Unit2_Day6PP_PhaseChange
advertisement

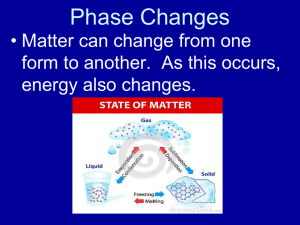
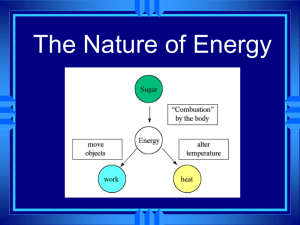
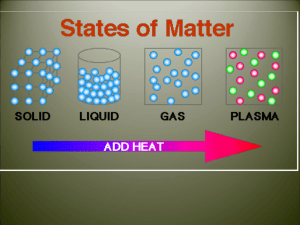
Do Now: • Silently, independently you 10 minutes • If you finish early you may read silently and independently • Have your homework out on the top right corner of your desk. • Today’s Topic: PHASE CHANGES! Let’s Review… Class Updates! • Those that need to take the test/quiz need to do it by the end of this week! NO EXCUSES! • Don’t forget about participation tickets! • Extra credit will be given for boxes of tissue • I also have binders (only 8 for sale) for those of you still do not have a binder for my class! SWBAT • Describe each of the six phase changes. • Identify phase changes as endothermic or exothermic. • By the end of the day you will be able to answer the following question: why does steam collect on the mirrors during a shower/bath? Let’s what some heat transfer and phase changes • Predict what you think will happen • Write your observations in your notes • Tea bag • Why? • Think-Pair-Share Phase Change! • Is a reversible physical change that occurs when a substance changes from one state of matter to another. • Melting • Freezing • Vaporization • Condensation • Sublimation • Deposition Temperature & Phase Changes • Temperature of a substance DOES NOT change during a phase change. Energy Transfer • Energy is either absorbed or released during a phase change. • Endothermic: the system absorbs energy from the surroundings. • Example: ice melting. • Exothermic: the system releases energy to it’s surroundings • Example:? How are we doing? •Name a phase change. •What happens to temperature? •What are the two types of energy of transfer? Melting & Freezing • The arrangement of molecules in water becomes less orderly as water melts and more orderly as water freezes • Melting: increase in average kinetic energy because energy (as heat) is added to the system and they begin to vibrate more quickly, until melting happens. • Example: ice-cream melting • Freezing: decrease in average kinetic energy because energy (as heat) leaves the system, thus molecules begin to slow until an orderly arrangement (frozen). • Example: an ice cube! Vaporization & Condensation • Vaporization: when changes from a liquid to a gas • Endothermic process, meaning? • Example: The refrigerators use evaporators to keep food cold • Evaporation is the process that changes a substance from a liquid to a gas at temperatures below the substance’s boiling point. • Example: puddles of rain disappear a few hours after a storm. • Boiling: takes place throughout a liquid, both the temperature and the vapor pressure of the water increases. • Kinetic energy increases! • What vapor pressure? • The pressure caused by the collisions of vapor particles on a container! Vaporization & Condensation Continued • Condensation: is the phase change in which a substance changes from a gas or vapor to a liquid. • Example: the steam on your bathroom mirror. • This is because water vapor cooled as it came in contact with the mirror. The water vapor transferred heat to the mirror and CONDENSED into a liquid. • It is an exothermic process. Sublimation & Deposition • Sublimation: is the phase change in which a substance changes from a solid to a gas or vapor without changing to a liquid at first. • This is an endothermic process • Examples: as dry ice melts, it sublimes because the cold carbon dioxide vapor causes the water vapor in the air to condense and form clouds Sublimation & Deposition Continued… • Deposition: when a gas or a vapor changes directly into a solid without first changing into a liquid. • This is an exothermic process (reverse of sublimation). • Examples: frost forming on windows, because when water vapor contacts windows it looses enough energy to change from a gas to a solid. Let’s Watch a Video! Essential Question Answered •So… why is there a ‘cloud’ on the mirror in the bathroom after a shower? • 1. The water molecule on the surface of the bath water evaporates (endothermic). • 2. Random motion carries it the surface of the mirror. • 3. The water molecule condenses on the mirror (exothermic). Exit Ticket = Summarize Today’s Notes •Take the change to review your notes from today. •Draw a line and under the line begin a summary. •Use your own words! •Use pictures!