so here it is…Welcome to a Totalitarian state!!!
advertisement

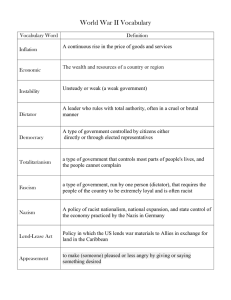
New Leaders and New Ideas in Europe during the 1930s AP World History Unit 5 Nazism Totalitarianism Communism Fascism These theories are completely different theories that are completed opposed to one another; however they demonstrate the same behavior. How did Totalitarianism come about? Step 1 – Treaty of Versailles. Step 2 – Stock Market Crash of 1929. Step 3 – Great Depression of the 1930s. Step 4 – Increased influence from new political parties that emphasized government control. Step 5 – Total control of the government by a dictator. You asked for it…so here it is…Welcome to a Totalitarian state!!! Characteristics of Totalitarianism Government establishes complete control of all aspects of the state. Highly nationalistic. Political, military, economy, social, and cultural. Flags, salutes, rallies, and uniforms. Strict controls and laws. Military state. Secret police, army, and navy. Characteristics of Totalitarianism Censorship. Opposing literature and ideas. Propaganda Media One leader Radio, newspapers, and posters. A charismatic dictator. Total conformity of people to ideas and the leader. Terror and Fear. Soviet Communism Also known as “Stalinism”. Stalin was the leader of the Soviet Union from 1922-1953. Combines elements of communism with a totalitarian and military state. Fascism Fascism’s name comes from the “fasces”. An ancient Roman symbol of authority. Intense nationalism and elitists mindset. Totalitarian control Interests of the state more important than individual rights. Maintains class system and private ownership. Most well known example is in Italy. Lead by Benito Mussolini from 1922-1943. Nazism Extreme form of Fascism, Nationalism, and Totalitarianism. Based on the beliefs of the National Socialist German Workers Party. Belief in a superior race. The Aryan or “master race”. Belief that all Germans should have a “living space” in Europe. Violent hatred of Jews. Belief that Jews were the cause of all of Germany’s problems. Led by Adolf Hitler from 1933-1945.