Canada and Conflict in the Cold War
advertisement

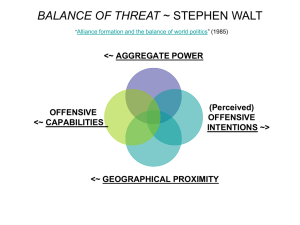
Canada and the Cold War Key Terms • • • • • • • • • • • Communist Capitalist Cold War Superpowers Gouzenko Affair Red Scare United Nations NATO Warsaw Pact DEW Line NORAD • Commonwealth of Nations • Colombo Plan • The Korean War • Suez Crisis • Cuban Missile Crisis • Avro Arrow • The Nuclear Issue • Vietnam War Cold War - Definition • A war with no direct military conflict but a conflict waged through various other means including: • • • • • espionage propaganda economic warfare surrogate wars the space and arms race. Cold War - Origins • After WWII, two Super Powers emerged - the United States and the Soviet Union (Russia). They engaged in a Cold War from 1945 - 1989. – The United States was a CAPITALIST country. This meant that private individuals invested in businesses trying to make a profit. – The Soviet Union was a COMMUNIST country. This meant that the government controlled the economy by owning the means of production and distribution such as farms, factories, stores and railroads. Cold War - Origins • Canada was involved in the Cold War as an ally to the United States. Our alliance with them evolved naturally because of our geographic proximity, history of co-operation, similar economic and political systems, and integrated cultures. Cold War - The Gouzenko Affair • The Cold War was brought home to Canada by the Gouzenko Affair. • Igor Gouzenko, a clerk at the Soviet Embassy in Ottawa exposed a Soviet spy ring in Canada in 1945. Newspaper headlines read: “It’s War! It’s Russia!”. • 18 people were arrested with 8 eventually convicted of spying - likely trying to get Atomic Bomb secrets. Cold War - The Red Scare • The Americans, too were afraid of Communism and Communist spies. • Senator Joseph McCarthy lead a witch-hunt which tried to expose spying in America. • Long lists of potential communists were accused and interrogated and eventually found guilty even if evidence was only a set of flimsy rumours. • The convicted lost their jobs and futures. Cold War - International Organizations • Canada was involved in a wide variety of international organisations. • Some were aimed at maintaining peace. • United Nations • Others were for defence or waging war. • NATO; NORAD • One was to maintain independence from the USA. • Commonwealth of Nations Cold War - Canada’s Red Scare • In Canada, artists, peace activists, union leaders and intellectuals were labelled ‘security risks’ and investigated by a special branch of the RCMP. • Some organisations refused to hire people who had been blacklisted. Cold War - United Nations • • • • • Formed after WWII goal of Collective security 51 original members, including Canada focus on negotiation and mediation but given 3 powers • condemnation - through speeches / resolutions • sanctions - urging members to suspend trade • military - send in armed forces if necessary Cold War - United Nations • Limited Success Resolving Conflicts Why? • No permanent armed force • charter forbids interference in ‘internal’ matters only between nations (ex. Cannot stop genocide or civil war) • now, over 190 members - difficult to reach agreement Cold War - United Nations • Limited Success Resolving Conflicts Why? • Security Council – 5 permanent members: USA; USSR; France; Britain; China and ten other nations for two year terms – any permanent member can veto any resolution – thus, conflicts between major powers cannot be resolved through UN Cold War - United Nations • Successes – – – – assistance after natural disasters building schools; roads; dams development aid as of 1999 Canadians had been involved in every single UN Peacekeeping operation • more than 100 Canadian soldiers have died in peacekeeping operations Cold War - NATO • North Atlantic Treaty Organisation – a military alliance of Western nations set up in opposition to the Soviets in 1949 – “Where force threatens it must be kept at bay by superior force.” (WLMK) Cold War - NATO • North Atlantic Treaty Organisation – Canada had to agree to meet military commitments to NATO – Canadian soldiers were permanently stationed in Europe in a state of war readiness – all members agreed that nuclear weapons could be used if necessary in war against Soviets • total nuclear war, it was agreed was only acceptable as a last resort Cold War - Warsaw Pact • Formed in 1955 • made up of largely Eastern European nations allied with the Soviet Union • a response to NATO • Who was the aggressor NATO or Warsaw Pact? Cold War - NORAD • Integrated defence of North America from attack by Soviet missiles – DEW lines - lines of distant early warning radar stations were set up across the Arctic in 1950 and 1957 – American military personnel were stationed on Canadian soil for the first time • Was the security gainde worth the loss of independence? Cold War - NORAD • Both sides soon developed Inter-Continental Ballistic Missiles (ICBM) • Launched from silos or subs into space could reach one another’s cities in less than 30 minutes • DEW lines were rendered obsolete Cold War - NORAD • The North American Aerospace Defence Command (NORAD) was established in 1957 – a system including fighter forces, missile bases, and air defence radar – controlled by and American general based in Colorado – moon or missiles? Cold War - Commonwealth of Nations • Clearly, NATO and NORAD were controlled by the USA • Canada joined the Commonwealth to link itself to other nations of the world - separate from the USA • focus was not military • rather, trade and aid Cold War - Commonwealth of Nations • Colombo Plan, 1950 – provide aid to less developed countries • experts gave technical assistance • overseas students encouraged to travel to Canada (doctors; engineers; public administration) • a nuclear reactor was sent to India for ‘peaceful purposes’ - oops... • Canadians used the Commonwealth as a forum to promote justice and human rights (ex. Spoke out against Apartheid in South Africa) Cold War - Origins • Canada was involved in the Cold War as an ally to the United States. Our alliance with them evolved naturally because of our geographic proximity, history of co-operation, similar economic and political systems, and integrated cultures. Cold War - Origins • Canada was involved in the Cold War as an ally to the United States. Our alliance with them evolved naturally because of our geographic proximity, history of co-operation, similar economic and political systems, and integrated cultures. Cold War - Origins • Canada was involved in the Cold War as an ally to the United States. Our alliance with them evolved naturally because of our geographic proximity, history of co-operation, similar economic and political systems, and integrated cultures. Cold War - Origins • Canada was involved in the Cold War as an ally to the United States. Our alliance with them evolved naturally because of our geographic proximity, history of co-operation, similar economic and political systems, and integrated cultures. Cold War - Origins • Canada was involved in the Cold War as an ally to the United States. Our alliance with them evolved naturally because of our geographic proximity, history of co-operation, similar economic and political systems, and integrated cultures.