The Reconstruction (1865-1876)
advertisement

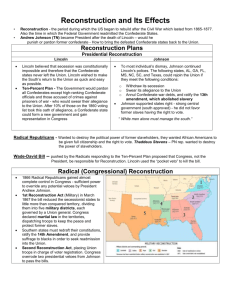
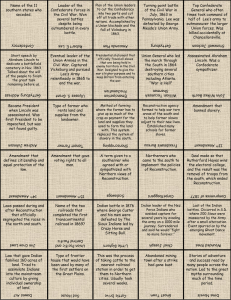
The Reconstruction (1865-1876) I am Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States. Welcome to a presentation about The Reconstruction. What was the Reconstruction? The Reconstruction was a plan that established rules and guidelines so former Confederate States could re-enter the Union. Since no state had ever seceded before, there was no precedent to guide leaders through the difficult issues the process needed to be addressed. What Were the Issues? There were four main issues that needed to be addressed. Remember these issues were complex because they involved finding solutions to many of the problems that had led to the Civil War. 1st. Issue of Reconstruction:Who was Responsible for the Confederate Rebellion and Should They be Punished. I felt we should bring back the rebels with “Malice toward none, with charity for all…” My plan did not seek to punish people and granted pardons and restored rights for many confederates. Only high ranking officers did not receive pardons. 2nd. Issue of Reconstruction. My “Ten Percent Plan” for readmission to the Union led to a debate about another issue of Reconstruction. The issue was: “What would the relationship be between the former Confederate states and the Federal Union? What should be demanded of those states before they were regarded as reconstructed? Congress did not agree with my plan and wanted tougher standards and penalties for readmission My plan called for ten % of the citizens of the former Confederate states, who were eligible to vote in 1860, to take an oath of loyalty. Their new state governments also had to agree to abolish slavery. Many Republicans disagreed with me and felt the south needed to be punished for seceding. Andrew Johnson’s Plan Following the assassination of President Lincoln, by John Wilkes Booth, I implemented my plan for reconstruction which was similar to Lincoln’s plan. I called for a quick restoration of the southern states to the Union & Amnesty for the southern rebels as long as they were not members of the elite, the confederate government, or former military officials. There Were Other Famous People with Different Plans. I am Frederick Douglas.Many abolitionists called for equal rights for all the former slaves. They felt these newly Freedmen also needed assistance from the government. They had no education, work, food, or lodging. The Freedman’s Bureau was a government agency set-up to help these people. The Radical Republicans I am Thaddeus Stevens. I am part of a group in Congress that was given the name “Radicals”. We believed the Freedmen should be granted free land and guaranteed citizenship. We wanted the south to abide by strict rules before being readmitted to the Union and we called for punishment for the leaders of the Confederacy The Radicals in Congress Feel New Laws Are Needed. 3rd. Issue of Reconstruction: What rights would the new Freedmen have? What would the government need to do to help them start new lives and take care of their new freedom? th 13 . Congress Passed the Amendment to Establish Rights for the Freedmen. In 1865 this amendment abolished slavery from the United States and its territories. Congress Expanded Rights for th the Freedmen by Passing the 14 . Amendment. Passed in 1868 this amendment gave citizenship to the former slaves and guaranteed no state could enforce a law that took away their rights as citizens. This reversed the Supreme Court’s Dred Scott decision The Last of the “Reconstruction Amendments” was the 15th Amendment. Passed in 1870 it gave the Freedmen the right to vote and Congress the ability to pass laws to ensure that they were not denied that right. The Union Sends the Military to Enforce Laws in the South. In 1867 we passed the Military Reconstruction Act. This law enabled the military to establish order, prevent violence, and begin political reform in the South. Southern farmers did not want to give up their way of life and fought against reforms. The th 4 . Issue of Reconstruction How should the Southern economy be converted from one based on slave labor to one based on free labor? Reading About Emancipations Effects of the Southern Way of Life. • Read the journal entries made by a southern slaveholder. • Answer the question at the bottom of your reading. • List three reasons to support your conclusion. The South Fights Back The KKK tried to maintain white dominance and preserve the pre-war way of life. Southern states passed laws called “black codes” that had the effect of making life in the south difficult for the Freedmen who, in many cases, were left to work for their former masters as sharecroppers. The End of Reconstruction. The Compromise of 1877 I’m Rutherford B. Hayes. The results to my Presidential election in 1877 were disputed and the legal winner was in doubt. In order for me, a Republican, to win, a compromise was reached with the Democrats. I agreed to remove the military from the south and end Reconstruction in exchange for being President. Without military protection former slaves were subject to discrimination, legal intimidation and lynching in the southern states.