Nationalism
advertisement

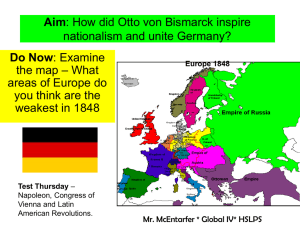
Rise of the Nation State SSWH15 The student will be able to describe the impact of industrialization, the rise of nationalism, and the major characteristics of worldwide imperialism. b. Compare and contrast the rise of the nation state in Germany under Otto von Bismarck and Japan under Emperor Meiji. Nationalism • Radical idea in the years after 1815 • Belief that each people had its own genius and own cultural unity based on a common language, history, and territory • Sought to turn this cultural unity into a political reality so that each people lived in an independent nation state • As a result, countries like Germany who were divided into many principalities wanted national unity and one form of government Impact of Nationalism • Triumphed in the long run because the development of complex industrial and urban societies required much better communication • Nations developed a strong sense of “we” and “they” • Lurking below the surface was ideas of national superiority and a national mission that could lead to conflict Information on the Rise of the Nation State • Chapter 19 Sections 2 and 3 • Chapter 20 Section 3 • Chapter 22 Section 3 Group Activity Complete the chart comparing and contrasting the rise of the nation state in Germany and Japan. Germany under Otto von Bismarck Industrialization Consolidation of Power Foreign Interactions Creating a Modern State Role of Leaders Japan under Meiji