hypertonic solution

Using the Scientific Method.
Investigating Osmosis in Potato
Cells.
AIM: to find out what happens to samples of potato when they are placed in a hypertonic solution.
Osmosis…what does it mean again?
Osmosis is the special diffusion of water from high water concentration to low water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
Plant Cells and Osmosis
Hypotonic solution : more water outside of the cell than inside, therefore water will move into the cell by osmosis. This causes the cell to swell and become turgid
Hypertonic solution: more water inside the cell than outside, therefore water will move out of the cell by osmosis.
This causes the cell to become softer or flaccid
Hypothesis
Since water moves from a HWC to a LWC, water will move out of the potato cells by osmosis in a hypertonic solution.
Apparatus Required
1. Safety goggles
2. Two beakers
3. Potato samples
4. Cork borer
5. Hypertonic solution
6. Stop clock
7. Measuring scales
8. Paper towel
9. Labels
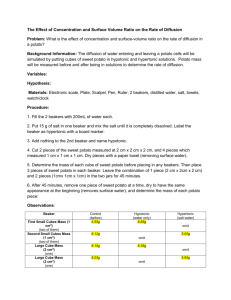
Method (Experimental procedure)
Beaker A containing
50ml of water
Beaker B containing
50ml of hypertonic solution
Potato cell samples
Results table
• Copy and complete:
Mass at 0 minutes (g) Mass at 30 minutes (g) Difference (+/-)
Beaker A
(water)
Beaker B
(hypertonic solution)
Your teacher may ask you to enter your results into a table, recording everyone's results in order to gain an average set of results.
Method (Experimental procedure)
1.
Collect a cork borer and cut out two samples of potato.
2.
Roll the potato samples in paper towel to dry off any excess water and measure mass separately.
3.
Record your initial results in your results table.
4.
Place each sample in a different beaker marked A or B.
5.
Cover the potato samples in beaker A with 50ml of water and potato sample in beaker B with 50ml of hypertonic solution.
6.
After 30 minutes, remove samples from beakers, dry off with fresh paper towel and re-measure mass of each piece of potato.
7.
Record final results in your table.
Variables
• In all scientific investigations, there are a number of variables.
• The independent variable
– What factors you will manipulate to test your hypothesis.
• The dependent variable
– What is changed / measured in the experiment.
• The control
– What you will keep the same in both experiments for a fair comparison.
What are the independent, dependent and controlled in this experiment?
Analysis of results
• Using the data from your completed results table, draw a bar graph to show the mass of the potato cylinders in both solutions at 0 minutes and 30 minutes.
• Repeat this process for the class average data for both solutions at 0 minutes and 30 minutes.
• Use a pencil and ruler to draw your graph!
Reliability
• All experiments are repeated several times and an average calculated.
• This is very important in science so that a
reliable set of results are obtained.
• Why do you think repeating and averaging
increases reliability of results?
Conclusion
• The aim of this scientific investigation was to find out what happens to samples of potato when they are placed in a hypertonic solution.
• Did your hypothesis match what you found out? If not, why not?