`New Course` under Kaiser Wilhelm II

HIST2086
Bismarck: The Iron Chancellor
Bismarck’s resignation and the ‘New Course’
(1890-1914)
Lecture 19
18 November 2010
Kaiser Wilhelm I and Bismarck,
1862-88
• Often stormy, emotional, noisy joint meetings
• Strong mutual comprehension of other
• Kaiser’s willingness to let Bismarck his own way
= Bismarck’s hold on power never in question
Kaiser Friedrich III and Bismarck, 1888
• Kaiser strongly influenced by his mother Augusta von Sachsen & his wife Viktoria with liberal ideas (≠ his father + Bismarck)
• Dismissal of Prussia’s conservative interior minister von Puttkamer + Bismarck’s position no longer secure
• Bismarck’s concerned about liberal and pro-British tendencies of imperial couple
= Kaiser’s rule too short (99 days) to help his liberal friends into long-lasting influential positions
Kaiser Wilhelm II
• Convinced German nationalist
• Committed to belief to rule by Divine Right
• Educated in Prussia’s military spirit
• Strongly interested in modern technologies & sciences
• Complex character + full of contradictions :
☺
Intelligent, talented, cultured, energetic
☻ Overbearing, arrogant, erratic
Kaiser Wilhelm II and Bismarck,
1888-90
• (+) Yearlong friendship between them
• (+) K.’s admiration for B. in public
• (-) Age difference: K. 29 y. ≠ B. 73 y.
• (-) B. underestimated K.’s determination to rule + to reign
• (-) K.’s wish to dispense with B. ASAP
= Continuing conflicts …
Conflicts
• Foreign policy: K.’s questioning Germany’s links with
Russia ≠ B.’s insistence on R.I.T. of 1887
• Social policy: K’s confidence of winning over working class by modest extension of welfare system (no child labour +
Sunday working)
≠ B.’s favour of further repression
→ B.’s attempt to make Anti-Socialist law permanent defeated in Reichstag (Jan 1890)
→ K.’s sole announcement of new social laws
= B.’s trapped between self-confident K. + hostile
Reichstag: His power crumbled
Bismarck’s resignation
• Quarrel about ministers’ right to advise monarch
(Mar 1890):
→ B.’s i nsistence of order of 1852: ‘Minister-
President as channel’
→ K.’s order to withdraw order
→ Stormy meeting + K.’s ultimatum to B. to resign
= B.’s resignation for ‘health reasons’
= Long-term estrangement between them
Imperial Chancellors, 1871-1918
• Fürst Otto von Bismarck , 1871-90
• Leo von Caprivi , 1890-94
• Fürst Chlodwig zu Hohenlohe -
Schillingsfürst, 1894-1900
• Bernhard von Bülow , 1900-09
• Theodor von Bethmann Hollweg , 1909-17
• Georg Michaelis , 1917
• Georg Graf von Hertling , 1917-18
• Prince Max von Baden , 1918
Germany’s Economy, 1815-1914
• Backward until 1830 but rapidly transformed by P
+ Customs Union (1834)
• Upsurge in agricultural production due to Ginvented chemistry (fertilizers)
• Strong growth of heavy industry + high technology:
Industrial Revolution starts ca. 1840s
• Surpassed GB ca. 1900-10 in production of iron, steel, electrics, chemicals
= Rise to top-economic power in EU
Rise of Rightist Movements
Agrarian League (Bund Deutscher Landwirte)
→ A manipulative strategy from Junkers AND reflection of growing concerns of rural population
Pan-German League (Alldeutscher Verband)
→ Nationalism: ‘membra disiecta’ + Germans abroad
+ colonies
= Mass agitation with strong influence on society
= Conflict + cooperation with government
Domestic Politics, 1890-1914
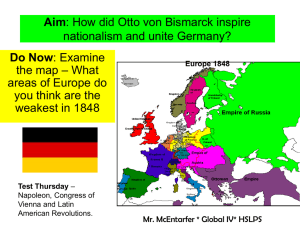
‘New Course’ under Kaiser Wilhelm II
• Personal semi-authoritarian regime of Emperor (Kaiser)
• Lack of parliamentary-constitutional reforms
• Prevention of democratisation
• Permanent struggles between government and political parties in parliament ( Reichstag )
• Rise of SPD and Left Liberals : Major victory in 1912
= Feeling of siege” in government + growing perception of being encircled by enemies from in- & outside G.
Foreign Politics, 1890-1900s
‘New Course’ under Kaiser Wilhelm II
• Imperialist power politics + colonialism in Africa &
Asia-Pacific
• Impulsive diplomatic actions of Wilhelm II
• General overestimation of G’s power position
= Non-renewal of alliance with R
→ Dual Alliance F + R: ‘ Encirclement of G ’ with only A + OE as major allies
= Rising tensions with GB due to Tirpitz’ naval race
Foreign Politics, 1900s-1914
• Weltpolitik
(world policy)
:
To secure new colonial territories + spheres of influence worldwide → Attempt to create formal & informal empires
• Flottenpolitik
(naval policy)
:
To extensively enlarge German navy →
Attempt to create 2nd largest battle fleet to rival GB
The German Colonies, 1913-14
Area in 1,000 square kilometres
88
Population in 1,000:
Natives
1,031 In Africa :
Togo
Cameroon
German South-West
Africa
German East Africa
In Asia and Pacific:
Palau, Caroline /
Marianne / Marshall
Islands, Samoa
504
830
1,020
13,2
3,326
80
7,645
15
Population in 1,000:
Whites
0,4
1,8
15
5
0,5
German New Guinea and Bismarck
Archipelago
230
Kiautschow
(Qingdao)
0,56
719
192
0,9
4,4
Collapse of Bismarck’s alliance system
• Franco-Russian Dual Alliance, 1894
• Germany’s naval construction program, 1898
• Britain abandons ‘splendid isolation’, 1898
→ British-Japanese Alliance, 1902
→‘ Entente Cordiale’ France-Britain , 1904
= Germany ‘encircled by enemies’: Two-Front-War danger extremely high
Results
• Weltpolitik :
A failure → political drawbacks and diplomatic isolation
• Flottenpolitik :
A failure → permanent estrangement with Britain
+ domestic stalemate after Reichstag elections of 1912
= Strong feeling of overall stalemate in G’s foreign AND domestic policies inside
German civilian + military leadership
Conclusion
• Long path to unified G. nation state made possible only by 3 wars vs. neighbours
• Liberalism weak due to strong position of conservatism & militarism: Split into National (Right) + Left Liberals
• Struggle of authoritarian monarchy , with democratic elements, vs. SPD & Left Liberals
• Overestimation of G’s power after Bismarck’s dismissal →
Isolation + tensions in EU
• Outdated political system ≠ economically & scientifically most-advanced and modern state in world