Presentation - Six Kingdoms and Trophic Pyramids
advertisement

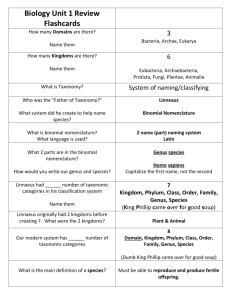
Description: Spark student interest using ‘gross’ pictures and a variety of life and different roles and characteristics of kingdoms of life. Goals: Describe the Concept of the Trophic Levels Objectives: Day 1 •List the 6 Kingdoms. •Describe each kingdom. •Explain what an Energy Pyramid represents. Warm-Up Q= 1. What are the different types of organisms in the world? (general not specific)? 2. Can microbes be both beneficial and dangerous? A= 1. Bacteria (Eu- & Archea-), Protist, Fungi, Plants, Animals 2. Yes… but the dangerous one get all the attention. Lets see why - Are you ready? Are you ready? Mucormycosis fungus in the eye This fungus lives in the soil and in rotting vegetation! Blastomycosis Fungal infection Eats away the tissue of the victim! Blastomycosis Caused by this Fungus (a type of yeast) Advanced Flesh Eating Bacteria Necrotizing fasciitis (aka flesh eating bacteria) 6 Kingdoms Eubacteria Archaebacteria Fungi Plants Animals Protists (“True-bacteria”) (“Ancient-bacteria”) Which of these kingdoms are microbes? Eubacteria Simple-single cell Organisms Help to maintain cycles of matter in the environment. Most bacteria are in this Kingdom In the soil, on plants and animals (inside and out), in the air, EVERYWHERE! Many are helpful to people: E. coli (live in our intestines) B. regularis (used in making yogurt) Some are Harmful to people: Streptococci (causes “strep throat”) Archaebacteria Live in extreme places Hot springs (boiling water!) Low / No oxygen areas High Acidity Simple Single celled organism Multicelled complex organism Examples: Fungi Mold Mildew Mushrooms Break down dead organisms Often look like plants Unlike plants they CANNOT make their own food (no photosynthesis) Obtain food from breaking down (decaying) Soil, plants, animals. (decomposer) Plants Multicelled organisms that produce their own food (producers) Over 250,00 thousand species ranging from: Flowering Plants Tiny Mosses Giant Trees Life could not exist without plants! Provide Oxygen Provide Food (transfers energy from sun to herbivores) Largest Kingdom Animals over 1 million known species! Multi-celled organisms found in very diverse (different) locations Keep populations in check and allow for complex organisms. Depend on plants and other animals for survival (can’t make their own food) Primary consumer (herbivores) Secondary & Top consumers (carnivores, omnivores) Scavengers “Odds and Ends” Kingdom Protists Organisms can be VERY different from each other. Single cell and multi-celled organism Protozoan (single celled) Algae (multi-celled and single-celled) Most are single celled organism Not in the bacteria kingdoms because they are complex cells! Basic Energy Pyramid Secondary Consumers Primary Consumers Primary Producers Carnivores Herbivores Autotrophs 6 Kingdoms of Living Organisms Complete the Six Kingdoms Chart. Objectives: Day 1 •List the 6 Kingdoms. •Describe each kingdom. •Explain what an Energy Pyramid represents. Photo credits http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Periorbital_fungal_infection_known _as_mucormycosis,_or_phycomycosis_PHIL_2831_lores.jpg http://www.mycology.adelaide.edu.au/gallery/dimorphic_fungi/ (co pyright information: http://www.adelaide.edu.au/legals/copyright.html) same as #2 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Necrotizing_fasciitis_left_leg.JPEG Wikipedia has a creative common license.