Domains
advertisement
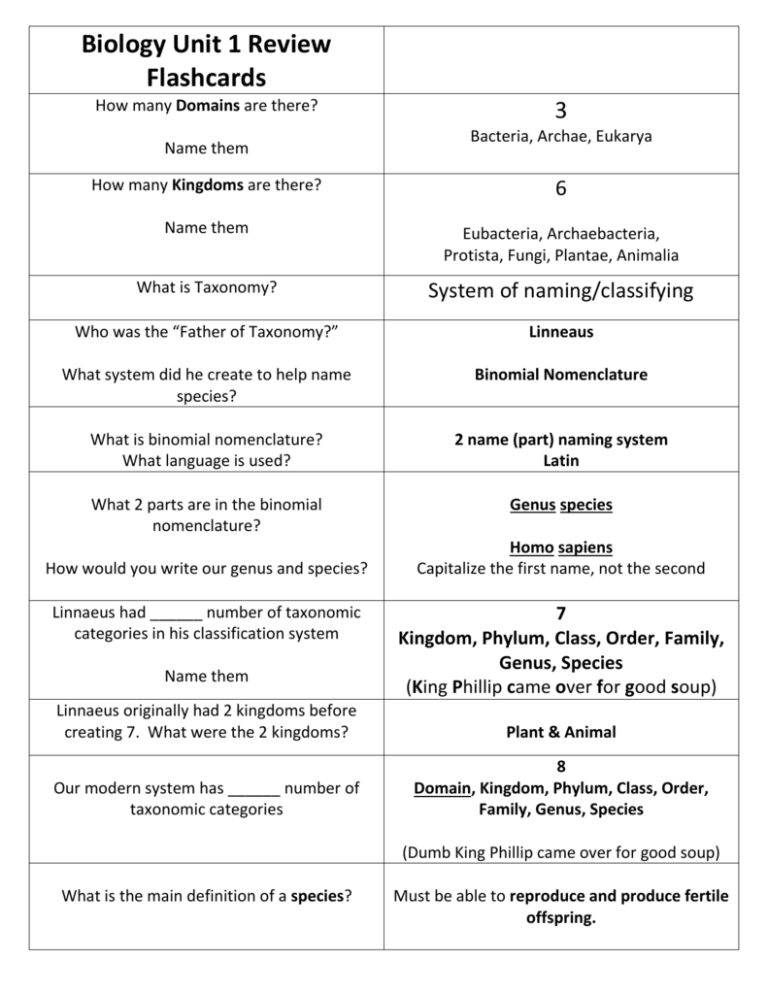
Biology Unit 1 Review Flashcards How many Domains are there? Name them 3 Bacteria, Archae, Eukarya How many Kingdoms are there? 6 Name them Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia What is Taxonomy? System of naming/classifying Who was the “Father of Taxonomy?” Linneaus What system did he create to help name species? Binomial Nomenclature What is binomial nomenclature? What language is used? 2 name (part) naming system Latin What 2 parts are in the binomial nomenclature? Genus species How would you write our genus and species? Linnaeus had ______ number of taxonomic categories in his classification system Name them Homo sapiens Capitalize the first name, not the second 7 Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species (King Phillip came over for good soup) Linnaeus originally had 2 kingdoms before creating 7. What were the 2 kingdoms? Plant & Animal Our modern system has ______ number of taxonomic categories 8 Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species (Dumb King Phillip came over for good soup) What is the main definition of a species? Must be able to reproduce and produce fertile offspring. Classes As you go down the taxonomy levels, you have more of classes in a phylum than kingdoms (Numbers are not exact; just examples) Does the category Phylum have more classes or kingdoms in it? Why do we classify organisms? Give 4 reasons What is a taxon? What do these organisms have in common? Canis Familiaris Canis latrans Canis lupus familiaris Traditional “Classic” classification is based on __________________ characteristics. 3 Domains 6 Kingdoms 36 Phylums 1000’s Classes 10,000’s Orders 100,000’s Families Millions of Genuses Billions of Species Universal Organization For studying Relationships A group at any level of a classification (taxonomy) system They are from the same Genus but different species. Physical Characteristics Early classification systems used this Evolutionary classification is based on __________________ characteristics. Evolutionary Characteristics (ancestors) Molecular classification (Clock) is based on __________________ characteristics. DNA What are prokaryotes? No Nucleus or membrane bound organelles inside them What are eukaryotes? Has Nucleus and membrane bound organelles What are autotrophs? Give example They can make their own food. Plants = Photosynthesis What are extremophiles? They cannot make their own food. Animals (Humans), Fungi (Mushrooms), some Protista (Paramecium) Organisms (bacteria) that can withstand extreme environmental conditions such as heat, cold, no oxygen. Original organisms on Earth (think Archae means “OLD”)) What Kingdom are they from? Archaebacteria What is a Dichotomous Key? What is a Cladogram? A two part system to identify an organism 1a/b; 2 a/b; 3 a/b etc. It uses derived characteristics to create a map to identify organisms ancestry Many species have different common names in different regions of the country or region. Give an example: Puma Mountain Lion Cougar What are heterotrophs? Give example Domains Archae and Bacteria have what similar features? Be familiar with the chart that has the characteristics of the Kingdoms and Domains handed out in class!!! Know the difference in old and new Cladograms like the ones in the book Ch18.1 Originally based on physical characteristics instead of evolutionary ancestral characteristics like more modern cladograms Unicellular Prokaryotes (no nucleus) Autotrophs and heterotrophs present Bacteria (Eubacteria & Archaebacteria) Eukarya Fungi are in what Domain? Describe fungi characteristics. What are the 8 Characteristics of Life? Think about what we as a human species need to survive and not become extinct. What is Biology? Not Plants Heterotrophs Mostly Multicellular Cell walls Mushrooms, yeasts Metabolize energy (Eat food) Made of cells (Our bodies are made of cells) Has DNA (Universal Genetic Code) React to environment (Put on coat when cold) Adapt to environment (Dark skin for hot areas) Evolve over time (Caveman to modern man) Grow and Develop (Baby to adult to old man) Reproduce (to keep our species alive) Study of Life (Living things) What is HOMEOSTASIS? Maintaining a stable internal environment (such as your body temperature) What is goal of science? To get answers to questions about our natural world. What is an observation? What you see happen in an experiment. Either qualitative or quantitative What is qualitative data? Observations (data) using your senses Feel, smell, hear, taste, see such as colors What is quantitative data? Numbers for data (length, volume, height, mass) What is the Scientific Method? What is an independent variable (IV)? What is the dependent variable (DV)? Problem or Question Hypothesis Experiment Data Analysis Conclusion Report your findings The thing that you change in the experiment (such as amount of light a plant gets) The data obtained from your experiment (such as the height the plant grew) What is a control? Used as a COMPARISON tool for your data. It does NOT get the IV. (such as the plant that gets normal amt of light) What are constants? The things that are given to the experimental group and control. (such as amount of water, type of soil, type of plant, size of container) What is a theory? A well tested hypothesis that is supported by repeated testing. Know the metric system and conversions. What phrase will help? Kilo Hecto Deka Base Unit - Meter, Liter, Gram Deci Centi Milli King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk Name the Levels of Biology from largest to smallest and define each Biosphere = All areas of earth with life Ecosystem = Living and non-living in an area Community = Diff species in an area Population = Same species (organisms) in an area Organism = Group of organ systems Organ system = Group of organs Organ = Group of tissues Tissue = Group of cells Cell= SMALLEST LIVING THING Molecule = Units that make up cells NOT LIVING Unit of measure in Metric System for Mass Length Volume Gram Meter Liter What is a Botonist? Studies plants What is a Zoologist? Studies animals Practice conversions using past worksheets!!











