Beginning of Human Society_6th

Beginnings of Human
Society
6 th grade
Types of Human Society
The Paleolithic period, also known as the
Stone Age, started about 2.5 million years ago and lasted until about 12,000 B.C.
The Mesolithic period lasted from about
12,000 B.C. until about 8000 B.C.
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, lasted from about 8000 B.C. until about 5000
B.C.
Paleolithic Cultures
• They hunted and gathered for food.
• They were nomads–people who traveled from place to place. They followed the movement of the animals they hunted.
• Ancient people did not build permanent homes. Instead, they carried tents with them that were light and could be easily moved.
• They made tools out of stone, clay, and wood.
• Men hunted while women cared for young and gathered food.
Paleolithic Cultures con’t
• PLACE: They lived in present-day Africa, southeast Asia, China, Japan, and Europe, and they spread out everywhere except Antarctica.
• TOOLS USED: Wooden digging sticks were the first tools that Paleolithic people used.
• stone axes to cut down trees, spears and bows and arrows to hunt wild animals.
Paleolithic Cultures con’t
• There was no government—people organized loosely around natural leaders and followers.
• fires allowed people to cook food and heat shelters.
• They developed art with paintings on cave walls.
Neolithic Cultures
They used slash and burn techniques to clear forests to make farmland.
Crops grown on farms became an important source of food.
They domesticated animals such as goats, cattle, and pigs for food.
Neolithic Con’t
They used tools: plow and the sickle in order to farm.
The plow could be used to bring nutrients to the surface of soil before crops were planted, and the sickle could be used to cut grain.
They established agricultural villages.
They began using metals such as copper, lead, and gold for weapons and tools.
Climate and Development
After the last ice age, the climate on Earth was unpredictable.
Global temperatures eventually leveled off (it was the same temperature) and have remained relatively stable(same) for thousands of years.
Climate and Development
CON’T
Animal herds migrated based on the changing temperatures. Because animals were their main source of food, hunter-gatherers followed where the herds migrated.
Which type of people followed animals?
Neolithic or Paleolithic
Climate and Development
CONT
Once the climate became more stable, animals, humans, and plants had many opportunities to grow
and thrive.
The hunter-gather society was slowly replaced with a society that planted and raised crops. This type of society was known as an agricultural society .
Early Migrations and
Settlements
It is believed that the earliest humans lived in the East African Rift Valley, in present-day
Ethiopia.
Ancient Egypt has been called the "gift of the
Nile.”
Most of Egypt is very dry, but people were able to thrive because they lived near the Nile
River.
The river would flood every year and make the ground fertile so the people could grow crops. The river was also used for irrigation .
Early Migrations and
Settlements con’t…
The Yellow River is considered the cradle of agriculture in China.
From China, farming spread across Eurasia through migration and contact with nearby societies.
Early humans arrived in Australia about
40,000–45,000 years ago. They migrated over a land bridge from Southeast Asia.
Early Migrations and
Settlements
River Valleys
Early civilizations developed in river valleys.
This is because the ancient civilizations relied on agriculture as their main source of food.
River valleys had fertile ground from the flooding that rivers went through, and this ground made it easier to grow crops.
All river civilizations discovered some form of irrigation, which allowed them to lead water from rivers to water the crops on farmlands .
The four Rivers
Tigris and Euphrates River
Nile River
Huang Ho River
Indus River
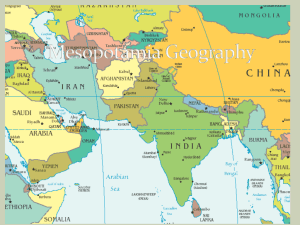
Tigris And Euphrates
Rivers
The first evidence of civilization has been found in
Mesopotamia, along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, which is in the present day countries of Iraq and Iran.
Mesopotamia was very dry, but the people who lived there were able to build canals to bring water from the rivers to irrigate their cropland.
Tigris And Euphrates
Rivers con’t…
What did they use?
Mesopotamians used the plow to make their farmland more productive.
They used oxen to pull plows through their fields.
The Mesopotamians also used the nearby rivers was for transportation. By using the sail, Mesopotamians were able to trade over long distances, including with Egyptians
Tigris And Euphrates
Rivers con’t…
The Sumerians were the first known group to invent writing (called cuneiform
).
FYI: They also invented the wheel, which they used for carts, wagons, chariots, and pottery wheels.
The Babylonians wrote the Code of
Hammurabi, which is one of the earliest examples of law that exists.
Mesopotamian civilizations were polytheistic, which meant they believed in more than one god.
Nile river...and its region
Nile River:
Nile was very important for the Egyptians.
Nile floods came during the same season every year.
The floods left silt on the soil, which was good for growing crops.
They made a writing system using hieroglyphs (pictures), and they wrote on sheets of a plant called papyrus .
Egypt was ruled by a pharaoh, and its religion was also polytheistic, having many different gods.
They believed in an afterlife. They mummified the dead to preserve the bodies for the afterlife.
Huang Ho River (or
Yellow River)
The Huang Ho is the second longest river in China.
The fertile floodplains of the river provided an excellent place to grow crops, and this was where the first
Chinese civilizations emerged.
The Shang Chinese civilization wrote oracles (religious predictions) on animal bones and turtle shells.
These oracle bones give us an example of early Chinese writing, which is similar to Chinese writing today.
Indus River and its region...
The Indus Valley (also called Harappan) civilization in western India was in some ways more advanced than later civilizations.
Archaeologists have found evidence that the
Harappans had a standard system of weighing things.
Indus River and its region...
Harappan houses even had indoor drainage systems, a basic type of plumbing.
This was a luxury that people would not regain until many years later. The Harappan civilization also planned their cities so that the streets were laid out in a grid.
Agricultural…
The development of agriculture allowed people to live in one place and establish permanent settlements.
These new settlements created innovations that were not possible in a society always on the move.
Invention of Agriculture
Agriculture is the growing of crops and the domestication of animals.
Where did agriculture develop?
For example, it also developed in North and South America even though those continents did not have contact with the
Middle East.
Agriculture developed in Guinea/West Africa, the
Nile River Valley, and the Ethiopian Highlands at about the same time but independently of each other
(see map in previous slide).
Invention of
Agriculture…etc.
The development of agriculture led to more reliable sources of food than hunting and gathering offered.
By growing crops and raising animals, people were able to establish permanent settlements.
These permanent settlements eventually developed into the first true civilizations.
Many civilizations were able to support standing armies with the large amount of food that they grew on their farms.
Invention of
Agriculture…etc.
Domestication allowed people to breed animals instead of hunting them.
This involved selective breeding
: choosing to breed animals with favorable traits.
These traits were passed on to make animals that were stronger, produced more meat or milk, or were tamer.
The first animals to be domesticated for agriculture were goats and sheep.
Problem in agriculture…
One early problem in agricultural societies was the spread of diseases from animals to humans.
What is the difference between nomads the farming society?
Unlike hunter-gatherer societies, farming societies were exposed to diseases like smallpox and measles.
How were they spread?
These diseases were spread through domesticated animals.
Invention of Metallurgy…
What is Metallurgy?
Metallurgy is the making of items with metal. Metalworking contributed to advances in making tools, jewelry, and weapons.
Some of the first metal-working societies included those of the
Bronze Age and the Iron Age.
Bronze was first used to make tools because it has a lower melting point than iron.
With the development of higher temperature smelting techniques, however, people could make iron more easily than before.
Iron is a stronger metal than bronze, so it made better tools and weapons.