The Age of Reform (1801
advertisement

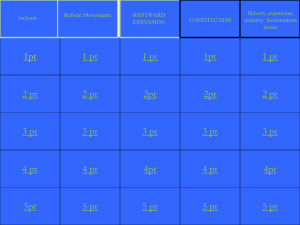
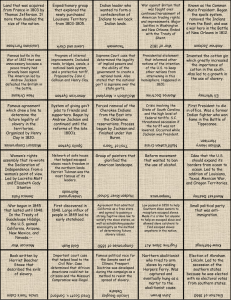
Contradictions that Bind: Expansion and Reform (1801-1861) Related Topics Covered in Lecture 3 • Louisiana Purchase (1803) – Jefferson’s victory • War of 1812 – A draw “spun” as a triumph • Missouri Compromise (1820) – uneasy handling of slavery issue • Andrew Jackson’s background and rise of Democratic Party – a gentleman of the frontier epitomizing new realities of massbased politics Jackson’s “War” on the National Bank Nullification Crisis (1832-1833) • Nominally fought over a protective tariff, but slavery was the proverbial 800 pound elephant in the room • Could states render individual federal laws null and void? • Jackson battled his own vice-president, John C. Calhoun, before a compromise was reached Emergence of Whig Party Trail of Tears Election of 1840 – “Log Cabin and Hard Cider” Campaign Manifest Destiny Mexican War (1846-1848) Consequences of Mexican War • Case of “territorial indigestion” – slavery question exacerbated due to Wilmot Proviso • Fears among anti-slavery advocates of “slave power” conspiracy • Heightened partisanship amidst claims of “Mr. Polk’s War” Spectrum of Opinion on Slavery (In order of greatest defenders to strongest opponents) • Southern Democrats (siege mentality) • Northern Democrats • Free Soilers and, eventually, Republicans Whigs • Abolitionists • John Brown Free Soilers as Third Party Compromise of 1850 – another “band aid” fix Uncle Tom’s Cabin Kansas-Nebraska Act (“slave power” conspiracy at work?) Birth of Republican Party (1854) • Moderate in that it advocated only containing the expansion of slavery rather than eliminating it where it already existed. • At this point only a sectional party. • Appealed to former Whigs and Free Soilers “Bleeding Kansas”/Caning of Charles Sumner Dred Scott Decision by Supreme Court (1857) • Ruling occurred at a time when the majority of justices were slaveholders and/or supported the practice. • Court found that Scott never should have been able to bring suit in the first place. • If a slave lives in a free territory, that has no bearing on one’s legal status. • Congress has no right to bar slavery in the territories (thus Compromise of 1820 was null and void). Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858) John Brown’s Raid at Harper’s Ferry Election of 1860 Useful Primary Sources • Webster-Hayne Debate (1830) • Speckled Snake reply to Andrew Jackson (1830) • “Appeal to the Christian Women of the South” by Angelina Grimke (1836) • “Annexation” by John O’Sullivan (1845) • First Republican Party Platform (1856) Useful Primary Sources • • • • Excerpts from Hinton Helper’s The Impending Crisis of the South (1857) Excerpts from Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858) “On the Death of John Brown” by William Lloyd Garrison (1859) South Carolina Declaration of Independence (1860) “Cornerstone” Speech by Alexander Stephens (1861)