Charlemagne Unites Germanic Kingdoms
advertisement
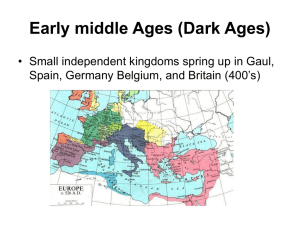
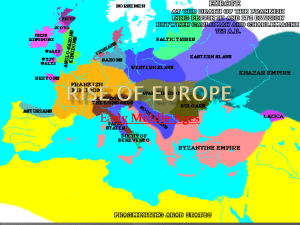
CHARLEMAGNE UNITES GERMANIC KINGDOMS Chapter 13 Section 1 VOCAB Middle Ages Franks Monastery Secular Carolingian Dynasty Charlemagne INVASIONS OF WESTERN EUROPE Disruption of trade: Constant invasion collapsed merchant businesses; destroyed Europe’s cities as economic centers; money was scarce Downfall of Cities: Fall of the Roman Empire cities were abandoned as places of administration Population Shifts: As cities were in decline people moved to the country to grow their own food. Europe’s population became mostly rural INVASIONS OF WESTERN EUROPE Decline of Learning Loss of Common Lang. German invaders were illiterate Only priest and church officials could read and write Knowledge of Greek and Roman literature, science, and philosophy almost lost completely German speaking people mixed with the Romans Latin changed 800’s French and Spanish had emerged Continued the break-up of a once unified empire GERMANIC KINGDOMS EMERGE The concept of Government Changes: Germanic society held together by family ties and loyalty; not written law or public government German citizens would fight along their kings Seen as a disgrace to outlive their king \ Felt no obligation to a king or emperor they have never met Impossible to govern large areas of land GERMANIC KINGDOMS EMERGE Clovis Rules the Franks: A people called the Franks were in control of the land of Gaul (France) Clovis was their leader In 496 out of fear of defeat Clovis prayed to the Christian God for aid. He won the battle and he and his 3,000 men were baptized (converted to Christianity) 511 Clovis united all the Franks The church in Rome supported Clovis and his military campaign GERMANS ADOPT CHRISTIANIT Y Politics play a large role in the spread of Christianity 600 the church with help of the Frankish rulers converted many Germanic people to Christianity Missionaries (religious travelers) help to spread as well Constant fear of Muslim attacks in Southern Europe also spur many converts GERMANS ADOPT CHRISTIANIT Y Monasteries, Convents, Manuscripts: Monastery: religious community where monks gave up private possessions and devoted life to serving God Convent: Monastery for women called nuns Monasteries become best educated communities in Europe; responsible for preserving Rome’s intellectual heritage GERMANS ADOPT CHRISTIANIT Y Papal Power Extends Under Gregory I: 590 C.E. Greg becomes Pope and turns the papacy into a secular power (worldly power involved in politics) Greg will use the church revenues to raise armies, fix roads, and help the poor, and negotiate treaties Considered Italy-England; and Spain to Germany his responsibility Creating a kingdom of the church ruled by the pope. AN EMPIRE EVOLVES Charles Martel and Pepin the Short 719 Frankish Kingdom falls into the hands of Charles Martel (Charles the Hammer) Expands Frankish Kingdom Defeats Muslims from Spain at Battle of Tours; preserve Christianity in Western Europe Martel dies power goes to his son Pepin the Short Pepin negotiates with the pope; he will fight the Lombards if the pope will grace him “king by the grace of God” Pope agrees and the Carolingian Dynasty is born CHARLEMAGNE BECOMES EMPEROR When Pepin died in 768 he left the kingdom to his two sons Carloman and Charles Carloman dies in 771 leaving Charles in charge of the entire kingdom Charles becomes known as Charlemagne; Charles the Great. CHARLEMAGNE BECOMES EMPEROR Charlemagne Extends Frankish Rule: Builds empire greater than any other since ancient Rome Through conquests he extends Christianity and reunites Western Europe for the first time since the Roman Empire 800 Charlemagne goes to defend the pope from an angry mob; in return Pope Leo III gives him the title “Roman Emperor” Symbolizing the joining of Germanic, Church, and Roman heritage CHARLEMAGNE BECOMES EMPEROR Charlemagne’s Heirs: 814 Charlemagne makes his son Louis the Pious Emperor; he is ineffective ruler Louis leaves the empire to his 3 sons, Lothair, Charles the Bald, Louis the German They fight over control and sign the Treaty of Verdun Divides the empire into 3 kingdoms Carolingian kings lose power and central authority over Western Europe Loss of strong leadership will lead to new kind of governing and landholding------feudalism POP QUIZ What were Pepin the Short’s two sons names? How many kingdoms did the Treaty of Verdun create? Who was the first Christian King of the Franks? Who extend the authority of the papacy? What important battle did Charles Martel win against the Muslims?