Diffusion & Osmosis
advertisement

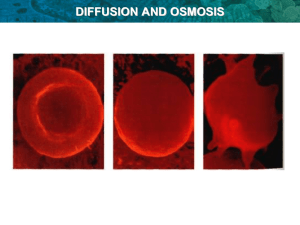
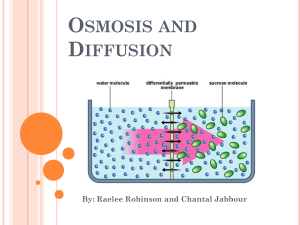
Patterns in Nature Compare the processes of diffusion and osmosis perform a first-hand investigation to demonstrate the difference between osmosis and diffusion perform a first-hand investigation to model the selectively permeable nature of a cell membrane Diffusion and Osmosis The processes of diffusion and osmosis account for much of the passive movement of molecules at the cellular level. DIFFUSION Molecules are in constant motion Movement tends to be from high concentration to areas of low concentration. Diffusion is the net movement of molecules down their concentration gradient. Diffusion can occur in gases and in liquids. OSMOSIS Osmosis is a specialized case of diffusion that involves the passive transport of water. In osmosis water moves through a selectively permeable membrane from a region of its higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration. LETS TAKE A CLOSER LOOK MOVEMENT OF MOLECULES IN SOLUTION There are several different types of molecules in a solution Movement of each molecule is random and independent of other molecules in a solution Each molecule moves down its own concentration gradient from a region of its HIGH concentration to a region of its LOW concentration. Common misconception is that this is the only way for molecules to move. Although the net movement of molecules is down their concentration gradient, at any time molecules can move in both directions as long as the membrane is permeable to the molecule. Concentration gradient Perform a first hand investigation to demonstrate the difference between osmosis and diffusion. Aim: Experiment A: To observe the process of osmosis using a unboiled potato and a boiled potato. Experiment B: To observe the process of diffusion using coloured dye. Materials: Experiment A: Unboiled potato Boiled potato Spatula Table salt Water 2 Petri dishes Experiment B: Beaker Water Coloured dye Perform a first hand investigation to demonstrate the difference between osmosis and diffusion. Method: Experiment A: 1. Using a spatula make a hole in the middle of the unboiled and boiled potato. Make sure not to reach the base of potato, however still deep. Put aside. 2. Fill the two petri dishes with ¾ of water. 3. Place the unboiled potato and boiled potato in the middle of each petri dish. 4. Add half a teaspoon of salt into each hole of the unboiled and boiled potato. 5. Leave aside for 10 minutes. Start experiment B. Perform a first hand investigation to demonstrate the difference between osmosis and diffusion. Method: Experiment B: 6. Collect a beaker, fill it with water. Do not overflow. 7. Add a few drops of dye into the beaker. 8. Observe the beaker for about 3 minutes, note what is happening. 9. Once finished with the beaker, observe the rested potato, note any changes. Let’s blog it out http://osmosisdiffusion.wordpress.com Types of solutions based on solute concentration In the illustration, the solution in the bag contains less solute than the solution in the beaker. The solution in the bag is hypotonic (lower solute concentration) to the solution in the beaker. The solution in the beaker is hypertonic (higher solute concentration) to the one in the bag. Water will move from the hypotonic solution into the hypertonic solution. In this illustration the two solutions are equal in their solute concentrations. We say that they are isotonic to each other. Water potential Because you will be working with potato cells in the laboratory, you need to understand the concept of water potential. Biologists use this term to describe the tendency of water to leave one place in favour of another. Water always moves from an area of higher water potential to an area of lower water potential. Water potential is affected by two factors: pressure and the amount of solute. For example, imagine a red blood cell dropped into distilled water. Water will move into the red blood cell and cause the cell to expand, stretching the flexible membrane. At some point, the pressure of the incoming water will cause the cell to pop, just like an over-filled balloon.