Conflict over Representation
advertisement

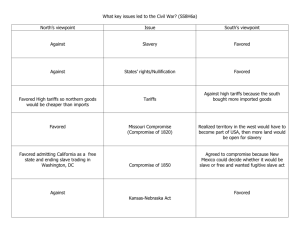
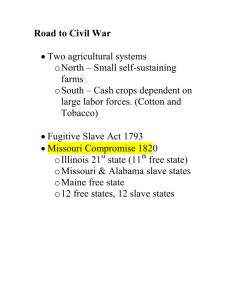
Conflict over Representation New Jersey Plan • Small states were afraid that large states would control the government • Each state should have the same number of representatives in Congress • Called equal representation • One house (unicameral) legislature Virginia Plan • Proposed by James Madison • Favored more representatives for states with larger populations • Called proportional representation • Two-house (bicameral) legislature The Great Compromise • Suggested by Ben Franklin and Roger Sherman • Congress would have two houses – the Senate and the House of Representatives • The House would be elected based on proportional representation. • The House would develop all money bills. Compromise continued • The Senate would be elected based on equal representation. • Senate could only accept or reject money bills. • House favored larger states; Senate favored smaller states • Compromise passed by one vote Conflicts between North and South • Protective tariffs – taxes on products imported • North – tariffs were necessary to allow businesses to be competitive • Wanted the Constitution to give government the power to control trade. Continued • South – tariffs would increase the cost of goods that they bought from Europe. • England might place tariffs on their farm products making them harder to sell. • Southern states were smaller giving them less power. Opposed giving the government power to control trade. Conflict over Slavery • • • • Many framers opposed slavery Delegates from the South favored slavery Slaves were considered personal property Would not be part of the government if slavery was abolished • Delegates from the North wanted all states to join the Union. Compromises • Section 8 – power to collect taxes and regulate trade • Section 9 – 20 years before Congress can regulate the slave trade • Three-fifths Compromise – each slave would be counted as three-fifths of a person • Fugitive slave clause – escaped slaves must be returned