The Rise of Totalitarianism

The Rise of Totalitarianism
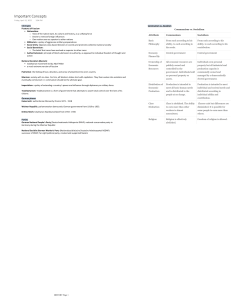
I. Totalitarianism
A.
B.
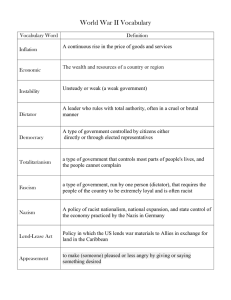
Definition: one-party dictatorship that regulates every aspect of citizens’ lives; everything is subordinated totally to the state vs. dictatorship, authoritarianism, autocracy, absolutism
I. Totalitarianism
C.
1.
Characteristics:
Forced to live by ruler’s beliefs
2.
3.
Demands total mass conformity
1 political party only
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Propaganda
Technology
Secret police / terror
Censorship
State-controlled economy
Strong military
Leader tries to convince people he is democratic or has democratic support
Youth, professional, cultural, sports groups
I. Totalitarianism
D.
A.
B.
“left” vs. “right”
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Left
Communism
Collective ownership of wealth
Arise in undeveloped countries
Working class support
Ex.: USSR under Stalin, China under Mao
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Right
Fascism & Nazism
Private ownership of wealth
Arise in developed countries
Middle class support
Ex.: Germany under Hitler, Italy under Mussolini
II. Fascism
A.
B.
C.
1.
2.
3.
Debate over definition
When it arose
1 or more?
Right or left? (1920 shift)
Political doctrine vs. action
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Definition (as best as it can be):
Anti- … socialist, communist, radical, democratic, republican, feminism, liberal, conservative
Pro- … new nationalist authoritarian state, volunteerism
Organization: mass party militia; use of violence
Youth movement
Technology
Not necessarily racist
III. Nazism
A.
B.
Germany / Hitler
Fascism + racism/anti-Semitism
IV. Communism
A.
B.
USSR / Stalin
Theory vs. practice