Totalitarianism, Fascism, and Communism
advertisement

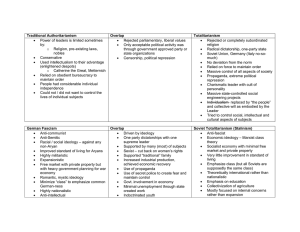
Totalitarianism, Fascism, and Communism Mark Manbeck Essential Question What are the major similarities and differences between Totalitarianism, Fascism, and Communism? Totalitarianism Totalitarianism—government that dominates every aspect of life A government of Total Control Totalitarian leader is often dynamic and persuasive Energetic, Cult active, forceful of Personality *Later Police State Government uses police to spy on and intimidate people Normally Police to protect citizens enforce the central government’s policies Education Slanted education Crucial to glorify leader and policies Propaganda Propaganda and Censorship Spread of Propaganda Government controls all mass media Crushes opposing views Scapegoats Usually, religious or ethnic minorities are “enemies of the state” Totalitarian Leaders in the 20th Century Adolf Hitler (Germany) 1933-1945 Benito Mussolini (Italy) 1925-1943 Joseph Stalin (Soviet Union) 1929-1953 Kim Il Sung (North Korea) 1948-1994 Saddam Hussein (Iraq) 1979-2003 Communism Russia Class Struggle Revolution is the only way All property is publicly owned NO Private Property Traditional Communism Refresher Karl Marx Bourgeoisie: New, Industrial Elite Proletariat: Workers Bourgeoisie had political and economic power Workers had the true power Stalin (More Next Time) Stalin aims to create Communist state in Russia. He began by destroying his enemies— real and imagined. Education Government controls all education, from early grades to college. Children learn the virtues of the Communist Party. Teachers and students who challenge the Party are punished. Religious Persecution Government attacks the Russian Orthodox Church. Magnificent churches and synagogues are destroyed. Religious leaders are killed. People lose all personal rights and freedoms. Totalitarianism vs Communism Totalitarianism Communism State is all-powerful Communist Party is all- State makes decisions powerful More Right Wing Communist Party makes decision State Ownership More Left Wing Common Ownership Fascism Started in Italy, transferred to Germany Fascism glorified action, violence, discipline, and blind loyalty to the state. Pursued territorial expansion through warfare. Distrusted reason and used emotion to their advantage. Nazism is a form of Fascism "Italy wants peace and quiet, work and calm. I will give these things with love if possible and with force if necessary." Benito Mussolini Police State Obsession with Security Fear is motivation of Government over population Military Supremacy Education Disdain for Intellectuals and Arts Boys taught to be soldiers Girls to be good mothers Propaganda and Censorship Powerful and Continuing Nationalism Censoring enemies Religion and Ethnicity Identification of Enemies/Scapegoats Unifies the people Religion and Government are Intertwined National Purity Racial Purity Fascism vs Totalitarianism Totalitarianism Individual Governs state State makes decisions Fascism State Governed by Single Political Party Communication controlled by state Type of Government Dictatorship • The two are not mutually exclusive • A fascist state is often ruled by a totalitarian leader • Totalitarian state does not necessarily have to be fascist