Reconstruction and Its Effects
advertisement

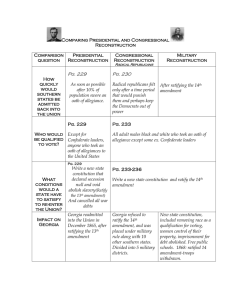
Reconstruction and Its Effects • Reconstruction - the period during which the US began to rebuild after the Civil War which lasted from 1865-1877. Also the time in which the Federal Government readmitted the Confederate States. Andrew Johnson (TN) became President after the death of Lincoln – would he punish or pardon former confederate - How to bring the defeated Confederate states back to the Union. • Reconstruction Plans Presidential Reconstruction Lincoln Lincoln believed that secession was constitutionally impossible and therefore that the Confederate states never left the Union. Lincoln wished to make the South’s return to the Union as quick and easy as possible. Ten-Percent Plan - The Government would pardon all Confederates-except high-ranking Confederate officials and those accused of crimes against prisoners of war - who would swear their allegiance to the Union. After 10% of those on the 1860 voting list took this oath of allegiance, a Confederate state could form a new government and gain representation in Congress Johnson To most individual’s dismay, Johnson continued Lincoln’s polices. The following states, AL, GA, FL, MS, NC, SC, and Texas, could rejoin the Union if they meet the following conditions: o o o Withdraw its secession Swear its allegiance to the Union Annul Confederate war debts, and ratify the 13th amendment, which abolished slavery Johnson supported states right - strong central government (south approved) - he did not favor former slaves having the right to vote. “ White men alone must manage the south.” Radical Republicans - Wanted to destroy the political power of former slaveholders, they wanted African Americans to be given full citizenship and the right to vote. Thaddeus Stevens – PN rep. wanted to destroy the power of slaveholders. Wade-David Bill – pushed by the Radicals responding to the Ten-Percent Plan proposed that Congress, not the President, be responsible for Reconstruction. Lincoln used the “pocket veto” to kill the bill. Radical (Congressional) Reconstruction 1866 Radical Republicans gained almost complete control in Congress - sufficient power to override any potential vetoes by President Andrew Johnson. 1st Reconstruction Act (Military) in March 1867 the bill reduced the secessionist states to little more than conquered territory, dividing them into five military districts, each governed by a Union general. Congress declared martial law in the territories, dispatching troops to keep the peace and protect former slaves. Southern states must redraft their constitutions, ratify the 14th Amendment, and provide suffrage to blacks in order to seek readmission into the Union. Second Reconstruction Act, placing Union troops in charge of voter registration. Congress overrode two presidential vetoes from Johnson to pass the bills. Major Reconstruction Legislation 1865-1870 Legislation Provision "Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States, or any place subject to their jurisdiction." This formally abolished and was passed by the Congress on January 31, 1865, and ratified by the states on December 6, 1865. In March 3, 1865, Congress created the Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands, commonly known as the Freedmen’s Bureau, the first federal agency dedicated to social welfare. The law granted relief to black and white persons displaced by the Civil War, but was aimed at assisting the freed slaves in their transition from enslavement to liberty. The freed slaves were provided basic shelter and medical care, assistance in labor-contract negotiation and the establishment of schools, and similar services. February 1866, Congress passed a second Freedmen’s Bureau Act, which extended the temporary agency’s life for two years and gave the United States Army the responsibility of protecting the civil rights of black Americans in the former Confederate states. Gave African Americans citizenship and forbade states from passing discriminatory laws, known as black codes, which severely restricted African American lives these Black Codes included - Prohibited carrying weapons, serving on juries, testifying against whites, marring whites. Ratified on July 9, 1868, and granted citizenship to “all persons born or naturalized in the United States,” which included former slaves recently freed. In addition, it forbids states from denying any person "life, liberty or property, without due process of law".” By directly mentioning the role of the states, the 14th Amendment greatly expanded the protection of civil rights to all Americans. The Reconstruction Acts of 1867-68 laid out the process for readmitting Southern states into the Union A key feature of the Acts included the creation of five military districts in the South, each commanded by a general, which would serve as the acting government for the region In addition, Congress required that each state draft a new state constitution, which would have to be approved by Congress. The states also were required to ratify the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution and grant voting rights to black men. In 1869 Congress passed the Fifteenth Amendment, granting all American males the right to vote. Congress also required secessionist states that had not yet reentered the Union to ratify the amendment in order to rejoin. By 1870, three-quarters of the Union had ratified the amendment, and it became law. The Enforcement Acts were passed by the United States Congress between 1870 and 1871. They were criminal codes which protected blacks’ right to vote, to hold office, to serve on juries, and receive equal protection of laws. The laws also said that if the states failed to act and enforce these laws, the federal government had the right to intervene. The Enforcement Acts did many things to help freedmen, the main purpose under this act was the prohibited use of violence or any form of intimidation to prevent the freedmen from voting and denying them this right 13th Amendment Freedman’s Bureau Acts Civil Rights Act of 1866 14th Amendment Reconstruction Act 1867-68 15th Amendment Enforcement Act The Ku Klux Klan The KKK was formed as a social group in Tennessee in 1866. The name probably came from the Greek word kuklos, meaning "circle." Klan was an alliterative version of "clan," thus Ku Klux Klan suggested a circle, or band, of brothers. With the passage of the Military Reconstruction Acts in March 1867, and the prospect of freedmen voting in the South, the Klan became a political organization. Former Confederate Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest served as the Grand Wizard The Klan's organized terrorism began most notably on March 31, 1868, when Republican organizer George Ashburn was murdered in Columbus, Georgia. Attacks on blacks became common during 1868. Freedmen's Bureau agents reported 336 cases of murder or assault with intent to kill on freedmen in Georgia alone from January 1 through November 15 of 1868.