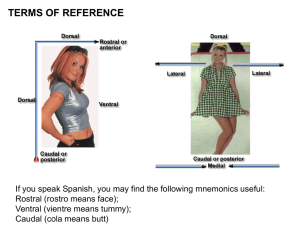
ClassPresentation07
advertisement

GAZE FIXATION AND THE NEURAL CIRCUITRY OF FACE PROCESSING IN AUTISM Sakina Dharsee Psychology - 260 Introduction • Autism: Developmental disorder, unique profile of social and emotional behavior. • Symptomatology: Diminished gaze fixation, lack of social or emotional reciprocity. Previous research: Fusiform gyrus less activated in autistic patients. Deficit: Which circuits are highly activated compared to normal? Hypothesis • Fusiform gyrus hypoactivation - Less time fixating on eye regions: Cause or consequence? • Hyperactivation in amygdala (region responsible for processing threatening, social and emotional cues) Experimental Task Stimulation: Mock-up of MRI scanner. MRI Scan Eye movement: Eye-tracking device. Study 1: • 14 autistic males (M:15.9, SD: 4.71) • 12 normal males (M: 17.1, SD: 2.78) • Task: Is the picture emotional or neutral? • Half straight, half turned. Study 2: • 16 autistic males (M:14.5, SD: 4.60) • 16 normal males (M: 14.5, SD: 4.56) • Task: Is the picture familiar to you? • Ten photographs of family or friends. Result Study 1: Autistic group: • Longer judgement time for emotional and straight ahead faces. • Significantly less time fixating on eyes. • More activation in left amygdala. Control group: • More activation in bilateral fusiform gyrus. a – Right fusiform gyrus b – Left fusiform gyrus Study 2: Control group: • More activation in bilateral fusiform gyrus. Autistic group: • Significantly less time fixating on eyes. • More activation in right amygdala. • No differences in judgement time. Average duration of fixation on mouth, eye region and face in general. Study 1: g – Left amygdala Study 2: e – Right amygdala Discussion • Individuals with autism scan and process faces differently. • Deficits in processing emotional cues and in processing socially engaging faces. • Greater amygdala activation in autistic group for both studies. • Eye fixation creates a negative over-arousal mediated by the amygdala – diminished gaze fixation reduces this. Negative over-arousal Increased sensitivity to social stimuli Diminished gaze fixation Hypoactivation of fusiform gyrus Strengths and Limitations Strengths: • Experimental control. • Attempt to reduce performance anxiety. • Stimulation session. Limitations: • Based solely on data obtained from males. • Inconsistency. Future directions: - Lateralization of amygdala – left for emotion, right for familiarity? (Baas et al., 2004) - Treatment research: Can autistic patients be trained to scan and process faces normally, resulting in normal levels of fusiform gyrus activation? Personal Opinion • Congruent with previous findings, and makes a new discovery. • Research can contribute towards the treatment and counselling of autistic children. • Leads into further research on the disorder – what are the circuits associated with other symptoms? Thank You! Any questions?