public research, development and demonstration (RD&D) © OECD/IEA 2012 A smart, sustainable energy system Co-generation Renewable energy resources Centralised fuel production, power and storage Distributed energy resources Smart energy system control H2 vehicle Surplus heat EV A sustainable energy system is a smarter, more unified and integrated energy system © OECD/IEA 2012 Clean energy: slow lane to fast track Cleaner coal power Nuclear power Renewable power CCS in power CCS in industry Industry Buildings Progress is too slow in almost all technology areas Significant action is required to get back on track Fuel economy Electric vehicles Biofuels for transport © OECD/IEA 2012 Low-carbon electricity: a clean core 45 000 Other Wind Solar Hydro Nuclear Biomass and waste Oil Gas with CCS Gas Coal with CCS Coal 40 000 35 000 TWh 30 000 25 000 20 000 15 000 10 000 5 000 0 2009 2020 2030 2040 2050 Renewables will generate more than half the world’s electricity in the 2DS © OECD/IEA 2012 Nuclear and Renewables need to dominate OECD Asia Oceania electricity 100% 2 500 2% 0.5% 6% Other renewables 90% 6% 8% 6% 5% 6% 80% Wind 2 000 24% 11% 8% Generation share 70% TWh 1 500 1 000 Wind 11% Solar Solar 60% 35% Hydro 50% Hydro 40% Nuclear 30% 47% 67% Fossil w CCS 20% 500 Other renewables Nuclear 3% Fossil w CCS 34% 6% 10% Fossil w/o CCS 11% Fossil w/o CCS 0% 0 4DS 2009 4DS 2DS 2050 2009 2DS 2050 Whereas today around two thirds of electricity are based on fossil fuels, nuclear and renewables play an important role to decarbonise electricity supply under the 2DS. © OECD/IEA 2012 Acceleration of nuclear, wind and PV needed Hydro Nuclear CSP 2021-50 PV Wind, offshore 2011-20 Wind, onshore 2001-2010 Biomass Gas with CCS Coal with CCS 0 1 2 3 GW per year 4 5 Massive deployment of low-carbon technologies needed, especially of nuclear and renewable technologies. 6 © OECD/IEA 2012 All flexibility sources will be needed Dispatchable power plants Demand side Response (via smart grid) Energy storage facilities Interconnection with adjacent markets Industrial Biomass-fired power plant residential Pumped hydro facility Scandinavian interconnections © OECD/IEA 2012 Smart grids offer net benefits Total benefits of smart-grid investments outweigh costs – but direct benefits of investment may be found in other sectors. © OECD/IEA 2012 Power Generation from Natural Gas TWh Natural Gas: a transitional fuel 7 500 5 000 2 500 0 2009 2020 OECD 2030 China India 2040 2050 Other non-OECD Around 2030, natural gas becomes ‘high carbon’ © OECD/IEA 2012 The CCS infant must grow quickly Mt CO2 Mt CO2 Mt CO2 Mt CO2 Mt CO2 Mt CO2 Note: Capture rates in MtCO2 /year © OECD/IEA 2012 GtCO2 Industry must become more efficient 12 6DS 10 Other industries 8 6 Chemicals and petrochemicals Aluminium 4 Pulp and paper 2 Iron and steel 0 2010 Cement 2020 2030 2040 2050 Significant potential for enhanced energy efficiency can be achieved through best available technologies. © OECD/IEA 2012 Electric vehicles need to come of age Passenger LDV sales (million) 200 FCEV Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles Electricity 150 Plug-in hybrid diesel Plug-in hybrid gasoline Diesel hybrid 100 Gasoline hybrid CNG/LPG 50 Diesel 0 2000 Gasoline 2010 2020 2030 2040 2050 More than 90% of light duty vehicles need to be propelled by an electric motor in 2050 © OECD/IEA 2012 Translating targets into action 8 million sales/year 7 Manufacturers production/sales 6 5 Projection (Estimated from each country's target) Projection (Estimated from each country's target) 4 3 2 1 0 2010 2012 2014 2016 2018 2018 2020 2020 Government targets need to be backed by policy action © OECD/IEA 2012 Building Blocks of a Cleaner Future Total energy savings 33 EJ Space heating 22% Other 15% Water heating 12% Services Lighting, 3% Residential Cooling and ventilation, 3% Water heating, 2% Cooking 15% Space heating, 7% Appliances 10% Lighting 6% Cooling and ventilation 5% About 70% of buildings’ potential energy savings between the 4DS and 2DS are in the residential sector © OECD/IEA 2012 Building sector challenges differ Billion households ,2.5 ,2.0 ,1.5 ,1.0 ,0.5 ,0.0 2010 OECD 2020 2030 2040 2050 Non OECD 75% of current buildings in OECD will still be standing in 2050 Heating & Cooling: huge potential Renewable heat Integration with electricity District heating and cooling network Co-generation Surplus heat Heating and cooling account for 46% of global energy use. Their huge potential for cutting CO2 emissions is often neglected. © OECD/IEA 2012 Emissions must be eliminated by 2075 A zero-carbon future looks possible but will be very challenging, even if 2050 targets are met in the 2DS. © OECD/IEA 2012 Increase public spending on RD&D 12% 25 6% 10 4% 5 4 3 2 2% 1 1990 1994 1998 2002 2006 2010 Energy efficiency Fossil fuels Renewable energy Nuclear Hydrogen and fuel cells Other power and storage technologies Other cross cutting technologies/research Share of energy RD&D in total R&D South Africa 1986 Russia 1982 Mexico 1978 India 1974 China 0 0% 0 Brazil USD billion 15 2008 non-IEA country spending USD billion 8% Share of energy RD&D in total R&D 10% 20 © OECD/IEA 2012 Clean energy investment pays off Total savings Fuel savings Additional investment Additional investment Power Power Industry With price effect Transport Industry Without price effect Residential Transport Commercial Undiscounted Fuel savings Residential 3% Biomass Coal Commercial 10% Oil - 160 - 120 - 80 - 40 0 40 Gas USD trillion Every additional dollar invested in clean energy can generate 3 dollars in return. © OECD/IEA 2012 For much more, please visit www.iea.org/etp © OECD/IEA 2012