Integumentary System: Anatomy & Physiology Presentation
advertisement

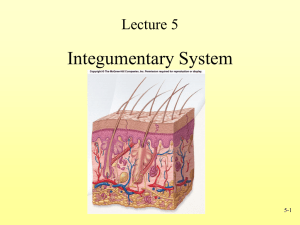
Integumentary System Chapter 5 From Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, Seeley, Stephens, and Tate, 5th Edition, 2005, McGraw Hill Companies Functions • Protection against abrasion and ultraviolet light • Protection from entry of microorganisms and dehydration • Sensation receptors for heat, cold, touch, pressure, and pain • Production of precursors to Vitamin D when exposed to ultraviolet light • Regulation of temperature by controlling blood flow to the skin and activity of sweat glands • Excretion of waste products through the skin and the gland secretions Facts • The integumentary system consists of the skin and the structures derived from it including hair, nails, and glands. • The skin is the largest organ of the body, covering approximately 2 square meters and having a mass of about 5 kilograms. • The study of the integument is called dermatology. Anatomy of Skin • Epidermis - the five outermost thin layers, mitosis in the deepest layer produces new cells as the older cells move towards the most superficial layer where they are sloughed off • Dermis - the thicker layer below the epidermis containing blood vessels, nerve endings, hair follicles, smooth muscles, lymphatic vessels, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands • Hypodermis - the layer of loose connective tissue under the dermis and not considered part of the skin, it contains half of the body’s stored fat which acts as padding and insulation, it attaches to underlying bones and muscles • This image shows the epidermis partially peeled away from the dermis. • Note the numerous blood vessels extending into the dermis from the hypodermis. • Note the fat in the hypodermis. This is a micrograph of actual skin sliced thinly and stained. Note the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The outer cells of the epidermis are sloughing off. The dermal papillae are projections of the dermis which extend into the epidermis. They contain tiny blood vessels that supply the epidermis and aid in regulation of body temperature. Fingerprints are projections of the dermal papillae into the epidermis of the fingertips. They increase friction and help improve grip. This image shows the five layers of the epidermis. The outermost layer is called the stratum corneum: -25 layers of dead skin cells -Keratinized Keratin is a protein that builds up in cells of the epidermis as they move from the deepest layer, the stratum basale, towards the skin’s surface. This process is called keratinization and takes 2-4 weeks. Epidermal Layers Composed primarily of keratinized stratified squamous epithelial cells -- consisting of 4-5 layers: 1. stratum corneum: outermost layer, keratinized dead epithelium 2. stratum lucidum: layer found in thickest areas of skin 3. stratum granulosum: 3-5 layers of flattened granular cells, developing keratin fibers 4. stratum spinosum: multiple layers of cells 5. stratum basale: deepest layer of single cuboidal or columnar cells, also contains melanocytes - Blisters, Calluses &Psoriasis Skin Color - Genetics, Environment & Physiology: 1. # of melanocytes - difference in kind, amount & size 2. sunlight, UV light, etc. 3. blood in dermis, blood vessels, freckles & moles 4. other pigments - carotinoids 5. jaundice – liver disorder Skin, hair, and eye color are all due to a molecule called melanin. This provides protection from the sun’s ultraviolet rays. Melanin is made by special cells in the stratum basale called melanocytes which have extensions reaching towards the skin’s surface. Note the pigment granules in these cell extensions. Variations in skin color are due to the color, amount, and distribution of melanin, not to the number of melanocytes present in the epidermis. Special Features of the Dermis • Hair follicles - hair grows from hair bulbs in the follicle, the follicles are actually extensions of the epidermis deep into the dermis • Arrector pili (muscles) - an arrector pili muscle is associated with each hair follicle, when the muscle contracts the hair stands on end, contraction of these muscles also causes goose bumps • Sweat glands - sweat is produced in these coiled glands and is secreted on the skin’s surface through pores, sweat is sometimes produced due to emotional stress but is usually produced in order to decrease body temperature by evaporative cooling • Sebaceous glands - most sebaceous glands are connected to hair follicles and produce an oily substance called sebum, the sebum protects against drying of the hair and skin and against some bacteria Skin Glands Sebaceous glands: - assoc. w/ hair follicles, secrete sebum - oils hair, lubricates skin & prevent water loss - acne vulgaris Sweat glands: Eccrine: deep in dermis or subcutaneous layer, odorless secretions, function in thermoregulation Apocrine: found near hair follicles, in axillary regions, released during pain, fear & stress or sexual arousal - Ceruminous & mammary glands Note the extension of the epidermis far into the dermis forming the hair follicle. Also, note the coiled sweat gland and the sebaceous gland connected to the hair follicle. Nails Wound healing