Document
advertisement

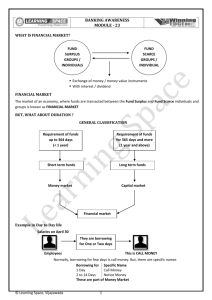
Money Market and Government Securities Market • Money market is the market for dealing in monitory assets of short term maturity. • Short term funds up to one year and financial assets that are close substitutes for money are dealt in the money market. • Instruments in the money market are liquid, with less transaction cost and no loss in value. • It provides the crucial function of providing a equilibrium in the short term liquidity of the market. Features: 1. Wholesale market with large volume 2. Daily settlement 3. Telephonic deal confirmed by written contracts by borrowers and lenders 4. Large number of participants including banks and mutual funds. 5. RBI is at the centre of all the activity which borrow or sale money and securities in the market Instruments: The money market instruments comprise of : 1. Call money (over night borrowing upto 14 days) 2. Certificate of Deposit (CD) 3. Commercial Paper (CP) 4. Money market mutual funds and 5. Commercial bills 6. Treasury bills and 7. Inter corporate lending Call/Notice money market: 1. Used to be predominantly inter-bank market till 1987. 2. DFHI was set up in 1988 and STCI was set up in 1994 to provide easy access to money market instruments 3. 11 MF approved by SEBI along with GIC, IDBI, NABARD, DFHI and STCI and al the banks are allowed to participate in the market. 4. Minimum size is Rs.3 crore per deal. 6. All lending to be routed trough DFHI as call deposit receipt 8. Transaction are reversed the next day 9. In case of requirement of fund DFHI can use Deposit receipts 10. In 1999 non banks were allowed in limited way to participate Term Money Market: 1. Dominate the market 2. RBI has actively looked into facilitating the market Treasury Bill: 1. They can range from 14 days, 91 days 182 days and 364 days treasury bill not issued as scripts. 2. Effected trough the Securities General Ledger (SLG) 3. Government can suspend the any treasury bill from operating at any point of time Certificate of Deposit: 1. They are like term deposit 2. Bulk is of 1, 3 and 6 months. However they vary from 2 weeks to 5 years in term. 3. They are bearer short term negotiable instrument mostly issued by banks 4. CD are issued at face value 5. They can be tailor made Commercial Paper: 1. Can be issued by companies with tangible net worth not less than Rs. 5 cr. And has fund based working capital not less than Rs.4 cr. Should have a current ratio of 1.33:1 2. Minimum issuance period 30 days with no grace period and maximum of 1 year. 3. Denomination of Rs. 5 lakhs and minimum lot of 5. 4. Mode: unsance promissory note 5. Can be issued to any person or institute 6. Issued through banks who have sanctioned working capital limits of the company. Commercial Bill Market: 1. Are bills drawn as a part of commercial activity 2. Banks give discounting facility for such bills which acts as cash buffer. 3. Financial institutions participate in the process of the bill discounting Money Market Mutual Funds: 1. Enable the small investors to participate in the money market 2. They are mostly set up by scheduled commercial bank Secondary market for Money market instruments: Both DFHI and STCI actively help in rediscounting and purchasing and selling of money market instruments and therefore help in creating a secondary market.