Unit 1B Stations Review
advertisement
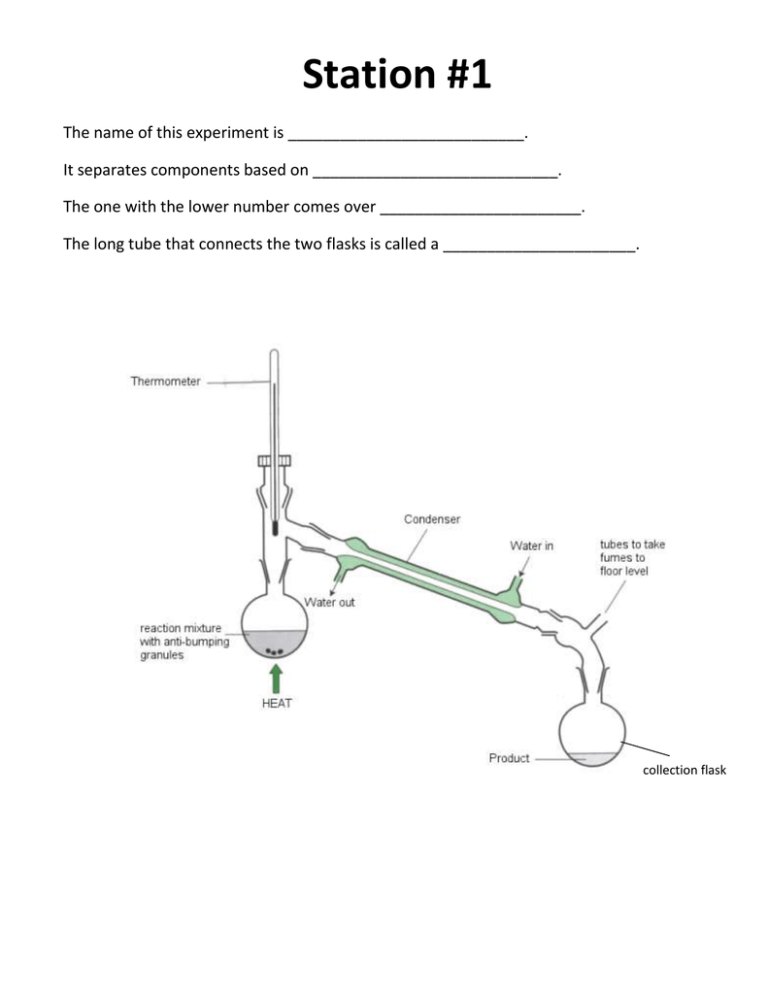
Station #1 The name of this experiment is ___________________________. It separates components based on ____________________________. The one with the lower number comes over _______________________. The long tube that connects the two flasks is called a ______________________. collection flask Station #2 Heating Curve (Energy is being absorbed or released (circle one) by the ice) This means a heating curve is endothermic or exothermic? 1. Identify what is happening at the various stages using the following words: Specific Heat Melting Boiling Heat of Vaporization Heat of Fusion Station #3 Heating curve 1. Identify what state(s) of matter the water is in: Between A and B, water is _______ Between B and C, water is __________ Between C and D, water is ___________ Between D and E, water is _________ Between E and F, water is _________ Station #4 1. What is the definition of specific heat? 2. What is the specific heat of water in joules? in calories? 3. What are specific heat values of metals, typically (high or low)? 4. What are the specific heat values of organic materials (wood, Styrofoam), typically (high or low)? 5. If a material has a higher specific heat – what does that mean in terms of heating up and cooling down? Station #5 1. What is the equation we use to solve for Heat (energy)? 2. What do each of the variables stand for? 3. What are the units of each variable? Station #6 A 1 carat diamond weighs .2000 grams. It consists of only one element! Diamond has a specific heat constant of .519 J/g oC). The diamond is heated to 74.21oC, then placed in a coffee cup calorimeter that contains 27.20oC water. There are 26.05 grams of water in the coffee cup. What is the temperature at which the diamond and the water reach thermal equilibrium? Station #7 Cooling Curve (Energy is being absorbed or released (circle one) by the steam) This means a cooling curve is endothermic or exothermic? A B C D E F 1. Identify what is happening at the various stages using the following words: Specific Heat Condensing Freezing Enthalpy of Vaporization Enthalpy of Fusion Station #8 Cooling Curve A B C A D E F 1. Identify what state(s) of matter the water is in: Between A and B, water is _______ Between B and C, water is __________ Between C and D, water is ___________ Between D and E, water is _________ Between E and F, water is _________ Station #9 1. How many molecules are present in 5.28 g of H2O? 2. How many grams are present in 34.9 moles of magnesium (Mg)? 3. How many molecules are present in 275 moles of H2SO4? Station #10 1. If a liquid sample has a volume of 128.0 mL and a density of 1.58 g/mL, what is the mass of this liquid sample? 2. A sample of metal has a mass of 42.80 g and a density of 22.5 g/mL. The sample is placed into a graduated cylinder that contains 22.5 mL of water prior to putting in the metal. What will be the new volume reading on the graduated cylinder after the metal sample is put in? 3. If you have a graph with volume plotted on the x axis and mass plotted on the y axis, how can you determine the density for the plotted data? Station #11 A layer of copper welded to the bottom of a skillet weighs 125 grams. How much heat is needed to raise the temperature of the copper layer from 25oC to 300.oC? The specific heat capacity of copper is o.387 J/g °C. Please mark the heat term + or – Station #12 Calculate the heat energy that will result when a 1500.0 g piece of wood experiences a temperature drops from 57.0oC to 32.0oC. The specific heat capacity of wood is 1.76 J/goC.