Wage and Tax PowerPoint
advertisement

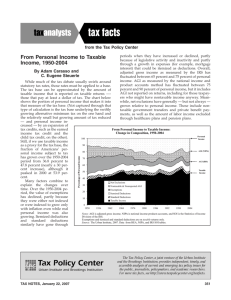
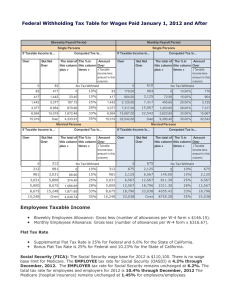
Money Counts: A Financial Literacy Series Wage and Tax Fundamentals January 21, 2015 5:30 – 6:30 p.m. Mann Assembly Room, 103 Paterno Library Dr. Daad A. Rizk Dr. Cathy F. Bowen MoneyCounts: A Financial Literacy Series 128H Outreach Building University Park, PA 16802 dar39@psu.edu 1-(814)-863-0214 Professor and Consumer Issues Specialist Department of Agricultural Economics, Sociology and Education 8B Ferguson Building University Park, PA 16803 cbowen@psu.edu 1-814-863-7870 Learning Objectives • Provide an overview of the federal taxing system • Describe tax withholding and wage statements • Review forms W4, W2 • Describe the completion of the Form 1040 using key documents. Overview of the Federal Taxing System • Pay as you earn or pay as you go system • Progressive tax-the more you earn the higher your tax bill (10% - 39.6% tax rates) • Tax language—terms to know Taxes • Internal Revenue Service (IRS) – Collects federal taxes, issues regulations, and enforces tax laws written by the United States Congress Taxes • Taxes – Compulsory charges imposed on citizens by local, state, and federal governments • Used to provide public goods and services – Largest amount of taxes a person pays is on his/her income 2014 Federal Tax Rates-Single If Taxable Income Is Then the Gross Tax Payable Is: Over But not over Amount $0 $9,075 --------10% of taxable income---------- 9,075 36,900 907.50 15% 9,075 36,900 89,350 5,081.25 25% 36,900 89,350 186,350 18,193.75 28% 89,350 186,350 405,100 45,353.75 33% 186,350 405,100 406,750 117,541.25 35% 405,100 406,750 ----------- 118,118.75 39.6% 406,750 Plus (percent) Of the amount over 2014 Federal Tax Rates-Married If Taxable Income Is Then the Gross Tax Payable Is: Over But not over Amount $0 $18,150 --------10% of taxable income---------- 18,150 73,800 1,815.00 15% 18,150 73,800 148,850 10,162.50 25% 73,800 148,850 226,850 28,925.00 28% 148,850 226,850 405,100 50,765.00 33% 226,850 405,100 457,600 109,587.50 35% 405,100 457,600 ----------- 127,962.50 39.6% 457,600 Plus (percent) Of the amount over Key Tax Terms • Income – – – – – Earned Unearned Tax exempt interest Taxable interest Dividends (ordinary and qualified) • Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) – – – – – Adjustments (subtract from income) Educator expenses Self-employed tax Student loan interest Tuition and fees Key Tax Terms • Tax Itemize Deductions – Standard deduction – Exemptions – Taxable Income • Other Taxes – Self-employment tax • Payments – Federal tax withheld – Earned Income credit – Premium tax credit Credits * Foreign Tax * Child and Dependent Care * Education * Retirement Saver’s W4 – Employee’s Withholding Allowance Certificate • Employee completes the certificate and files with employer at the beginning of employment (Human Resources) and after life events. • Employer uses the information on the w-4 to determine the amount of tax to withhold each pay period. • Rules of Thumb: The more allowances on w-4, the fewer taxes withheld from pay The fewer allowances on w-4, the more taxes withheld from pay • Action Item: Review form w-4 each year. Adjust withholdings as needed so only the needed amount of tax is withheld. irs.gov Withholding Calculator • IRS Withholding Calculator Wage and Tax Statement W-2 1099 and 1098 • 1099 Misc – Non-employee independent contractor services, rental income, etc. • 1099 INT – Interest income on investment accounts, saving bank account, etc. • 1098 – Mortgage Interest Statement, mortgage points, mortgage insurance premiums • 1098 T – Tuition Statement • 1098 E – Student Loan Interest Statement 1099-Miscellaneous Income 1099-Interest Income 1099 Dividends & Distributions 1098 Mortgage Interest Statement 1098-T Tuition Statement 1098-E Student Loan Interest Which statement best describes how you get taxes prepared? I…. 1. Use VITA-volunteer income tax assistance or a similar free service 2. Prepare my own federal/state tax returns using a computer program (i.e., Turbo tax ) 3. Prepare my own federal/state tax returns by hand (paper forms or printable pdfs from irs.gov) 4. Hire a professional to prepare my federal and state taxes each year Rule of Thumb Use only Form 1040 • Changes are minimal from year to year. • Used for most complicated returns. • Decreases chance you will overlook a tax benefit. • You learn the form Completing a Tax Return Think! • Basic addition and subtraction problem! • • • • • • • Income (+) Adjusted Gross Income (-) Taxes and Credits (+ and -) Other Taxes (+) Payments (+) Overpayment=refund Underpayment=Amount you Owe Standard Deduction -2014 Personal Exemption - 2014 • Personal Exemptions. The personal exemption amount is $3,950 in 2014, up from $3,900 in 2013. • Phase-outs for personal exemption amounts begin with adjusted gross incomes (AGI) of $254,200 for individuals and $305,050 for married couples filing jointly; • The personal exemptions phase out completely at $376,700 for individual taxpayers ($427,550 for married couples filing jointly.) Step 1—List Personal Information Step 2—Add income Step 3- Subtract Adjustments Step 4-Subtract deductions, exemptions. Figure tax on taxable income and subtract credits. Step 5-Add/Total other taxes NEW--ACA Check this box if you had non Marketplace health insurance Step 6- Add payments made and refundable tax credits NEW--ACA Step 7- Finishing Details Health Insurance—New in 2014 NEW--ACA Check this box if you had non Marketplace health insurance Step 6- Add payments made and refundable tax credits NEW--ACA Health Insurance—New in 2014 • For taxpayers who purchased health insurance from The Marketplace (Healthcare.gov) • Look for Form 1095-A in the mail. Use it to help you fill out Form 8962 on your federal tax return. • No Form 1095-A if health coverage was from Medicaid, Medicare, CHIP-Children’s Health Insurance Program or received an exemption. Schedule A Schedule A Schedule A-continued Schedule A (itemized deductions) • Allowable deductions for taxpayers – Medical and dental expenses – – – – – – Taxes you paid Interest you paid Gifts to charity Casualty and theft losses Job expenses Other miscellaneous deductions Tax Tips for College Students 1. If you have earned income, file even if not required to get taxes withheld back and/or Earned Income Tax Credit 2. Create a tax folder at the beginning of each year. Store tax related documents in the folder 3. Practice doing your current return using a paper form 4. Understand your family situation. Can your parents claim you on their return? Confirm this before filing 5. Generally, state taxes are paid in the state earned 6. Use the Form 1040 exclusively Tax Tips for College Students 7. Understand the education credits that apply to you 8. Self-employed or have taxable fellowships—send in estimated quarterly payments (see Form 1040-ES) 9. Avoid underpayment penalty. Pay 90% of current filing year tax bill, 100% of tax shown on prior year bill. Less than $1000 owed = no penalty 10. See IRS apps and topical videos 11. Lesson—Understanding Taxes Additional Resources For help completing the 2014 tax return @ PSU-University Park. PSUVITA.org or call 814-863-4147, Mon.-Fri. (effective 1/26/2015). VITA is available for U.S. citizens or resident aliens with a household income of $53,000 for 2014. IRS Assistance. www.irs.gov Search for VITA sites nationwide by zip code Look for “Where’s My Refund” web page Refund Hotline—1-800-829-1954 Tax-Help 1-800-829-1040 PA Dept. of Revenue. www.revenue.pa.gov Online Customer Service Center: https://revenue-pa.custhelp.com/ Thank you for participating! Questions and Comments? Dr. Cathy F. Bowen Professor and Consumer Issues Specialist Department of Agricultural Economics, Sociology and Education 8B Ferguson Building University Park, PA 16803 cbowen@psu.edu 814-863-7870 (o) Dr. Daad A. Rizk MoneyCounts: A Financial Literacy Series 128H Outreach Building University Park, PA 16802 dar39@psu.edu 1-(814)-863-0214