Sheep Brain Dissection
advertisement

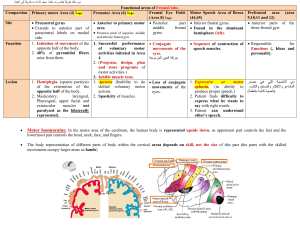
Sheep Brain Dissection By: Ryan Begun and Nick Palladino and Mr. Davis The Dura Mater • The dura mater is a thick durable membrane covering the brain and closest to the skull. • Surrounds and supports the large venous channels carrying blood from the brain toward the heart. Pia Mater • Thin white coating on the brain surface • Contains blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. The Cerebrum • The largest part of the human brain. • Associated with higher brain functions such as thought and action. • Cerebrum is divided into five lobes. • Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal, and insula. The Cerebellum • Also known as the “little brain” • Associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. Involuntary Control The Brain Stem • Responsible for vital life functions such as breathing, heartbeat and blood pressure. • The brain stem is made of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Medulla Oblongata • Controls autonomic functions, such as heart rate, respiratory rate, coughing, vomiting etc. • Relays nerve signals between the brain and spinal cord The pons • Involved in the motor control and sensory analysis. Midbrain • Relay station for auditory and visual information • Eye movement Frontal Lobe • Involved in our motor functions. • Problem solving • Memory • Language • Judgment • Impulse control • Houses our personality Temporal Lobe • Associated with perception and recognition of the auditory stimuli, memory, and speech. Occipital Lobe • Associated with visual processing • Helps interprets what the eyes see Parietal Lobe • Associated with movement • Orientation • Recognition • Perception of the stimuli to the body • Sense of Touch • Primary Somatosensory Cortex Gyri and Sulci • Gyri is the bumps, elevated ridges in the cerebral cortex as shown by the circles. • Sulci: the indentations, shallow grooves, as shown by the solid lines Gyrus Sulcus Pre central gyrus • Located in front of the central sulcus. First Gyrus in the frontal lobe. • Voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Post central gyrus • In parietal lobe first gyrus behind the central sulcus. • Receives sensory feed back from all over the body; including • From joints • And tendons • Internal Organs Central Sulcus • Groove, separates frontal and parietal lobes. Longitudinal Cerebral Fissure • Separates the two sides of the cerebrum Diencephalon • Thalamus • Hypothalamus Thalamus • Processes and relays movement and sensory information Hypothalamus • Controlling hunger and thirst • Emotions • Body Temperature regulation • Circadian rhythms • Other Homeostatic Controls. Read in your book about this little but important part of the brain. Corpus Callosum • Communication between the left and right hemispheres • Forms roof of lateral and third ventricles • Myelinated White Matter White Matter • Area where messages pass through • Develops throughout life. • Myelinated Grey Matter • • • • • • • Muscle Control Sensory Perception Seeing Hearing Memory Speech Emotions • UNMYELINATED