Breech Presentation

Breech
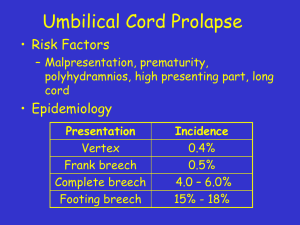
Presentation
Incidence
3-4% of fetus present by breech at term
7% at 32 weeks
25% at 28 weeks
20% diagnosed in labour
External Cephalic Version
Best evidence states that ECV should be offered late in pregnancy
Success rate increased with:
multiparity
adequate liquor
station of breech above the pelvic brim
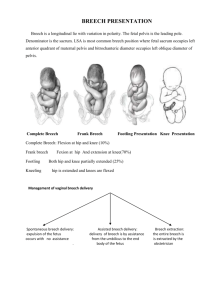
Types of Breech
Frank Complete Footling
Breech Delivery
The essence of the vaginal breech delivery is allowing as much spontaneous delivery by uterine action and maternal effort as possible
Operator intervention should be limited to the following manoeuvres
Breech Delivery
Breech birth process
Breech Delivery
The cervix should be fully dilated and the fetal anus visible on the perineum for active second stage.
Breech Delivery
Consider lithotomy position.
Breech Delivery
Delivery of the breech should be
‘hands off’
Legs and abdomen are born spontaneously.
Breech Delivery
Ensure that the fetal back rotates uppermost by carefully grasping the fetal pelvis with fingers & thumbs.
Leg delivery may need knee flexion by pressure in popliteal fossa
Breech Delivery
The fetus should be allowed to hang once the legs and abdomen have emerged until the wings of the scapula are seen.
Lovset’s Manoeuvre
Grasp the fetus around the bony pelvis with the thumbs across the sacrum.
The fetal back should then be turned through 180 degrees until the posterior arm comes to lie anteriorly…….
Lovset’s Manoeuvre
The elbow will appear below the symphysis pubis and the arm is delivered by sweeping it across the fetal body.
The manoeuvre is repeated in reverse to deliver the other arm.
Breech Delivery
Allow the fetus to hang from the vulva until the nape of the neck is visible.
Then carry out
Mauriceau-Smellie-
Veit manoeuvre
Breech Delivery
Breech Delivery