IntroductiontoManagerialEconomics - finishingschool
advertisement

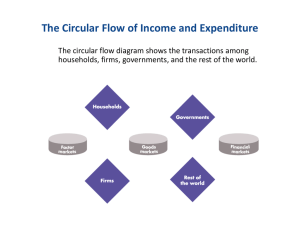
We have numerous choice: 67 varieties of toothpaste, 487 styles of shoes, 186 brands of cell phones with 137 telephone companies. There are 87 varieties of lawyers, and 75 specialties inside medicine. Yehi Hai Right Choice ? ????? Questions • How do markets work? • How do customers value products? • What are the relevant production and cost measures for decision making? • How does competition affect business decisions in different market structures? • What prices should be set? • What would be the impact of changes in interest rates on costs, accounting, or capital budgeting? • How important to managerial and marketing decisions are changes in: foreign exchange rates, GDP, inflation, government regulations, sources of energy, and the balance of payments? Introduction: Economic Issues By- Rahul Jain (MBA, FCS) Aim of the Course To introduce economic concepts to the fashion marketing students to enable them to use various forms of economic analysis to extract useful information from economic data Our strategy for achieving objectives360 Degree Learning • Concepts, Practice and Class Discussion • Punctuality, Participation and Preparation (Its compulsory to bring your own calculators, Pen, Stationary, Registers, Prescribed Book, Course Handouts - Otherwise disciplinary action will be taken) • Judgment challenge • Learning to communicate ideas • Learning from each other • Learning through discovery What is “Good” Participation? • Quality, not quantity. • Analyzing and discussing course material. • Questioning the analysis of others. • Seeking clarification. • Contrasting issues within other settings, courses, and / or other • countries. • Changing the direction of discussion. • Summarizing / synthesizing. • Adherence to guidelines for professional conduct. Some Important rules • Switch off your Mobiles • Attendance rules will be strictly applied • Non completion of Assignment will lead to strict disciplinary measures • Students can gather additional bonus points by being a “Performer” 4 times in the whole course. • Students falling in the “Improvement category” would be penalized. Economics as the context of business • Management, marketing & accounting focus on specifics – How to manage a company… – How to market a product… – How to quantify & compare corporate performance… Focus is your personal input to business • Economics is the context of business – “Men make their own history, but they do not make it as they please; they do not make it under self-selected circumstances, but under circumstances existing already, given and transmitted from the past” • Focus on constraints on and circumstances of your input. Both opportunities & dilemmas – Quick quiz: who made the above statement? Economics as the context of business •Often the best wisdom in economics isn’t found in standard textbooks! •considers theories & data are more relevant to business The Managerial economics • What is managerial economics? – decision making in business • external influences on the firm – the business environment • internal decisions of the firm • the external effects of business decision making Managerial Economics can be defined as the study of economic theories, logic and tools of economic analysis that are used in the process of business decision- making. “The firm”: real world vs economic theory • The real world: an incredible diversity – Size: from corner store to Microsoft – Operations: from one outlet to almost all countries – Diversity: • from single product (wheat farm) to many (Sony) • From one industry to many – Ownership: from sole proprietor to multinational listed company – Structure: • from one person operations to multi-department • From sole operations (production to sale) to specialization in manufacturing, wholesale, retail, marketing, consulting… Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies how individuals, households and firms make decisions to allocate limited resources, typically in markets where goods or services are being bought and sold. Micro-Economics Applied to Operational Issues The issues that arise within the business are operational issues, and the following are the theories applied: Theory of Demand Theory of Production and Production Decisions Analysis of Market-Structure and Pricing Theory Profit Analysis and Profit Management Theory of Capital and Investment Decisions Macroeconomics, on the other hand, involves the "sum total of economic activity, dealing with the issues of growth, inflation and unemployment and with national economic policies relating to these issues" and the effects of government actions (such as changing taxation levels) on them. Macro-Economics applied to Business Environment The issues that pertain to the business environment in planning and formulation of the future strategy under these three categories: Issues related to Macroeconomic trends in the Economy Issues related to Foreign Trade Issues related to Government Policies The Economic Problem • Economic problems – production and consumption – scarcity: the central economic problem • Macroeconomic issues – growth – unemployment – inflation – deficits – cyclical fluctuations The Economic Problem • Microeconomic issues – choices: • what • how • for whom – the concept of opportunity cost – rational decision making • weighing up marginal costs and marginal benefits – the social implications of choice The Firm and Its Economic Problem • Firm – An institution that hires productive resources and that organises those resources to produce and sell goods and services • A firm’s goal is to maximize wealth of the shareholders The Types of Business Organisation • Sole Proprietorship – a firm with a single owner • Partnership – a firm with two or more owners who have unlimited liability • Company – a firm owned by one or more limited liability stockholders Discussion What kind of Economic factors will be considered by SRK while launching King Khan merchandize? • • • • • • • Managerial Decisions Areas Assessment of investible funds Selecting business area Choice of Product Determining Optimum Output Determining Price of the Product Determining Input-Combination and technology Sales Promotion Use of Quantitative Methods Application of Economic Concepts and Theories in Decision-Making • Mathematical tools • Statistical tools • Econometrics Managerial Economics Application of Economic Concepts, Theories and Analytical Tools to find Optimum Business Problems Opportunity Cost • Firms incur opportunity costs when they produce goods. – Opportunity cost of producing — the best alternative investment opportunity that the firm foregoes to produce a good or service – Look at it as the opportunity costs of the factors of production the firm employs (labor, capital, entrepreneurs) Opportunity Cost • Components of a firm’s opportunity cost – Explicit costs (money costs) • The amount paid for factors of production – Implicit costs (non-money costs) • The value of foregone opportunities. • The firm incur implicit costs when it: – uses its own capital – uses its owner’s time or financial resources Opportunity Cost • Cost of Owner’s Resources – The income that the owner could have earned in the best alternative job. – Normal profit is the expected return for supplying entrepreneurial ability. Economic Profit • Economic Profit – A firm’s total revenue minus its opportunity costs. – Not the same as accounting profit. The Firm and Its Economic Problem • Technology Constraints – A firm’s resources and the available technology limit its production. • Information Constraints – The cost of coping with limited information itself limits profit. • Market Constraints – Willingness to pay of its customers and by the prices and marketing efforts of rival firms. – Willingness of people to work for and invest in the firm. The Economic Problem • The circular flow of income – firms and households The circular flow of goods and incomes The Economic Problem • The circular flow of income – firms and households – goods markets • real flows: goods and services The circular flow of goods and incomes The circular flow of goods and incomes Goods and services The Economic Problem • The circular flow of income – firms and households – goods markets • real flows: goods and services • money flows: consumer expenditure The circular flow of goods and incomes Goods and services The circular flow of goods and incomes Goods and services £ Consumer expenditure The Economic Problem • The circular flow of income – firms and households – goods markets • real flows: goods and services • money flows: consumer expenditure – factor markets The Economic Problem • The circular flow of income – firms and households – goods markets • real flows: goods and services • money flows: consumer expenditure – factor markets • real flows: services of labour and other factors The circular flow of goods and incomes Goods and services £ Consumer expenditure The circular flow of goods and incomes Goods and services £ Consumer expenditure Services of factors of production (labour, etc) The Economic Problem • The circular flow of income – firms and households – goods markets • real flows: goods and services • money flows: consumer expenditure – factor markets • real flows: services of labour and other factors • money flows: wages and other incomes The circular flow of goods and incomes Goods and services £ Consumer expenditure Services of factors of production (labour, etc) The circular flow of goods and incomes Goods and services £ Consumer expenditure Wages, rent dividends, etc. £ Services of factors of production (labour, etc) The Economic Problem • The circular flow of income (cont.) – macroeconomic issues • the size of total flows – microeconomic issues • individual markets • choices within goods and factor markets Website activity • Each one of you write your bio in your course page. • Bio will be written as per following guidelines: – Include your name, prior education background and institute’s name – Include your hobbies, 2 strengths and 2 unique talents – Include your achievements – Include what you want to learn from this course • www.finishingschool.pbworks.com Class Assignment – I A) Individual Assignment- 3 minute presentation on Business News Analysis (Refer Economic times and other business news papers/ magazine) –Compulsory for first 3 roll numbers. Also submit a report on A4 size paper (Give intext citations) : Second Week onwards. Following should be the headings in the News analysis • Description of the news • Analysis, Interpretation and Implication • Conclusion B) Individual Assignment – 2 minute presentation on Key learnings of the previous class. (Compulsory for all) Class Assignment – I C) Individual Assignment: Read Google PPT and Make a one page analysis of factors affecting the demand of Google products and services, from the Google PPT. You can also do additional secondary research on the company. (Provide references) Submit on A4 Page. Assignment – I Contd. Main Readings Note: Chapters of the Text Book, PPT , Internet, Hand Outs and Library Text Book: Managerial Economics, DN Dwivedi. Vikas Publications • Academic Honesty – Do Not Copy Work – Reference Any Source – When Confused Ask Instructor Contact me: Rahul Jain (9811228852, rahulkjain16@yahoo.co.in, Yahooid:rahulkjain16)