PPT Constitution
advertisement

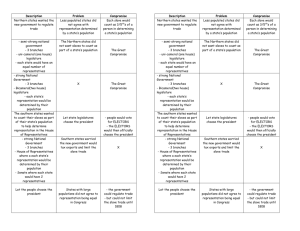
Compromises of the Constitutional Convention Essential Skill: 1) State implications and consequences 2) Examine information from more than one perspective Great Compromise / Connecticut Compromise Conflict between small & large states over voting in Congress NJ Plan: all states have equal vote (similar to AOC) VA Plan: larger states have more votes THE SOLUTION: Bicameral Congress (two houses) One house has # representatives based on population of state (House of Representatives) One house has equal representation for every state (Senate = 2 senators per state) Three-Fifths Compromise Conflict b/w S. slave states and N. states – Should slaves count for # representatives in Congress? Should slaves count for $ taxes paid? WHAT HAPPENED? The word “slave” was never used in the Constitution. They counted slaves as “three fifths of all other persons” for amount of taxes paid and number of representatives in the House. Commerce and Slave Trade Compromise Conflict b/w S. slave states and N. states over regulating commerce and slavery WHAT HAPPENED? 3-part compromise: S. states agreed to give Congress Power to Regulate Commerce (Trade) N. states agreed not to ban “importation of such persons” until 1808 N. states agreed to NO Taxes on Exports Other Compromises EXECUTIVE Compromise: The problem: Should there be one Chief Executive or a Committee of Chief Exec’s? They chose ONE (the President) ELECTORAL COLLEGE Compromise: The problem: Should Congress or the citizens elect the President? They let STATE legislatures choose the Electors of the President (gave states more power over the vote)