Week#1 - mrmilewski
advertisement

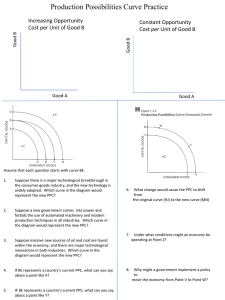
AP Econ F14 Week#1 Economics 9/2/14 http://mrmilewski.com • OBJECTIVE: First day of school administrative stuff. AP Micro/Macro-I.A • Language objective: Discuss norms for the class and what economics is. • I. Welcome Back • II. Attendance • III. Distribution of: -syllabus, points, test dates, & textbooks -desks, fans, floor, & bags -discuss scarcity • IV. Homework: Read p. 3-8 What you need each day • 1.) Textbook • 2.) Something to write with • 3.) Notebook • 4.) Planner Cell Phones • There is a time and a place for cell phones, but… 1.) During instruction, there is no place for it. 2.) During class, there is no time for games. 3.) During class, there is no time for social media. The Fundamental Economic problem is: • Scarcity - the condition that results from society not having enough resources to produce all the things people would like to have. • Economics - the study of how people try to satisfy what appears to be seemingly unlimited & competing wants through the careful use of relatively scarce resources. Need v. Want • Need - a basic requirement for survival & includes food, clothing, and shelter. • Want - a way of expressing need. Homework Tonight • Read pages 3-8 • Get your syllabus signed • Get a notebook Economics 9/3/14 http://mrmilewski.com • OBJECTIVE: Examine the factors of production and the Production Possibilities Curve. AP Micro/Macro-I.B • Language objective: Discuss land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship, and production. • I. Macroeconomics pre-test • II. Journal#1 -Factors of production & the PPC • III. Video on PPC • IV. Practice problems on PPC (p.12) • IV. Homework -Read p. 9-18 -Answer question#1,3,7 & Problem #5 p.20-21 The Factors of Production • LAND – the gifts of nature • LABOR – people with all their efforts & abilities • CAPITAL – the tools, equipment, machinery, and factories used in the production of goods & services • ENTREPRENEURS – a risk taker in search of profits who does something new with existing resources Production Possibilities Curve http://www.harpercollege.edu/mhealy/eco212/lectures/econgrow/econgrow.htm • PPC is a diagram that represents various combinations of goods and/or services an economy can produce when all productive resources are fully employed. • The line of the PPF shows what is possible if all of the factors of production are fully employed. PPC Opportunity Cost on the PPC Measuring Opportunity Costs • Opportunity costs are measured in terms of what you give up. • The cost of using a pass in Mr. Milewski’s class is the extra credit you lose. • The cost of increasing gun production is the butter you give up. Graphing Choices • Passes Remaining 3 2 1 0 Extra Credit Lost 0 10 20 25 AC DC Econ • Video on PPC Monsters Inc. • Example p.12 • Video on PPC Shift Devo “Shift it” • 1.) Faster Computers/ Better Tech • 2.) Destruction of Power Plants • 3.) High Unemployment • 4.) Better education Homework Tonight • Read pages 9-18 • Answer question#1,3,7 & Problem #5 p.20-21 • Additional video: Khan PPC Economics 9/4/14 http://mrmilewski.com • OBJECTIVE: Examine the factors of production and the Production Possibilities Curve. AP Micro/Macro-I.B • Language objective: Discuss production. • I. Journal#2 -review factors of production/homework • II. Journal#2 -question#12 & TINSTAAFL TINSTAAFL • There is no such thing as a free lunch Other terminology: • Inverse relationship – as one number goes up, the other number goes down • Direct relationship – as one number goes up, so does the other number. Economics 9/5/14 http://mrmilewski.com • OBJECTIVE: Examine the factors of production and the Production Possibilities Curve. AP Micro/Macro-I.B • Language objective: Discuss production. • I. Journal#3 -Do now: PPC -notes on marginal benefit & basic math • II. Homework -Answer questions#9&10 & Problem #7 p.20-21 & Read p.30-32 Marginal Benefit and Cost • For our purposes in studying economics, “marginal” means “extra”, “additional”, or a “change in” the status quo or the existing state of affairs. • Marginal benefit (MB) is the extra (additional) benefit of consuming one more unit of some good or service. The change benefit when one more is consumed. • Marginal cost (MC) is the extra (additional) cost of producing one more unit of output equal to the change in total cost divided by the change in output. Example #2 Example #2 Example #2 Direct and Inverse Relationships • A direct relationship (positive relationship) has two variables that change in the same direction. For example: An increase in consumption is associated with an increase in income. (See Figure 1, page 22) • An inverse relationship (negative relationship) has two variables that change in the opposite direction. For example: When the price of tickets to a sporting event decreases, attendance will increase. (See Figure 2, page 23) Income and Consumption • In regards to income and consumption, income is generally the independent variable and consumption is the dependent variable. You have to make money to consume goods and services. • As income rises, consumption rises. (Figure 1, page 22) Dependent and Independent Variables • Economists try to determine which variable is the cause and which variable is the effect in any given relationship. • The independent variable is the cause or source; it is the variable that changes first. • The dependent variable is the effect or outcome; it changes because the independent variable changes. Game Tickets and Attendance • Ticket prices are the independent variable and attendance is the dependent variable. • The price of a ticket to attend a sporting event is set before the season begins and it determines the attendance at games. If the price is set too high, less people will buy the ticket. If the price is lower than what consumers expect, they will buy more tickets. Attendance does not determine the price of a ticket. (Figure 2, page 23) Homework Tonight • Answer question#9&10 & Problem #7 p.20-21 • Read p.30-32 • Additional video: Khan PPC