Breech Presentation: Types, Diagnosis & Management
advertisement

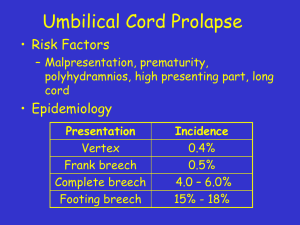
Prof. Abdulhafid Abudher MBBch,DGO,MD,FABOG,FRCOG Definetion This is a malpresentation where the podalic pole presents at the pelvic inlet. The lie is longitudinal The denominator is sacrum Various positions Anterior RSA-right sacroanterior (common) SA-sacroanterior LSA-left sacroanterior Posterior RSP-right sacroposterior SP- Sacroposterior LSP-left sacroposterior Incidence At term 29-32 weeks Accounts for 2.2% to3.7% up to 25% 4.8% of all births in USA (Haugley 1985) Types of Breech (Seed and Cafalo 1982) Complete 5-12% Frank 48-73% Incomplet 10-30% Footling Kneeling Etiology Predisposing Factors Abnormal uterine shape Excessive fetal mobility Interference in fetopelvic relationship 1-Maternal factors 2-Placental,Liquor and cord factors 3-Fetal Factors Maternal Factors Cephalopelvic disproportion at the pelvic inlet Soft tissue dystocia Congenital uterine anomalies Grand multipara Anticonvulsants and maternal alcohol intake (Robertson 1984) Placental,Liqure,Cord Factors Placenta previa Cornufundal implantation of placenta(fainu and vaclavinkova 1978) Polyhydramnios Oligohydramios Very long or very short cord Fetal Factors Multiple gestation Congenital anomalies Prematurity Large baby Postdate Intra uterine fetal death Fetal aneuploidy (Zhang and Schingle 1993) Diagnoses of Breech Abdominal examination Fetal heart sounds Vaginal examination Ultrasound examination Mechanism of labour Delivery of lower limbs and buttocks Delivery of shoulders and arms Delivery of aftercoming head Delivery of lower limbs and buttocks Engagement Descent Flexion Internal rotation Birth of Buttocks Delivery of shoulders and arms Engagement Descent continuous Internal rotation Birth of shoulders Restitution Birth of after coming head Engagement Descent Flexion Internal rotation Birth of the head Mechanism of labour in other positions Sacroanterior position Sacroposterior position Moulding Investigations Routine antenatal investigations US Anomalies Head extension Maturity Site and grade of placenta Adequacy of liquor Multiple gestation Confirming fetal presentation Investigations X-ray abdomen (history) Skeletal anomalies Maturity Pelvimetry Multiple gestation Management during pregnancy External cephalic version Trial of labour Caesarean delivery Vaginal breech delivery Spontaneous Assisted Total breech extraction Indications for trial of labour Frank breech Gestational age 36 to 42 weeks Estimated fetal weight 1500 to 3900 grm Flexed fetal BPD less than 9.5 Adequate maternal pelvis Breech Vaginal Delivery First Stage Second stage Episiotomy Assisted Lovset’s maneuver Aftercoming head Kristellar’s maneuver Bracht’s maneuver Wigand-Martin maneuver Mauriceau-Smellie-Veit maneuver Forceps delivery (Savage’s maneuver) Occipto-posterior position Rotating face posterior Prague maneuver Total breech extraction Rapid delivery -FD Pre-requisites: No fetopelvic disproportion Fully dilated cervix Empty balder and rectum Anesthesia Good assistance Hyper extension of the head Etiology Spasm or congenital shortening of the extensors muscles of neck Umbilical cord looped around the neck Congenital tumors of the neck ,teratoma or cystic hygroma Uterine anomalies Placental tumors Hyper extension of the head Diagnosis X-ray (star gazing foetus) Ultrasound (measurement of the craniospinal angle) • Risk of spinal cord damage Excessive longitudinal stretching Extreme flexion of neck during delivery Marked tortion Indications for elective C/S Contracted, border line or abnormal pelvis Placenta previa Large baby Hyperextension of head Footling breech Premature baby Previous caesarean section Elderly primgavida , BOH ,primary infertility IUGR BPD more than 9.5 cm Prognosis for breech presentation Maternal Genital laceration Bleeding Fetal Injury to the brain and skull Intracranial hemorrhage Fracture of skull bones Brain dysfunction Prematurity Congenital anomalies Congenital dislocation of hip Hydrocephaly Anencaphaly meningomyelocele Prognosis for breech presentation Birth asphyxia may occur due to: Prolonged compression of cord Cord prolapse Aspiration of liquor and vaginal secretions Prolonged labor Fetal injuries Fracture of neck,humerus,clavical,femur Cervical and brachial plexus palsies Hepatic rupture Splenic laceration Adrenal gland rupture Pharyngeal injury