CHAPTER 4 The Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions, and
advertisement

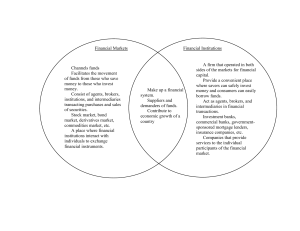
CHAPTER 2 The Financial Environment: Outlines Financial Markets Financial Institutions 4-1 The Capital Flow Process In a well-functioning economy, capital flows efficiently from those who supply capital to those who demand it. Suppliers of capital – individuals and institutions with “excess funds.” These groups are saving money and looking for a rate of return on their investment. Demanders or users of capital – individuals and institutions who need to raise funds to finance their investment opportunities. These groups are willing to pay a rate of return(interest) on the capital they borrow. 4-2 2-2 Three ways capital flow from savers to borrowers? Direct transfer Investment Bank Securities pass through the investment bank Financial intermediary Intermediary create new securities for savers. 4-3 What is a market Market: A place/venue where goods and services are exchanged FM: A place where funds/financial assets are traded. lender: those with surplus of funds (individual, firms, Gov.) borrower: those need funds ( individual, households, firms) Who are lender/borrower: stock M, bond4-4M Types of financial markets Money vs. Capital Primary vs. Secondary Spot vs. Futures Public vs. Private 4-5 FM F Asset /F instruments: contracts specifying borrowing/lending terms, claims on real assets i. Money M (borrowed for less than 1 Y) and Capital M (1 Y or longer) ii. Primary M and secondary M 1. PM: New issues are sold to the public 2. SM: outstanding issues traded among investors iii. Private M vs. Public 1. Private: transactions between two parties 2. Public: standardized contracts traded on exchanges. iv. Spot M vs. Future M 1. SM: transaction “on-the-spot” 2. FM: Contract specifying terms of future trading 4-6 Types of Financial Institutions Banks Commercial banks Investment banks Middleman between savers and borrowers An organization that helps to sell new investment securities (bonds, stocks). Financial services corporations A firm that offers a wide range of financial services, including investment banking, commercial banking, brokerage and insurances. Citi, B of A, JPM 4-7 2-7 Types of Financial Institutions Funds-pool money to invest Mutual funds Pension funds-retirement plans Hedge funds Exchange traded funds-ETF Other financial institutions Life Insurance companies: Collect premiums and invest Private equity: company borrows money to invest/mange the whole 4-8 2-8 The stock market Types of stock market transactions The secondary market The primary market: IPO market: Initial Public Offering additional new shares Basics of stock market and stock investing 4-9