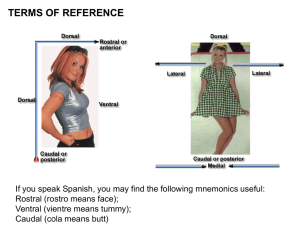
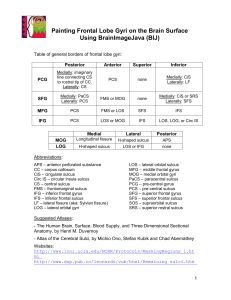
Postcentral gyrus
advertisement

The Telencephalon Xiaoming Zhang The Telencephalon External features: 2 Cerebral hemispheres (separated by longitudinal cerebral fissure) Transverse cerebral fissure intervenes between the hemispheres and cerebellum. 3 poles, 3 surfaces 3 borders The Telencephalon External features: 3 Main fissures on surface of each hemisphere: The Lateral sulcus The Central sulcus The Parietooccipital sulcus Sulci and gyri of Superolateral surface Postcentral gyrus Postcentral sulcus Superior parietal lobule Intraparietal sulcus Supramarginal gyrus Parietooccipital sulcus 5 Lobes: (divided by 3 sulci) The Frontal lobe The Parietal lobe The Occipital lobe The Temporal lobe The Insular lobe (insula) Main gyri and sulci Dorsolateral surface: in frontal lobe: — precentral sulcus, superior and inferior frontal sulcus precentral gyrus superior frontal gyrus middle frontal gyrus inferior frontal gyrus in parietal lobe: — postcentral sulcus supermarginal gyrus — intraparietal sulcus angular gyrus — postcentral gyrus — superior and inferior parietal lobule in temporal lobe: superior temporal sulcus inferior temporal sulcus superior middle inferior temporal gyrus transverse temporal gyrus Right superior figure: Lateral view of cerebral hemisphere Transverse temporal gyri Sulci and gyri of Superolateral surface Precentral gyrus Precentral sulcus Postcentral gyrus Postcentral sulcus Superior frontal sulcus Superior parietal lobule Inferior frontal sulcus Superior, middle and inferioe frontal gyri Supramarginal gyrus Angular gyrus Superior temporal sulcus Superior temporal gyrus Inferior temporal sulcus Middle temporal gyrus Inferior temporal gyrus Sulci and gyri of medial surface Corpus callosum Callosal sulcus cingulate gyrus Paracentral lobule Marginal ramus Parietooccipital sulcus Cingulate sulcus Cuneus Calcarine sulcus Lingual gyrus Inferior surface Olfactory bulb Olfactory tract Uncus Occipitotemporal sulcus Parahippocampal gyrus Medial and lateral occipitotemporal gyri Collateral sulcus Olfactory trigone Anterior perforated substance Hippocampus Dentate gyrus Hippocampal formation Limbic lobe and limbic system: Limbic lobe: composed of cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus and uncus. Limbic system: comprises of limbic lobe and relative cortex and other structures of brain (hippocampal formation, part of amygdaloid nucleus, hypothalamus and anterior nucleus of thalamus) Internal structures: Gray matter White matter Lateral ventricle Gray matter: Cortex: Functional localizations of cerebral cortex — somatic motor area: in precentral gyrus and anterior part of paracentral lobule; mainly control skeleton muscles on the opposite side of body. — somatic sensory area: in the postcentral gyrus and posterior part of paracentral lobule; receive the sensory signals from skin, proprioceptors and taste receptors on the opposite side of body. First somatic motor area Characters • Representation is inverted, but head and face are upright • A body part is represented by a cortical area proportional to its use rather than its size • Receiving fibers from postcentral gyrus, VA, VL and VPL, sending out fibers to form pyramidal tract, controlling voluntary movements First somatic sensory area Characters • Sensory representation, like motor area, is crossed and inverted • Receiving and interpret sensation from opposite side of body — visual area (striate area): surrounds the calcarine sulcus ; receive the data from the temporal half of ipsilateral retina and nasal half of the contralateral retina. — auditory area (acoustic area): in the transverse temporal gyri; efferent fibers of medial geniculate nucleus of bilateral side end in this area. — visceral moter area: in the limbic lobe. — The language areas: 1. Writing area—posterior part of middle frontal gyrus. 2. Motor speech area— posterior part of inferior frontal gyrus. 3. Auditory language area posterior part superior temporal gyrus 4. Visual language area -angular gyrus basal ganglion : Corpus striatum: Caudate nucleus: “C” – shaped head, body and tail of caudate nucleus Lentiform nucleus: Claustrum: between the lentiform nucleus and insula. Amygdaloid body: holds the amygdaloid nucleus and lies at the end of tail of caudate nucleus. White matter: 3 kinds of fibers Association fibers: — connect cortical areas in same hemisphere. — Superior longitudinal fasciculus — Inferior longitudinal fasciculus — Cingulum —Uncinate fasciculus — Arcuate fibers Commissural fibers: — Corpus callosum * at the bottom of longitudinal cerebral fissure * 4 parts : rostrum, genu, trunk and splenium — anterior commissure — commissure of fornix: Projection fibers: — connect the cortex and subcortical structures — internal capsule: * a plate of white matter * position: medially to the lentiform nucleus; laterally to the caudate nucleus and thalamus. * “X” – shaped in the horizontal section * 3 parts: anterior limb; posterior limb and genu. * projection fibers passing through each part of the internal capsule: anterior limb—frontopontine tract; anterior thalamic radiation genu—corticonuclear tract posterior limb—corticospinal tract thalamocortical tract parieto-occipito-temporo-pontine tract optic radiation auditory radiation Anterior thalamic radiation Head of caudate nucleus Frontopontine tract Corticonuclear tract Corticospinal tract Dorsal thalamus Central thalamic radiation Lentiform nucleus Corticorubral tract Parieto-occipitotemporo-pontine tract Acoustic radiation Medial geniculate body Optic radiation Lateral geniculate body Lateral ventricles: “C”- shaped cavity in each cerebral hemisphere. filled with cerebrospinal fluid 4 parts: — anterior horn (in frontal lobe) — central part (in parietal lobe ) — posterior horn (in occipital lobe) — inferior horn (in temporal lobe) communicated with the third ventricle through the interventricular foramen. The Coronary section of the brain Superior view of lateral ventricle RMB: 35.00