Reconstruction - Teaching American History in South Carolina
advertisement
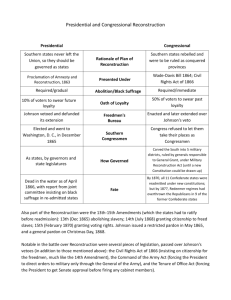
Reconstruction The Destruction of the War Presidential Reconstruction Abraham Lincoln Wartime acts Emancipation Proclamation* War still in doubt Fugitive slaves Slaves boost Confed. Cause Northern morale Public opinion France and Britain Morality Presidential Reconstruction Lincoln - 10% Plan* 10% loyalty oath Abolish slavery Northern opposition Wade-Davis Bill* 50% Ironclad oath 13th Amendment Presidential Reconstruction Andrew Johnson* General pardon Col. M.F. Pleasants* Voting = state issue Secession illegal Repudiate Confed. debt Abolish slavery Why? Black Codes* Control Disregard federal govt. Fear black retaliation Labor supply Racism Examples: Freedmen no testify vs. whites Vagrancy laws Taxes Whipped Blacks called “servant”, whites called “master” Johnson’s declining popularity Memphis riot* Disputes with Congress Freedmen’s Bureau Civil Rights bill 14th Amendment 1866 Civil Rights Act 1866 14th Amendment Citizenship for all persons - regardless of race - born or naturalized in US Forbade states from abridging privileges of citizens Guaranteed due process of the law Equal protection of the law “Swing Around the Circle”*, 1866 Congressional Reconstruction Radical Republicans Who were they? Thaddeus Stevens, PA Charles Sumner, MA What were their goals? Protection of freedmen and supporters Full citizenship of freedmen Win conservative support Some extreme views Strip Southerners of citizenship Confiscate land Congressional Reconstruction The Stevens Plan* Federal officials supervise elections Blacks vote Whites stripped of citizenship Congressional Reconstruction 1867 Congressional Reconstruction Act 5 military districts Military make arrests, trials Military directs constitutions Not extremely radical Johnson Impeachment Impeachment of Johnson Radical crusade Failure: Bring down presidential office Lack of clear crime Successor = Ben Wade Lawyers Johnson quiet Reconstruction Laws & Acts 1870 15th Amendment Forbade states to deny any citizen the right to vote on grounds of race, color, or previous condition of servitude Decline of the Radicals Small in number Johnson quiet Radicals divided Trouble staying in office Death U.S. Grant Scandals: political appointments, favors to businessmen and railroads New Leadership in the South Grant presidency Northern military Freedmen’s Bureau Carpetbaggers, scalawags, black politicians 1870, Union restored Black politicians 22 Congressmen Too few for great impact Republican Reconstruction Positive aspects: Public education Efficiency of government Public buildings, roads, manufacturing Social services (orphanages, hospitals, welfare) Capital/investment Political democracy Republican Reconstruction Decline 1870s Other concerns Corruption, depression Colfax Massacre U.S. v. Cruikshank “Compromise of 1877” Dem. – Samuel J. Tilden, NY Rep. – Rutherford B. Hayes, OH Hayes wins, 185-184 Republicans withdraw N support Legacy of Reconstruction “America’s unfinished revolution”