Diffusion & Osmosis: Cell Membrane Transport Explained
advertisement

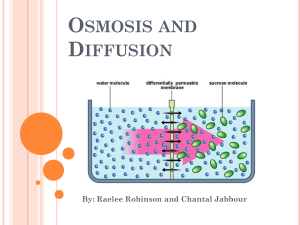
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS 3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis KEY CONCEPT Materials move across membranes because of concentration differences. Diffusion and Osmosis Concentration Gradient: the gradual difference in the concentration of solutes in a solutes in a solution between two regions. 3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis Passive transport does not require energy input from a cell. • Molecules can move across the cell membrane through passive transport. • There are two types of passive transport. • diffusion • osmosis 3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis Diffusion and osmosis are types of passive transport. • Molecules diffuse down a concentration gradient. 3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis Diffusion and osmosis are types of passive transport. • Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. 3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis Diffusion and osmosis are types of passive transport. • There are three types of solutions. • isotonic • hypertonic • hypotonic Diffusion and Osmosis In terms of the solution: Hypertonic: When the solution is more concentrated than what’s inside the cell. This means water moves out to try and even out the concentration gradient. (The cell shrinks..i.e your fingers in the bathtub) Hypotonic: When the concentration is less concentrated than what’s inside the cell the water moves in to try and even out the concentration gradient. (The cell bursts or “lyses”.) Isotonic: When the concentration inside the cell is equal to that outside. No net change in water. Gizmo 3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis Some molecules can only diffuse through transport proteins. • Some molecules cannot easily diffuse across the cell membrane. • Facilitated diffusion is diffusion through transport proteins. Review Plants Cells vs Animal Cells Two organelles that are in plants that are not in animals: Chloroplasts- which is where photosynthesis occurs Cell Wall-Which helps make the plant rigid and support the change in water pressure. You will not see these in animal cells. Lab Report 6 Pieces of Information: Purpose- raises the question that you sought to investigate with the experiment Hypothesis- is a tentative explanation for an observation. Often written in an “if/then” format. Lab Report Materials-List of things needed and used (Needs to be as precise as possible include dependent and independent variable, make sure you know or indicate your control group) Procedure- Exactly what you did to test your hypothesis. Use action verbs , perhaps number the steps Lab Report Observations and Data- Anything you measured during the experiment. (also anything you saw, touched, felt, smelled or heard) Data Analysis/Results- Did your test support you hypothesis. What conclusions can you draw by looking at the data.