End of Life care - National Homecare Council
advertisement

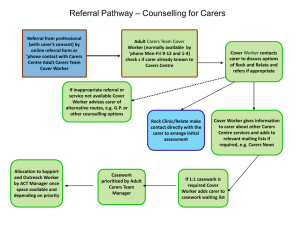
Introduction to the Gold Standards Framework Domiciliary Care Training Programme Maggie Stobbart-Rowlands, Lead Nurse, GSF Central Team “Its about living well until you die” Our aspiration is to deliver training and support that brings about individual and organisational transformation, enabling a ‘gold standard’ of care for all people nearing the end of life . End of Life care is everybody’s business Do any of the people you care for ever die? Then you need to think about end of life care. Clarification of Terms • End of Life care • ‘Care that helps all those with advanced progressive incurable illness well as possible until they die’ to live as • Supportive Care • Helping the patient and family cope better with their illness • Palliative care • specialist / palliative care -holistic care (physical psychological, social, spiritual ) • Final days/Terminal care • Diagnosing dying-care in last hours and days of life End of Life Care Supportive Care Palliative Care Final days/ Death Terminal Care End of Life Care in Numbers • 1% of the population dies each year • 17% increase in deaths from 2012 • 60-70% people do not die where they choose • 35% home death rate – 18% home, 17% care home • 40% of deaths in hospital could have occurred elsewhere • 75% non-cancer ,85% of deaths occur in people over 65 • £19k non cancer ,£14k cancer - av.cost/pt/final year . Hospice and Specialist Palliative Care 1) Specialists 2) Generalists - GSF Workforce 5,500 Enabling Generalists • Primary Care • Care Homes • Hospital • Domiciliary care Workforce -2.5 m 3) Lay People- general public • Public Awareness • Community Care • Carers Support etc • Population 60m The key role of generalist frontline carers ‘Its less about what you know… …its more about what you do and how you do it’ • Identifying important triggers - being aware of patients nearing end of life • Assessing needs and wishes • Planning care - Knowing when and where to get help Playing role in system – cross boundary care • Communicating well-Sharing information What is The Gold Standards Framework? Enabling generalists in end of life care Frameworks to deliver a ‘gold standard’ of care for all people nearing the end of life “Every organisation involved in providing end of life care will be expected to adopt a coordination process , such as the GSF” DH End of Life Care Strategy July 08 Aim of GSF • Aim is to develop an organisational -based system to improve the organisation and quality of care of service users in the last year/s of life in the community. What does GSF aim to do? 3 Key messages 1. Improve quality of care 2. Decrease hospitalisation and cost 3. Improve cross boundary teamwork + collaboration GSF is about … • Enabling Generalists - improving confidence of staff • Person- led -focus on meeting person and carer needs • Care for all people -non-cancer, frail • Pre-planning care in the final year of life -proactive care • Organisational system change • Cross boundary care- home ,care home, hospital, hospice, Care closer to home – decrease hospitalisation Improve organisation of care Head Hands and Heart HANDS HEAD - knowledge - organisation - clinical competence - systems - ‘what to do’ - ‘how to do it’ HEART -compassionate care -experience of care ’why’ - human dimension- -GSF GSF Training Programmes • GSF Primary Care – – – – From 2000- foundation GSF mainstreamed (QOF) 90% GP practices have palliative care register and meeting June 09 Next Stage GSF launched updated GSF New training programme + quality recognition • GSF Care Homes – From 2004 -Over 1500 care homes trained – Developed training and accreditation programmes – 100 / year accredited • GSF Acute Hospitals – From 2008 -Phase 1 pilot 15 hospitals – Phase 2 Spring 2011 – Improving cross boundary care GSF Domiciliary Care – From 2011 –phase 1 –Manchester, Birmingham, Rotherham – 8-10 domiciliary care agencies, 80-100 carers per agency Deliver coordinated care in line with preferences Three key bottlenecks that GSF helps with • Identification of all patients particularly those with non cancer • Difficult conversations with patients and families, advance care planning discussions • Effective team pre-planningpredicting needs- change to more proactive care GSF 3 Steps identify patients who may be in the last year of life and identify their stage (‘Surprise’ Question + Prognostic Indicator Guidance + Needs Based Coding) assess current and future, clinical and personal needs (using assessment tools, passport information, patient & family conversations, Advance Care Planning conversations) plan Plan cross boundary care and care in final days (Use Needs Support Matrix, GSF Care Plan/Liverpool Care Pathway and Discharge Information/Rapid Discharge Plan) G o ld S ta n d a rd s F ra m e w o rk a n d th e S u p p o rtive C a re P a th w a y D ra ft 7 T h in k in g A h e a d - A d va n c e C a re P la n n in g GSF Toolkit G o ld S ta n d a rd s F ra m e w o rk A d va n c e S ta te m e n t o f W is h e s T h e a im o f A d va n ce C a re P la n n in g is to d e ve lo p b e tte r co m m u n ica tio n a n d re co rd in g o f p a tie n t w ish e s. T h is sh o u ld su p p o rt p la n n in g a n d p ro visio n o f ca re b a se d o n th e n e e d s a n d p re fe re n ce s o f p a tie n ts a n d th e ir ca re rs. T h is A d va n ce S ta te m e n t o f w ish e s sh o u ld b e u se d a s a g u id e , to re co rd w h a t th e p a tie n t D O E S W IS H to h a p p e n , to in fo rm p la n n in g o f ca re . T h is is d iffe re n t to a le g a lly b in d in g re fu sa l o f sp e cific tre a tm e n ts, o r w h a t a p a tie n t D O E S N O T w is h to h a p p e n , a s in a n A d va n ce d D e cisio n o r L ivin g W ill. Id e a lly th e p ro ce ss o f A d va n ce C a re P la n n in g sh o u ld in fo rm fu tu re ca re fro m a n e a rly sta g e . D u e to th e se n sitivity o f so m e o f th e q u e stio n s, so m e p a tie n ts m a y n o t w ish to a n sw e r th e m a ll, o r to re vie w a n d re co n sid e r th e ir d e cisio n s la te r. T h is is a ‘d yn a m ic’ p la n n in g d o cu m e n t to b e re vie w e d a s n e e d e d a n d ca n b e in a d d itio n to a n A d va n ce d D e cisio n d o cu m e n t th a t a p a tie n t m a y h a ve a g re e d . P a tie n t N a m e : T ru st D e ta ils: A d d re ss: DOB: H osp / N H S no: D a te co m p le te d : N a m e o f fa m ily m e m b e rs in vo lve d in A d va n ce d C a re P la n n in g d iscu ssio n s: C o n ta ct te l: N a m e o f h e a lth ca re p ro fe ssio n a l in vo lve d in A d va n ce d C a re P la n n in g d iscu ssio n s: R o le : C o n ta ct te l: T h in k in g a h e a d … . W h a t e le m e n ts o f ca re a re im p o rta n t to yo u a n d w h a t w o u ld yo u like to h a p p e n ? W h a t w o u ld yo u N O T w a n t to h a p p e n ? A C P D ec 0 6 v 1 3 Advance Care Planning – Thinking Ahead Prognostic Indicator Guidance – PIG + Surprise Questions Use of templates in Locality Registers Passport Information Pt needs Support from hospital/SPC Years Months Weeks Days Needs Support Matrix After Death Analysis - ADA Support from GP GSF 7 C’s Support Support from your local trainer/ facilitator 2 whole day Workshops GSF Resources • GPG • Workbook folder • DVD 2. Needs Based Coding Identify stage of illness- to deliver the right care at the right time for the right patient • • • • A - All – stable from diagnosis years B – Unstable, advanced disease months C – Deteriorating, exacerbations weeks D - Last days of life pathwaydays Identify- GSF Prognostic Indicator Guidanceidentifying pts with advanced disease in need of palliative/ supportive care/for register Three triggers: 1. Surprise question‘Would you be surprised if this person was to die within the next year?’ 2. Patient preference for comfort care/need 3. Clinical indicators Suggested that all pts on register are offered an ACP discussion The Gold Standard of end of life care “The care of ALL dying patients is raised to the level of the best.” (NHS Cancer Plan 2000) Applications of learning from cancer pts to the other 3 out of 4 patients Goals of GSF Patients are enabled to have a ‘good death’ 1) symptoms controlled 2) in their preferred place of choice 3) Safe +secure with fewer crises. 4) Carers feel supported, involved, empowered, and satisfied. 5)Staff confidence, teamwork, satisfaction, co-working with specialists and communication better. Skills for Care and Skills For Health Common Core Competences: Care planning Symptom control Advance care planning Communication Skills What are the issues you face in providing good end of life care? The Challenges in Domiciliary Care • Isolation/Lone workers • Communication with others e.g. GPs, DNs • Not being valued by other professionals • No Pathways or plans for end of life care • Lack of collaboration & identification of people at the end of life • Inappropriate admissions at the end of life • Confidence of staff Key Challenge Lone Workers Valued Consistency of carers Collaboration GP/DN GSF in Domiciliary Care Key Question What is the importance of End of Life care, and the role of the Domiciliary care worker? Key Topic Context of End of Life Care, GSF Training Programme, and next steps Communication Lack of structure Understanding what to do People admitted to hospital in the last stages of life Are we identifying the people in the last year or so of life? Identify – Needs Based Coding Are we providing the right care for people with life limiting conditions Assess– clinical needs Do we know about people’s ‘personal preferences’ Lack of planning Lack of consistency Communication – GPs/DNs Lack of information re condition Are we supporting people at the end of life? Are we working together as a team? Assess – personal needs Plan 1 Care in the final days Plan 2 Cross Boundary Care How GSF addresses these challenges Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Context of end of life care and the role of the carer within the extended team Identify people nearing the end of life Assess – Clinical understanding of what to do • Session 4 • Session 5 • Session 6 Assess – Personal preferences Plan- care in the final days of life Plan – Cross Boundary Care Reactive patient journeyMR B in last months of life• GP and DN ad hoc arrangements-no PPOD discussed or anticipated/no anticipatory care • Problems with symptom control-high anxiety • Crisis call e.g. OOH-no plan or drugs available • Admitted to hospital (?Bed blocks?) • Dies in hospital -?over intervention/medicalised • Carer given minimal support in grief • No reflection/improvements by team/PCT • ? Inappropriate use of hospital bed? GSF Proactive pt journey- Mrs W in last mths of life • • • • • • • • • • On SC Register-discussed at PHCT meeting DS1500 and info given to pt +carer(home pack) Home care team involved in planning & delivery Regular support, visits phone calls-proactive Assessment of symptoms-?referral to SPC-customised care to pt and carer needs Carer assessed including psychosocial needs Preferred place of care noted and organised Handover form issued –drugs issued for home End of Life pathway/LCP/protocol used Pt dies in preferred place-bereavement support Staff reflect-SEA, audit gaps improve care, learn Better team-working and collaboration with GPs and others • Talking a common language (incl coding) • Earlier prediction of needs • Advance Care Planning helps focus on personal goals of care • Better agreed documentation eg DNAR • Preparation eg anticipatory prescribing, LCP • Better morale and mutual confidence Benefits to Patients of Cross Boundary GSF better access to GPs and nurses easier prescriptions prioritised support for patient and carers ACP & DNAR noted and recognised care homes staff speak to hospital staff daily updating always get a visit on request Primary Care coding collaboration flagged up as prioritised care proactive planning of respite advance care plan – preferred place of care documented Out of Hours GSF Patients Care Home passed on to doctor to phone back within 20 mins visit more likely if needed GSF patient flagged on system Hospital collaboration with GP and GSF register ? open visiting referral letter recommends discharge back home quickly car park free? noted on readmission to hospital and STOP THINK policy and ACP Reduce hospitalisation 1. Admissions avoidance policy 2. Reduced length of staycommunication with hospitals – discharge - better turnaround 3. Appropriate admissions criteria 4. Reflective practice as a team 5. Proactive care- coding, communication, ACP, drugs, team planning, training etc better rapid GSFDC Training Programme GSF for Domiciliary Care Teams Assessment After Assessment Before Session 1 Training Event 6 Learning Sessions Session 6 Training & Feedback Planning Its about living well until you die www.goldstandardsframework.org.uk info@gsfcentre.co.uk