Energy Flow in Ecosystems: Food Chains & Pyramids
advertisement

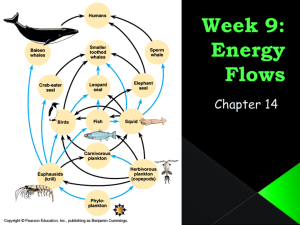
Energy Flow 3-2 • Sunlight - main source of energy for life on Earth – Of all the sunlight that reaches Earth’s surface, only <1% is used by living things • Some organisms rely on energy stored in chemical compounds Producers • Autotrophs - organisms that capture energy from sun or chemicals to produce their own food – Ex. Plants, some algae, and certain bacteria – a.k.a. producers • All producers are essential to the flow of energy through the biosphere Energy from the Sun • Photosynthesis - autotrophs use sun’s energy to convert CO2 and H2O to O2 and C6H12O6 – This process is responsible for adding O2 to atmosphere and removing CO2 • Plants - main autotroph on land • Algae- main autotroph in sunlit layer of ocean • Cyanobacteria (photosynthetic bacteria) important in tidal flats & salt marshes Life without Light • Bacteria can produce food without sunlight – Use energy stored in chemical bonds of inorganic molecules like hydrogen sulfide – Known as chemosynthesis • Chemosynthetic bacteria live in very extreme environments, like volcanic vents on the ocean floor & hot springs Consumers • Organisms that cannot harness energy directly need to acquire energy from other organisms • Ex: animals, fungi, & many bacteria • a.k.a. heterotrophs Types of Heterotrophs • • • • Herbivores - plant eaters Carnivores - meat eaters Omnivores - plant and meat eaters Detritivores - feed on plant and animal remains (detritus) – Ex: earthworm, snails, crabs • Decomposers - break down organic matter – Ex: bacteria, fungi Feeding Relationships • Energy flows in an ecosystem in 1 direction: sun-->producers-->consumers • Relationships between producers & consumers connect organisms into a feeding network based on who eats whom Food Chains • Diagrams that show energy being passed through an ecosystem in series of steps, in which organisms transfer energy by eating & being eaten • Require at least 3 organisms: producer, herbivore, carnivore/omnivore • Can also have detritivore &/or decomposer • Organisms are connected by arrows • Arrows point to who is eating, not to who is being eaten • Imagine arrow head as an open mouth • Raspberry-->rabbit-->coyote • Grass-->mouse-->snake • Grass<--mouse <--snake (WRONG) • Sun-->mouse-->owl (WRONG) • Dirt-->grass-->vole Food Webs • Diagram that shows all the complex feeding relationships in an ecosystem • Several food chains (from same ecosystem) together • Arrows still point to who is doing the eating • Trophic level - each step in food chain or food web – Producers - 1st trophic level – Herbivores - 2nd trophic level – Carnivores - 3rd trophic level • Each consumer depends on the trophic level below it for energy Energy and Food • Of all the sunlight that reaches Earth, plants use less than 1% of it • However, they are able to store over 30% of the energy they capture, and produce 170 billion metric tons of food each year • The total amount of organic matter present in a trophic level is called biomass • Biomass is the amount of energy, in the form of food, available to the next trophic level • About 90% of the energy contained in a trophic level is used by organisms in that level • Only 10% of the stored energy is passed on to the consumers in the next trophic level • Known as the “10% law” or “rule of 10%” – Main reason most food chains have 5 or less links Ecological Pyramids • Diagrams that show relative amount of energy or matter contained in each trophic level • There are 3 types of pyramids: energy, biomass, and numbers Energy Pyramid • There is no limit to the number of trophic levels a food chain can support, but determined by # of producers • However, only part of stored energy is passed on to the next level • Most energy consumed is used for respiration, movement, & reproduction • Some remaining energy is released into environment as heat • Out of all stored energy, only 10% of that energy is available to the next trophic level • So, each succeeding trophic level can only support 1/10 the amount of living tissue as the level below it • Units on energy pyramids are usually calories Biomass Pyramid • Biomass - total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level • Units of biomass - grams or lbs/unit area • Represents potential food available for each trophic level Numbers Pyramid • Based on number of organisms for each trophic level • May not be typical pyramid shape depending on the ecosystem • Energy moves between trophic levels in the form of food • Food also contains matter – Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, & oxygen are the most common element in food • Molecules composed of these elements store energy as they move from 1 trophic level to the next • Without even 1 of these elements, food cannot be produced • The growth of producers in most ecosystems is limited by the lack of one or more of these elements, not by the sun