Progresses and Challenges of Infrastructure Spending in Timor
advertisement

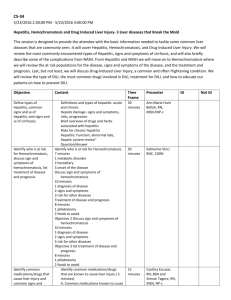
Progresses and Challenges of Infrastructure Spending in Timor-Leste The 2013 Timor-Leste Update - ANU By: Antonio Vitor ADB Consultant & MPW Adviser Outline: 1. Background 2. The Targets in Strategic Development Plan 3. Some Progresses 4. The Challenges Background • The status of infrastructure : inadequate and inefficient • Source of Financing : Self + co-financing • Implementation issues • Low execution • High budget diversion Timor-Leste’s Strategic Development Plan 2011-2030 • SDP Goal: achieving a middle income country by 2030. • Infrastructure Tasks : building & maintaining core and productive infrastructures to support growth, increase productivity, create jobs, and national private sector development • Targets for: • Roads: - rural roads are fully rehabilitated by 2015 - district roads fully rehabilitated by 2020 - national roads fully upgrade by 2020 - comprehensive maintenance program - national ring road highway (2 + 2 lanes) by 2030 (to start with Suai-Beaco) • Water: - by 2030, all citizens will have access to clean water and improved sanitation • Power/ Electricity: by 2015 everyone in Timor-Leste will have access ( 24/7); and by 2020 reduce fuel dependency by half. • Ports: Tibar - by 2020 - new, fully operational and efficient major port Suai – by 2015, fully operational and efficient • Airports: Dili: extension of the runway and a new terminal building Progresses: National roads: • upgraded Liquica-Maubara (Dec 2013) – 14 km • by 2017 will upgrade about 600 km out of 1,426 kilometers (40%) • Key links (Dili to Motain; Tibar-Gleno, DiliBaucau, Baucau-Viqueque, BaucauLoapalos (Com), Dili-Ainaro, and ManatutoNatarbora Rural roads: 240 kilometres out of 3,025 km of rural roads rehabilitated & maintained (70% of the population living in rural areas) Pilot National Roads Upgrading (Liquica-Maubara) Progresses (continued) Electricity : • 2 new power plants with 250 mgws capacity in place • 9 Sub-stations, • connection of 506 km of transmission lines out of 603 km • June 2013, ---106.072 hhs access to electricity, • 97,072 hhs connected to the grid -- 9,000 hhs renovable energy. Tibar Port (PPP) at procurement stage Challenges • Reform the current system, practices and institutional arrangement? • lacks capacities (human resources & institutions) to deliver SDP targets • under-developed national private sector (construction, design, supervision) • still low performance in public investment management and public finance management • relative small market for private investment low participation – lack competitionhigh cost) Challenges (continued): • under-developed financial markets, high-cost in doing business, weak macro-economy environment, poor governance (led to low return on capital) • political economy influences investment logics • institutional arrangement in delivering infrastructure (overlapping responsibilities , coordination issues) • Ineffective investments prioritization • political interference and of multiple, changing and competing stakeholders. • clear separation of political and technical responsibilities MPW 5-year Action Plan “100% of Dili households with safe 24-hr supply by 2017 ~4000 new connections / year? Dili households with pipe connections 50,000 45,000 40,000 Housholds 35,000 30,000 25,000 20,000 15,000 10,000 5,000 0 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Year Target Current Trend? 4000 / yr 2017 Figure 2: Dili Water Supply System zoning showing estimated supply continuity level of service (source: ADB TA-7981 in consultation with DNSA)