Cell Transport
advertisement

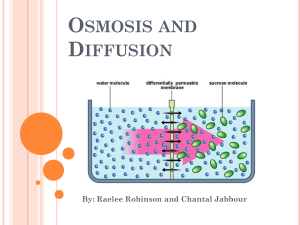
Cell Transport How do materials move into and out of the cell? Cell Membrane • The cell membrane is like a security door controlling what materials can enter and exit the cell. • We describe this cell part as: “selectively permeable.” • THINK! - What does selective mean? • Very Choosy • THINK! - What does permeable mean? • To pass through Cells Move Materials Using… NO ENERGY! Passive Transport Diffusion OR ENERGY! Active Transport Osmosis Today’s Question: What is diffusion? What is Diffusion? • You can figure it out by observing 3 examples. • Example #1: Perfume Demo • Example #2: Sugar in Water • Example #3: Food Coloring in Water Example #1: Perfume Demo Directions: 1. Your teacher will spray perfume. 2. Raise your hand when you can smell it. What molecules moved? Perfume molecules Did we use energy? Yes or No In what direction did the molecules move? More crowded to less crowded Less crowded to more crowded Example #2: Food Coloring Directions: 1. 2. 3. Put 1 drop of food coloring in your beaker of water. Watch how the molecules move for 5 minutes. Sketch your beaker at start and end. START END. What molecules moved? Food Dye molecules Did you use energy? Yes or No In what direction did the molecules move? More crowded to less crowded Less crowded to more crowded Example #3: Sugar Cubes Directions: 1. 2. 3. 4. Fill your beaker ¼ of the way up with warm water. Drop in a sugar cube. Watch how the molecules move for 5 minutes. Sketch your beaker at start and end. START END What molecules moved? Sugar molecules Did you use energy? Yes or No In what direction did the molecules move? More crowded to less crowded Less crowded to more crowded What is Diffusion? Fill in the definition using what you learned. MOLECULES from The Movement of ______________ HIGH concentration (more crowded) to _______ LOW concentration (less crowded) using _______ ______________. NO ENERGY EVENLY The molecules move until they spread out _________. This is called equilibrium. WORD BANK Molecules No Energy High Evenly Low Diffusion Animations • Check out these 2 animations!! • Perfume Example http://www.biosci.ohiou.edu/introbioslab/Bios1 70/diffusion/Diffusion.html • Sugar Cube Example -How Diffusion Works http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chap ter2/animation__how_diffusion_works.html • Food Dye Example -Go Animate (Diffusion runs from start until 2:40) • http://goanimate4schools.com/public_movie/0Z Vm9NFo0EC8 C.e.l.l. Solutions ™ Creating Excellent Living Links for the future Phase 1 –Drug Creation The Innovation Center is creating a new chemical that will enter cancer cells. This chemical will kill the cell as it passes through the cell membrane. The Center is very close to finishing their drug. However, we need to add one more molecule to make the drug complete. Which molecule(s) will be small enough to pass through the cell membrane: Iodine or Starch? Use the principle of diffusion to figure out the answer. 1. 2. 3. 4. Build a cell model for diffusion to work. Fill out the data table. Analyze data & tell Center which molecule(s) to use. Call your supervisor over for clearance to clean up. C.e.l.l. Solutions ™ Creating Excellent Living Links for the future • Which molecule should the Center use? Why? The Center should use IODINE because it is small enough to pass through the membrane. Starch is TOO big and stayed inside the cell. Cells Move Materials Using… NO ENERGY! Passive Transport OR NO ENERGY! Active Transport Diffusion Osmosis Today’s Question: What is osmosis? C.e.l.l. Solutions ™ Creating Excellent Living Links for the future Phase 2: Drug Testing on Cell Models Now that we’ve made our cancer drug we are ready to test it on animal cells. However, in order for the drug to pass through the membrane we need cells that are BIG! Which solution will help our cells grow larger: Freshwater or Saltwater? Please use the principle of osmosis and soak your gummi cells overnight to figure out the answer. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Complete Day 1: Set up bears & take measurements Leave overnight for osmosis to happen. Complete Day 2: Check bears & take measurements Analyze data and make a recommendation Call your supervisor over for clearance to clean up. C.e.l.l. Solutions ™ Creating Excellent Living Links for the future • Which solution should the Innovation Center use: Freshwater or Saltwater? Why? The Center should use FRESHWATER because the gummi bear grew larger. Osmosis caused the water to move from HIGH concentration in the cup to low concentration inside the gummi bear. What is Osmosis? Fill in the definition using what you learned. WATER The Movement of ______________ from HIGH concentration (more crowded) to _______ LOW concentration (less crowded) using _______ ______________. NO ENERGY EVENLY The molecules move until they spread out _________. This is called equilibrium. WORD BANK Water No Energy High Evenly Low Osmosis Problems • Problem #1 – A cell is placed in pure Freshwater. Which way will the water flow? CELL SWELLS Osmosis Problems • Problem #2 – A cell is placed in saltwater. Which way will the water flow? Salt molecule CELL SHRINKS Osmosis Problems • Problem #3 – A cell is already at equilibrium. Which way will water flow? SAME SHAPE Osmosis Animations • Animation #1 http://www.stephsnature.com/lifescience/osmosisanimations. htm • Animation #2http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/transport/os mosis.swf • Animation #3-Go Animate (Osmosis runs from 2:40 until end) http://goanimate4schools.com/public_movie/0ZVm9NFo0EC8 Activity: Osmosis in Animal Cells How would you explain this cartoon using your knowledge of osmosis? My Answer: Slugs are afraid because salt will make their cells shrink. Low High The water will move from HIGH conc. (inside cell) to LOW conc. (outside cell). Activity: Osmosis in Plant Cells • What happens when plant cells are in freshwater? Water moves into cell • What happens when plant cells are in saltwater? Water Leaves the cell C.e.l.l. Solutions ™ Creating Excellent Living Links for the future Phase 3: Drug Delivery You have already completed two phases of this project. In this last phase we must deliver the drug inside the cell. Unfortunately, with all the extra modifications that we did, the drug turned out to be TOO BIG to pas through the membrane. How can we get LARGE molecules to enter the cell? Please use the idea of active transport to model a way that the cell can do this using materials provided. 1. 2. 3. 4. Read instructions Use materials and model a method Share your solution Call your supervisor over for clearance to clean up. C.e.l.l. Solutions ™ Creating Excellent Living Links for the future • The Question: • • The Task: • • How can we get LARGE molecules to enter the cell? For this task gather the following materials to work with. • 1 plastic shopping bag • 1 pair of scissors • ~ 15 cm of string • 1 small wrapped candy Rules: • • • • 1. The candy must enter through the solid part of the bag. 2. The inside of the bag can NOT be open to the outside. 3. The candies entering the bag must remain clustered together. 4. You many work with your hands inside the bag. What is your solution? Cells Move Materials Using… NO ENERGY! ENERGY! Passive Transport Active Transport Diffusion Osmosis Today’s Question: What is active transport? Active Transport • The movement of Large particles across the cell membrane • The cell uses ENERGY • Active Transport is like pedaling a bike uphill. Molecules move from LOW concentration to HIGH Concentration. Engulfing • One type of active transport is called engulfing. • The cell membrane wraps around the large particle. • It is then brought into the cell as a vesicle. Englufing Animations (also called endocytosis) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4gLtk8Yc1Zc (Narrated) http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/cellstructure s/phagocitosis.swf http://www.maxanim.com/physiology/Endocytosis%20and%20E xocytosis/Endocytosis%20and%20Exocytosis.htm