Basic Concepts and National Income Calculation
advertisement

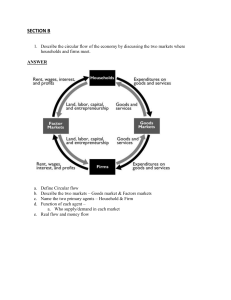
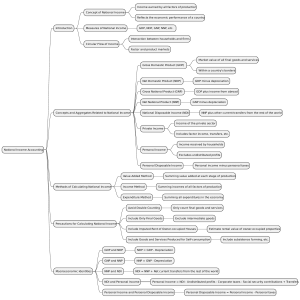
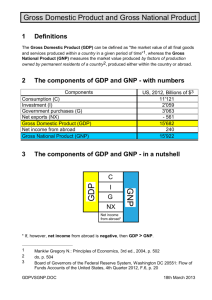
Basic Concepts and National Income Calculation Dr. Asok Das Associate Professor in Economics Prabhu Jagatbandhu College First Year Economics General Class What is basic idea of Economics ■ ■ Choice between alternatives out of scarce means having alternative uses Scarce means viz. Fixed income to households or limited means to the firms, give us a downward PPC curve to firms and downward budget line to the households What are then the basic economic problems arising out of scarcity of usable means ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ What to produce? For whom to produce? How to produce? Optimal use of resources Problem of growth Who or how these problems be solved? ■ ■ Some reasonable answers are related to find out what are the basic units of an economic system Household, firm and government are three basic units who are to deliver something expected from each of them to solve the problems ❑ ❑ Production and its distribution is the key to solve all these problems Production results from resources. It is pattern of ownership of resources that finds whether it is capitalistic, socialistic or mixed economic system. Laissez faire or capitalistic system and how market forces play the key role of allocating resources ■ ■ ■ For example USA, UK and othe OECD countries etc. Here state has also a roledevelopmental and planning and they adopt indicative planning As market forces are guiding force, trade cycles often crop up ,and may obstruct the economy for a long time. 1930s depression is an example. Socialist system crops as an antidote ❑ ❑ Here state plays the key role The mixture of the two systems- mixed economy, often plays a constructive role taking units of the two systems. India is an example in this regard National income calculation ■ Production is the centre of all economic activities, so its calculation is necessary in order to assess ❑ ❑ ❑ Whether growth is taking place What about the distribution of income What about the uses of production What is N.I. ■ ■ Income from various agents of production spreading across different parts of world in a particular fiscal year. To define it from various aspectsOn the basis of one angle, there is one way of defining National Income. There are three angles:Production Method To value final products of all sources in terms of market prices called by GDP during that year. Income Method To define it in terms of summation of factor incomes less transfer earnings give an income angle Expenditure Method Income or production is used up either by consumption or by forming capital ■ Accuracy in measuring production or income needed some caution ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Avoidance of multiple counting Exclusion of transfer income in income method Depreciation of capital or CCA to be deducted from GDP to calculate NDP or from GNP to get NNP NNP at factor cost gives N.I. Difference between NNP at market price and factor cost results due to appearance of indirect taxes and/or subsidies GNP indicates production of a particular year, whether sold or not in that year. The part which is not sold called inventory accumulation and becomes a part of capital accumulation Resale value, lottery value or prices of company shares do not become a part of N.I. Brokerage value of agents involved in above activities are part of N.I. Tabular framework ■ ■ ■ GNP less depreciation = NNP NNP less indirect taxes = National Income N.I. Less (i) corporate profit taxes (ii) Personal Tax ❑ (iii) contributions for social insurance Plus ❑ (i) (ii) (iii) Government transfer payments Net government interest payments =Disposable income Contd. Disposable income Less undistributed corporate profit Plus business transfer payments = Personal disposable income Personal disposable income may be spent in following ways Personal consumption expenditure Personal Savings Personal transfer to foreigners Difference between GDP and GNP is defined as GDP + Net income from abroad = GNP = GDP + Export value- Import value